Targeting miRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs as a Therapeutic Approach: An Update
- PMID: 37104009
- PMCID: PMC10145226
- DOI: 10.3390/ncrna9020027
Targeting miRNAs and Other Non-Coding RNAs as a Therapeutic Approach: An Update
Abstract
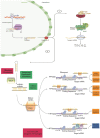
Since the discovery of the first microRNAs (miRNAs, miRs), the understanding of miRNA biology has expanded substantially. miRNAs are involved and described as master regulators of the major hallmarks of cancer, including cell differentiation, proliferation, survival, the cell cycle, invasion, and metastasis. Experimental data indicate that cancer phenotypes can be modified by targeting miRNA expression, and because miRNAs act as tumor suppressors or oncogenes (oncomiRs), they have emerged as attractive tools and, more importantly, as a new class of targets for drug development in cancer therapeutics. With the use of miRNA mimics or molecules targeting miRNAs (i.e., small-molecule inhibitors such as anti-miRS), these therapeutics have shown promise in preclinical settings. Some miRNA-targeted therapeutics have been extended to clinical development, such as the mimic of miRNA-34 for treating cancer. Here, we discuss insights into the role of miRNAs and other non-coding RNAs in tumorigenesis and resistance and summarize some recent successful systemic delivery approaches and recent developments in miRNAs as targets for anticancer drug development. Furthermore, we provide a comprehensive overview of mimics and inhibitors that are in clinical trials and finally a list of clinical trials based on miRNAs.
Keywords: cancer; drug delivery; miRNA; microRNA; resistance; therapeutics.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA therapeutics: towards a new era for the management of cancer and other diseases.Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017 Mar;16(3):203-222. doi: 10.1038/nrd.2016.246. Epub 2017 Feb 17. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2017. PMID: 28209991 Review.
-
MicroRNA as an Important Target for Anticancer Drug Development.Front Pharmacol. 2021 Aug 25;12:736323. doi: 10.3389/fphar.2021.736323. eCollection 2021. Front Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34512363 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA: Promising Roles in Cancer Therapy.Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020;21(12):1186-1203. doi: 10.2174/1389201021666200420101613. Curr Pharm Biotechnol. 2020. PMID: 32310047 Review.
-
The crosstalk between miRNAs and signaling pathways in human cancers: Potential therapeutic implications.Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2024;386:133-165. doi: 10.1016/bs.ircmb.2023.12.001. Epub 2024 Jan 23. Int Rev Cell Mol Biol. 2024. PMID: 38782498 Review.
-
RNAi-based therapeutics and tumor targeted delivery in cancer.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022 Mar;182:114113. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2022.114113. Epub 2022 Jan 19. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2022. PMID: 35063535 Review.
Cited by
-
The Role of the MiR-181 Family in Hepatocellular Carcinoma.Cells. 2024 Jul 31;13(15):1289. doi: 10.3390/cells13151289. Cells. 2024. PMID: 39120319 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Non-coding RNAs as skin disease biomarkers, molecular signatures, and therapeutic targets.Hum Genet. 2024 Jul;143(7):801-812. doi: 10.1007/s00439-023-02588-4. Epub 2023 Aug 14. Hum Genet. 2024. PMID: 37580609 Review.
-
lncRNA-microRNA axis in cancer drug resistance: particular focus on signaling pathways.Med Oncol. 2024 Jan 9;41(2):52. doi: 10.1007/s12032-023-02263-8. Med Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38195957 Review.
-
Exploring the Therapeutic Significance of microRNAs and lncRNAs in Kidney Diseases.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;15(1):123. doi: 10.3390/genes15010123. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275604 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Literature Review and Meta-Analysis on the Potential Use of miR-150 as a Novel Biomarker in the Detection and Progression of Multiple Sclerosis.J Pers Med. 2024 Jul 31;14(8):815. doi: 10.3390/jpm14080815. J Pers Med. 2024. PMID: 39202006 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

