Targeting XBP1 mRNA splicing sensitizes glioblastoma to chemotherapy
- PMID: 37151848
- PMCID: PMC10158625
- DOI: 10.1096/fba.2022-00141
Targeting XBP1 mRNA splicing sensitizes glioblastoma to chemotherapy
Abstract
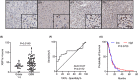
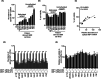
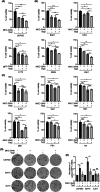
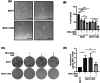
Glioblastoma (GBM) is the most frequent and deadly primary brain tumor in adults. Temozolomide (TMZ) is the standard systemic therapy in GBM but has limited and restricted efficacy. Better treatments are urgently needed. The role of endoplasmic reticulum stress (ER stress) is increasingly described in GBM pathophysiology. A key molecular mediator of ER stress, the spliced form of the transcription factor x-box binding protein 1 (XBP1s) may constitute a novel therapeutic target; here we report XBP1s expression and biological activity in GBM. Tumor samples from patients with GBM (n = 85) and low-grade glioma (n = 20) were analyzed by immunohistochemistry for XBP1s with digital quantification. XBP1s expression was significantly increased in GBM compared to low-grade gliomas. XBP1s mRNA showed upregulation by qPCR analysis in a panel of patient-derived GBM cell lines. Inhibition of XBP1 splicing using the small molecular inhibitor MKC-3946 significantly reduced GBM cell viability and potentiated the effect of TMZ in GBM cells, particularly in those with methylated O6-methylguanine-DNA methyl transferase gene promoter. GBM cells resistant to TMZ were also responsive to MKC-3946 and the long-term inhibitory effect of MKC-3946 was confirmed by colony formation assay. In conclusion, this data reveals that XBP1s is overexpressed in GBM and contributes to cancer cell growth. XBP1s warrants further investigation as a clinical biomarker and therapeutic target in GBM.
Keywords: XBP1s; cancer biomarkers; glioblastoma; therapeutic targets.
© 2023 The Authors. FASEB BioAdvances published by Wiley Periodicals LLC on behalf of The Federation of American Societies for Experimental Biology.
Conflict of interest statement
None of the authors have declared a conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
ProNGF Expression and Targeting in Glioblastoma Multiforme.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jan 13;24(2):1616. doi: 10.3390/ijms24021616. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36675126 Free PMC article.
-
Sustained production of spliced X-box binding protein 1 (XBP1) induces pancreatic beta cell dysfunction and apoptosis.Diabetologia. 2010 Jun;53(6):1120-30. doi: 10.1007/s00125-010-1699-7. Epub 2010 Mar 29. Diabetologia. 2010. PMID: 20349222
-
XBP1U inhibits the XBP1S-mediated upregulation of the iNOS gene expression in mammalian ER stress response.Cell Signal. 2010 Dec;22(12):1818-28. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2010.07.006. Epub 2010 Jul 15. Cell Signal. 2010. PMID: 20637858
-
Temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma multiforme.Genes Dis. 2016 May 11;3(3):198-210. doi: 10.1016/j.gendis.2016.04.007. eCollection 2016 Sep. Genes Dis. 2016. PMID: 30258889 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of XBP1s in Transcriptional Regulation of Target Genes.Biomedicines. 2021 Jul 8;9(7):791. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines9070791. Biomedicines. 2021. PMID: 34356855 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Stupp R, Mason Wp, van den Bent MJ, et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):987‐996. - PubMed
-
- Hegi ME, Diserens AC, Gorlia T, et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. N Engl J Med. 2005;352(10):997‐1003. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
