Identification of Key Functional Genes and LncRNAs Influencing Muscle Growth and Development in Leizhou Black Goats
- PMID: 37107639
- PMCID: PMC10138011
- DOI: 10.3390/genes14040881
Identification of Key Functional Genes and LncRNAs Influencing Muscle Growth and Development in Leizhou Black Goats
Abstract
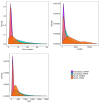
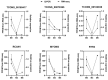
Meat yield and quality are important economic traits of livestock. Herein, longissimus dorsi (LD) muscles of Leizhou black goats aged 0, 3, and 6 months were used to identify differentially expressed messenger RNAs (mRNAs) and long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) by high-throughput RNA sequencing. Gene Ontology (GO) and Kyoto Encyclopedia of Genes and Genomes (KEGG) analyses were used to analyze differentially expressed genes. Expression levels of regulator of calcineurin 1 (RCAN1) and olfactory receptor 2AP1 (OR2AP1) were significantly different in LD muscles of goats aged 0, 3, and 6 months, indicating potentially important roles in postnatal muscle development. Differentially expressed lncRNAs and mRNAs were mainly enriched in biological processes and pathways related to cellular energy metabolism, consistent with previous studies. Three lncRNAs, TCONS_00074191, TCONS_00074190, and TCONS_00078361, may play a cis-acting role with methyltransferase-like 11B (METTL11B) genes and participate in the methylation of goat muscle proteins. Some of the identified genes may provide valuable resources for future studies on postnatal meat development in goat muscles.
Keywords: Leizhou black goat; lncRNA; longissimus dorsi; mRNA; meat quality; meat yield; protein methylation; skeletal muscle.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Genome-wide identification and characterization of long non-coding RNAs in developmental skeletal muscle of fetal goat.BMC Genomics. 2016 Aug 22;17(1):666. doi: 10.1186/s12864-016-3009-3. BMC Genomics. 2016. PMID: 27550073 Free PMC article.
-
Integrated transcriptome analysis reveals roles of long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) in caprine skeletal muscle mass and meat quality.Funct Integr Genomics. 2023 Feb 22;23(1):63. doi: 10.1007/s10142-023-00987-4. Funct Integr Genomics. 2023. PMID: 36810929
-
Identification of differentially expressed long non-coding RNAs and messenger RNAs involved with muscle development in Dazu black goats through RNA sequencing.Anim Biotechnol. 2023 Nov;34(4):1305-1313. doi: 10.1080/10495398.2021.2020804. Epub 2022 Jan 5. Anim Biotechnol. 2023. PMID: 34985384
-
Transcriptome Analysis Reveals the Profile of Long Non-Coding RNAs during Myogenic Differentiation in Goats.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 28;24(7):6370. doi: 10.3390/ijms24076370. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37047345 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of Long Non-Coding RNAs Related to Skeletal Muscle Development in Two Rabbit Breeds with Different Growth Rate.Int J Mol Sci. 2018 Jul 13;19(7):2046. doi: 10.3390/ijms19072046. Int J Mol Sci. 2018. PMID: 30011879 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Transcriptomic and metabolomic dissection of skeletal muscle of crossbred Chongming white goats with different meat production performance.BMC Genomics. 2024 May 4;25(1):443. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10304-3. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 38704563 Free PMC article.
-
Temporal Transcriptome Dynamics of Longissimus dorsi Reveals the Mechanism of the Differences in Muscle Development and IMF Deposition between Fuqing Goats and Nubian Goats.Animals (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;14(12):1770. doi: 10.3390/ani14121770. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929389 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Quiat D., Voelker K.A., Pei J., Grishin N.V., Grange R.W., Bassel-Duby R., Olson E.N. Concerted regulation of myofiber-specific gene expression and muscle performance by the transcriptional repressor Sox6. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2011;108:10196–10201. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1107413108. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials