Phytoconstituent-Loaded Nanofibrous Meshes as Wound Dressings: A Concise Review
- PMID: 37111544
- PMCID: PMC10143731
- DOI: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041058
Phytoconstituent-Loaded Nanofibrous Meshes as Wound Dressings: A Concise Review
Abstract
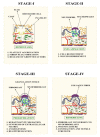
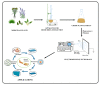
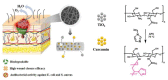
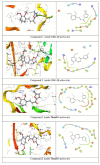
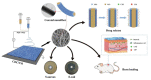
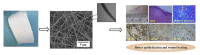
In the past, wounds were treated with natural materials, but modern wound dressings include functional elements to expedite the process of healing and to improve skin recovery. Due to their exceptional properties, nanofibrous wound dressings are now the most cutting-edge and desirable option. Similar in structure to the skin's own extracellular matrix (ECM), these dressings can promote tissue regeneration, wound fluid transportation, and air ductility for cellular proliferation and regeneration owing to their nanostructured fibrous meshes or scaffolds. Many academic search engines and databases, such as Google Scholar, PubMed, and Sciencedirect, were used to conduct a comprehensive evaluation of the literature for the purposes of this investigation. Using the term "nanofibrous meshes" as a keyword, this paper focuses on the importance of phytoconstituents. This review article summarizes the most recent developments and conclusions from studies on bioactive nanofibrous wound dressings infused with medicinal plants. Several wound-healing methods, wound-dressing materials, and wound-healing components derived from medicinal plants were also discussed.
Keywords: nanofibers; phytoconstituents; polysaccharides; wound; wound dressings; wound healing.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
An Overview on Application of Natural Substances Incorporated with Electrospun Nanofibrous Scaffolds to Development of Innovative Wound Dressings.Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018 Feb 14;18(5):414-427. doi: 10.2174/1389557517666170308112147. Mini Rev Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28271816 Review.
-
Antibacterial biohybrid nanofibers for wound dressings.Acta Biomater. 2020 Apr 15;107:25-49. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2020.02.022. Epub 2020 Feb 19. Acta Biomater. 2020. PMID: 32084600 Review.
-
Electrospun Nanofibers/Nanofibrous Scaffolds Loaded with Silver Nanoparticles as Effective Antibacterial Wound Dressing Materials.Pharmaceutics. 2021 Jun 26;13(7):964. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics13070964. Pharmaceutics. 2021. PMID: 34206857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chelidoniummajus L. Incorporated Emulsion Electrospun PCL/PVA_PEC Nanofibrous Meshes for Antibacterial Wound Dressing Applications.Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021 Jul 9;11(7):1785. doi: 10.3390/nano11071785. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2021. PMID: 34361171 Free PMC article.
-
Human Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Secreted Extracellular Matrix Incorporated into Electrospun Poly(Lactic-co-Glycolic Acid) Nanofibrous Dressing for Enhancing Wound Healing.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Oct 3;11(10):1609. doi: 10.3390/polym11101609. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31623334 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
From Nature to Healing: Development and Evaluation of Topical Cream Loaded with Pine Tar for Cutaneous Wound Repair.Pharmaceutics. 2024 Jun 26;16(7):859. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics16070859. Pharmaceutics. 2024. PMID: 39065556 Free PMC article.
-
Nanofiber Scaffolds as Drug Delivery Systems Promoting Wound Healing.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jun 26;15(7):1829. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071829. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514015 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Advancements in wound management: integrating nanotechnology and smart materials for enhanced therapeutic interventions.Discov Nano. 2024 Oct 2;19(1):159. doi: 10.1186/s11671-024-04116-3. Discov Nano. 2024. PMID: 39354172 Free PMC article. Review.
-
From Plants to Wound Dressing and Transdermal Delivery of Bioactive Compounds.Plants (Basel). 2023 Jul 16;12(14):2661. doi: 10.3390/plants12142661. Plants (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37514275 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Qiao Y., Qiao L., Chen Z., Liu B., Gao L., Zhang L. Wearable Sensor for Continuous Sweat Biomarker Monitoring. Chemosensors. 2022;10:273. doi: 10.3390/chemosensors10070273. - DOI
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

