Functional heterogeneity of human skin-resident memory T cells in health and disease
- PMID: 37144705
- PMCID: PMC10952320
- DOI: 10.1111/imr.13213
Functional heterogeneity of human skin-resident memory T cells in health and disease
Abstract
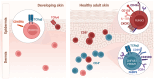
The human skin is populated by a diverse pool of memory T cells, which can act rapidly in response to pathogens and cancer antigens. Tissue-resident memory T cells (TRM ) have been implicated in range of allergic, autoimmune and inflammatory skin diseases. Clonal expansion of cells with TRM properties is also known to contribute to cutaneous T-cell lymphoma. Here, we review the heterogeneous phenotypes, transcriptional programs, and effector functions of skin TRM . We summarize recent studies on TRM formation, longevity, plasticity, and retrograde migration and contextualize the findings to skin TRM and their role in maintaining skin homeostasis and altered functions in skin disease.
Keywords: adaptive barrier immunity; allergy; cutaneous T-cell lymphoma; inflammatory skin diseases; skin cancer; tissue-resident memory T cells.
© 2023 The Authors. Immunological Reviews published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no potential commercial or financial conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tissue-Resident Memory T Cells in Allergy.Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024 Feb;66(1):64-75. doi: 10.1007/s12016-024-08982-8. Epub 2024 Feb 21. Clin Rev Allergy Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38381299 Review.
-
Pathophysiology of Skin Resident Memory T Cells.Front Immunol. 2021 Feb 3;11:618897. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2020.618897. eCollection 2020. Front Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33633737 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Heterogeneity and plasticity of tissue-resident memory T cells in skin diseases and homeostasis: a review.Front Immunol. 2024 May 8;15:1378359. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1378359. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38779662 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A narrative review of tissue-resident memory T cells and their role in immune surveillance and COVID-19.Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022 Jun;26(12):4486-4496. doi: 10.26355/eurrev_202206_29088. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35776050 Review.
-
Advancements in the characterization of tissue resident memory T cells in skin disease.Clin Immunol. 2022 Dec;245:109183. doi: 10.1016/j.clim.2022.109183. Epub 2022 Nov 10. Clin Immunol. 2022. PMID: 36371067 Review.
Cited by
-
Aetiopathogenesis of Vitiligo.Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023 Dec 1;13(4S2):e2023314S. doi: 10.5826/dpc.1304S2a314S. Dermatol Pract Concept. 2023. PMID: 38241397 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Immune cell trafficking: a novel perspective on the gut-skin axis.Inflamm Regen. 2024 Apr 24;44(1):21. doi: 10.1186/s41232-024-00334-5. Inflamm Regen. 2024. PMID: 38654394 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A guide to adaptive immune memory.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Nov;24(11):810-829. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01040-6. Epub 2024 Jun 3. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38831162 Review.
-
Redefining our vision: an updated guide to the ocular immune system.Nat Rev Immunol. 2024 Dec;24(12):896-911. doi: 10.1038/s41577-024-01064-y. Epub 2024 Aug 30. Nat Rev Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39215057 Review.
-
Why drug exposure is frequently associated with T-cell mediated cutaneous hypersensitivity reactions.Front Toxicol. 2023 Sep 19;5:1268107. doi: 10.3389/ftox.2023.1268107. eCollection 2023. Front Toxicol. 2023. PMID: 37795379 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gebhardt T, Wakim LM, Eidsmo L, Reading PC, Heath WR, Carbone FR. Memory T cells in nonlymphoid tissue that provide enhanced local immunity during infection with herpes simplex virus. Nat Immunol. 2009;10(5):524‐530. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources