The effect of nintedanib on lung functions and survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: real-life analysis of the Czech EMPIRE registry
- PMID: 37138274
- PMCID: PMC10155319
- DOI: 10.1186/s12890-023-02450-3
The effect of nintedanib on lung functions and survival in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: real-life analysis of the Czech EMPIRE registry
Abstract
Introduction: The antifibrotic drug nintedanib is used for the treatment of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF). We analysed the effect of nintedanib on antifibrotic treatment outcome in real-world cohorts of Czech EMPIRE registry.
Patients/methods: Data of 611 Czech IPF subjects, 430 (70%) treated with nintedanib (NIN group), 181 (30%) with no-antifibrotic treatment (NAF group) were analysed. The influence of nintedanib on overall survival (OS), pulmonary function parameters as forced vital capacity (FVC) and diffusing lung capacity for carbon monoxide (DLCO), as well as GAP score (gender, age, physiology) and and CPI (composite physiological index) were investigated.
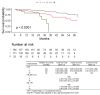
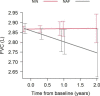
Results: During 2 year follow-up we observed that nintedanib treated patients had longer OS, compared to those treated with no-antifibrotic drugs (p < 0.00001). Nintedanib reduces risk of mortality over no-antifibrotic treatment by 55% (p < 0.001). We have observed no significant difference in the rate of FVC and DLCO decline between the NIN and NAF group. Changes within 24 months from baseline in CPI were not significant between the groups (NAF and NIN).
Conclusion: Our real-practice study showed the benefit of nintedanib treatment on survival. There were no significant differences between NIN and NAF groups in changes from baseline in FVC %, DLCO % predicted and CPI.
Keywords: Idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis; Lung function decline; Nintedanib; Overall survival.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effect of pirfenidone on lung function decline and survival: 5-yr experience from a real-life IPF cohort from the Czech EMPIRE registry.Respir Res. 2019 Jan 21;20(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s12931-019-0977-2. Respir Res. 2019. PMID: 30665416 Free PMC article.
-
DSP rs2076295 variants influence nintedanib and pirfenidone outcomes in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: a pilot study.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021 Jan-Dec;15:17534666211042529. doi: 10.1177/17534666211042529. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2021. PMID: 34515605 Free PMC article.
-
Lung function outcomes in the INPULSIS® trials of nintedanib in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Respir Med. 2019 Jan;146:42-48. doi: 10.1016/j.rmed.2018.11.012. Epub 2018 Nov 19. Respir Med. 2019. PMID: 30665517 Clinical Trial.
-
Clinical use of nintedanib in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.BMJ Open Respir Res. 2017 Jun 28;4(1):e000192. doi: 10.1136/bmjresp-2017-000192. eCollection 2017. BMJ Open Respir Res. 2017. PMID: 28883926 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Nintedanib in the management of idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: clinical trial evidence and real-world experience.Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018 Jan-Dec;12:1753466618800618. doi: 10.1177/1753466618800618. Ther Adv Respir Dis. 2018. PMID: 30249169 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Pirfenidone and Nintedanib in Pulmonary Fibrosis: Lights and Shadows.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 May 30;17(6):709. doi: 10.3390/ph17060709. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931376 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lysophosphatidic acid receptor 1 inhibition: a potential treatment target for pulmonary fibrosis.Eur Respir Rev. 2024 Jun 12;33(172):240015. doi: 10.1183/16000617.0015-2024. Print 2024 Apr. Eur Respir Rev. 2024. PMID: 39009409 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Raghu G, Collard HR, Egan JJ, Martinez FJ, Behr J, Brown KK, Colby TV, Cordier JF, Flaherty KR, Lasky JA, Lynch DA, Ryu JH, Swigris JJ, Wells AU, Ancochea J, Bouros D, Carvalho C, Costabel U, Ebina M, Hansell DM, Johkoh T, Kim DS, King TE, Jr, Kondoh Y, Myers J, Müller NL, Nicholson AG, Richeldi L, Selman M, Dudden RF, Griss BS, Protzko SL, Schünemann HJ. An official ATS/ERS/JRS/ALAT statement: idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis: evidence-based guidelines for diagnosis and management. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2011;183:788–824. doi: 10.1164/rccm.2009-040GL. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Doubková M, Švancara J, Svoboda M, Šterclová M, Bartoš V, Plačková M, Lacina L, Žurková M, Binková I, Bittenglová R, Lošťáková V, Merta Z, Šišková L, Tyl R, Lisá P, Šuldová H, Petřík F, Pšikalová J, Řihák V, Snížek T, Reiterer P, Homolka J, Musilová P, Lněnička J, Palúch P, Hrdina R, Králová R, Hortvíková H, Strenková J, Vašáková MEMPIRE, Registry. Czech Part: Impact of demographics, pulmonary function and HRCT on survival and clinical course in idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. Clin Respir J. 2018;12:1526–35. - PubMed
-
- King TE, Jr, Bradford WZ, Castro-Bernardini S, Fagan EA, Glaspole I, Glassberg MK, Gorina E, Hopkins PM, Kardatzke D, Lancaster L, Lederer DJ, Nathan SD, Pereira CA, Sahn SA, Sussman R, Swigris JJ, Noble PW. ASCEND Study Group. A phase 3 trial of pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis. N Engl J Med. 2014;370:2083–92. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1402582. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Noble PW, Albera C, Bradford WZ, Costabel U, Glassberg MK, Kardatzke D, King TE, Jr, Lancaster L, Sahn SA, Szwarcberg J, Valeyre D, du Bois RM, CAPACITY Study Group CAPACITY study group Pirfenidone in patients with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (CAPACITY): two randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;377:1760–9. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60405-4. - DOI - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

