Nanoparticles as a Delivery System of Antigens for the Development of an Effective Vaccine against Toxoplasma gondii
- PMID: 37112645
- PMCID: PMC10142924
- DOI: 10.3390/vaccines11040733
Nanoparticles as a Delivery System of Antigens for the Development of an Effective Vaccine against Toxoplasma gondii
Abstract
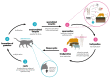
Nanoparticles include particles ranging in size from nanometers to micrometers, whose physicochemical characteristics are optimized to make them appropriate delivery vehicles for drugs or immunogens important in the fight and/or prevention of infectious diseases. There has been a rise in the use of nanoparticles in preventive vaccine formulations as immunostimulatory adjuvants, and as vehicles for immunogen delivery to target immune cells. Toxoplasma is important worldwide, and may cause human toxoplasmosis. In immunocompetent hosts, infection is usually asymptomatic, but in immunocompromised patients it can cause serious neurological and ocular consequences, such as encephalitis and retinochoroiditis. Primary infection during pregnancy may cause abortion or congenital toxoplasmosis. Currently, there is no effective human vaccine against this disease. Evidence has emerged from several experimental studies testing nanovaccines showing them to be promising tools in the prevention of experimental toxoplasmosis. For the present study, a literature review was carried out on articles published over the last 10 years through the PubMed database, pertaining to in vivo experimental models of T. gondii infection where nanovaccines were tested and protection and immune responses evaluated. This review aims to highlight the way forward in the search for an effective vaccine for toxoplasmosis.
Keywords: Toxoplasma gondii; adjuvant; immune system; nanoparticles; toxoplasmosis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Toxoplasmosis in pregnancy: prevention, screening, and treatment.J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013 Jan;35(1):78-81. doi: 10.1016/s1701-2163(15)31053-7. J Obstet Gynaecol Can. 2013. PMID: 23343802 English, French.
-
PLGA Nanoparticles as an Efficient Platform in Protein Vaccines Against Toxoplasma gondii.Acta Parasitol. 2022 Jun;67(2):582-591. doi: 10.1007/s11686-021-00499-w. Epub 2022 Jan 11. Acta Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35013939 Review.
-
Porous nanoparticles as delivery system of complex antigens for an effective vaccine against acute and chronic Toxoplasma gondii infection.Biomaterials. 2015 May;50:164-75. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2015.01.056. Epub 2015 Feb 19. Biomaterials. 2015. PMID: 25736506
-
Immune response against toxoplasmosis-some recent updates RH: Toxoplasma gondii immune response.Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022 Jan-Dec;36:3946320221078436. doi: 10.1177/03946320221078436. Int J Immunopathol Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35227108 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Toxoplasma gondii: Vaccination with a DNA vaccine encoding T- and B-cell epitopes of SAG1, GRA2, GRA7 and ROP16 elicits protection against acute toxoplasmosis in mice.Vaccine. 2015 Nov 27;33(48):6757-62. doi: 10.1016/j.vaccine.2015.10.077. Epub 2015 Oct 27. Vaccine. 2015. PMID: 26518401
Cited by
-
Nanospheres as the delivery vehicle: novel application of Toxoplasma gondii ribosomal protein S2 in PLGA and chitosan nanospheres against acute toxoplasmosis.Front Immunol. 2024 Oct 1;15:1475280. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1475280. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 39416787 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Deng H., Devleesschauwer B., Liu M., Li J., Wu Y., van der Giessen J.W.B., Opsteegh M. Seroprevalence of Toxoplasma gondii in pregnant women and livestock in the mainland of China: A systematic review and hierarchical meta-analysis. Sci. Rep. 2018;8:6218. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-24361-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Delgado I.L.S., Zúquete S., Santos D., Basto A.P., Leitão A., Nolasco S. The Apicomplexan Parasite Toxoplasma gondii. Encyclopedia. 2022;2:189–211. doi: 10.3390/encyclopedia2010012. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

