Efficient Cross-Screening and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies against Marek's Disease Specific Meq Oncoprotein Using CRISPR/Cas9-Gene-Edited Viruses
- PMID: 37112797
- PMCID: PMC10142107
- DOI: 10.3390/v15040817
Efficient Cross-Screening and Characterization of Monoclonal Antibodies against Marek's Disease Specific Meq Oncoprotein Using CRISPR/Cas9-Gene-Edited Viruses
Abstract
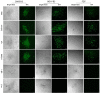
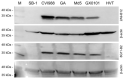
Marek's disease (MD) caused by pathogenic Marek's disease virus type 1 (MDV-1) is one of the most important neoplastic diseases of poultry. MDV-1-encoded unique Meq protein is the major oncoprotein and the availability of Meq-specific monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) is crucial for revealing MDV pathogenesis/oncogenesis. Using synthesized polypeptides from conserved hydrophilic regions of the Meq protein as immunogens, together with hybridoma technology and primary screening by cross immunofluorescence assay (IFA) on Meq-deleted MDV-1 viruses generated by CRISPR/Cas9-gene editing, a total of five positive hybridomas were generated. Four of these hybridomas, namely 2A9, 5A7, 7F9 and 8G11, were further confirmed to secrete specific antibodies against Meq as confirmed by the IFA staining of 293T cells overexpressing Meq. Confocal microscopic analysis of cells stained with these antibodies confirmed the nuclear localization of Meq in MDV-infected CEF cells and MDV-transformed MSB-1 cells. Furthermore, two mAb hybridoma clones, 2A9-B12 and 8G11-B2 derived from 2A9 and 8G11, respectively, displayed high specificity for Meq proteins of MDV-1 strains with diverse virulence. Our data presented here, using synthesized polypeptide immunization combined with cross IFA staining on CRISPR/Cas9 gene-edited viruses, has provided a new efficient approach for future generation of specific mAbs against viral proteins.
Keywords: CRISPR/Cas9; MDV; Meq; gene editing; herpesvirus; monoclonal antibody.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
A New Strategy for Efficient Screening and Identification of Monoclonal Antibodies against Oncogenic Avian Herpesvirus Utilizing CRISPR/Cas9-Based Gene-Editing Technology.Viruses. 2022 Sep 14;14(9):2045. doi: 10.3390/v14092045. Viruses. 2022. PMID: 36146851 Free PMC article.
-
Targeted Deletion of Glycoprotein B Gene by CRISPR/Cas9 Nuclease Inhibits Gallid herpesvirus Type 3 in Dually Infected Marek's Disease Virus-Transformed Lymphoblastoid Cell Line MSB-1.J Virol. 2022 Mar 23;96(6):e0202721. doi: 10.1128/jvi.02027-21. Epub 2022 Feb 2. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35107377 Free PMC article.
-
Application of CRISPR/Cas9 Gene Editing System on MDV-1 Genome for the Study of Gene Function.Viruses. 2018 May 24;10(6):279. doi: 10.3390/v10060279. Viruses. 2018. PMID: 29794970 Free PMC article.
-
Critical roles of non-coding RNAs in lifecycle and biology of Marek's disease herpesvirus.Sci China Life Sci. 2023 Feb;66(2):251-268. doi: 10.1007/s11427-022-2258-4. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Sci China Life Sci. 2023. PMID: 36617590 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Latency and tumorigenesis in Marek's disease.Avian Dis. 2013 Jun;57(2 Suppl):360-5. doi: 10.1637/10470-121712-Reg.1. Avian Dis. 2013. PMID: 23901747 Review.
Cited by
-
Emerging Hypervirulent Marek's Disease Virus Variants Significantly Overcome Protection Conferred by Commercial Vaccines.Viruses. 2023 Jun 25;15(7):1434. doi: 10.3390/v15071434. Viruses. 2023. PMID: 37515122 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

