Combined PacBio Iso-Seq and Illumina RNA-Seq Analysis of the Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) Transcriptome and Cytochrome P450 Genes
- PMID: 37103178
- PMCID: PMC10146655
- DOI: 10.3390/insects14040363
Combined PacBio Iso-Seq and Illumina RNA-Seq Analysis of the Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) Transcriptome and Cytochrome P450 Genes
Abstract
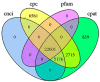
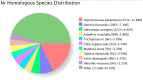
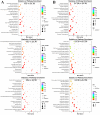
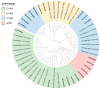
Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) is a devastating invasive pest worldwide. The abamectin and chlorantraniliprole complex have become an alternative option for chemical control because they can enhance insecticidal activity and delay increased drug resistance. Notably, pests are inevitably resistant to various types of insecticides, and compound insecticides are no exception. To identify potential genes involved in the detoxification of abamectin and chlorantraniliprole complex in T. absoluta, PacBio SMRT-seq transcriptome sequencing and Illumina RNA-seq analysis of abamectin and chlorantraniliprole complex-treated T. absoluta were performed. We obtained 80,492 non-redundant transcripts, 62,762 (77.97%) transcripts that were successfully annotated, and 15,524 differentially expressed transcripts (DETs). GO annotation results showed that most of these DETs were involved in the biological processes of life-sustaining activities, such as cellular, metabolic, and single-organism processes. The KEGG pathway enrichment results showed that the pathways related to glutathione metabolism, fatty acid and amino acid synthesis, and metabolism were related to the response to abamectin and chlorantraniliprole complex in T. absoluta. Among these, 21 P450s were differentially expressed (11 upregulated and 10 downregulated). The qRT-PCR results for the eight upregulated P450 genes after abamectin and chlorantraniliprole complex treatment were consistent with the RNA-Seq data. Our findings provide new full-length transcriptional data and information for further studies on detoxification-related genes in T. absoluta.
Keywords: Illumina RNA-seq analysis; PacBio Iso-Seq analysis; Tuta absoluta; cytochrome P450.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Lethal and Sublethal Effects of Some Chemical and Biological Insecticides on Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Eggs and Neonates.J Econ Entomol. 2017 Jun 1;110(3):1138-1144. doi: 10.1093/jee/tox079. J Econ Entomol. 2017. PMID: 28334249
-
Integration analysis of PacBio SMRT- and Illumina RNA-seq reveals P450 genes involved in thiamethoxam detoxification in Bradysia odoriphaga.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2022 Aug;186:105176. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2022.105176. Epub 2022 Jul 13. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2022. PMID: 35973766
-
Role of Enterococcus mundtii in gut of the tomato leaf miner (Tuta absoluta) to detoxification of Chlorantraniliprole.Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024 Sep;204:106060. doi: 10.1016/j.pestbp.2024.106060. Epub 2024 Jul 30. Pestic Biochem Physiol. 2024. PMID: 39277378
-
Susceptibility of Tuta absoluta (Lepidoptera: Gelechiidae) Brazilian populations to ryanodine receptor modulators.Pest Manag Sci. 2015 Apr;71(4):537-44. doi: 10.1002/ps.3835. Epub 2014 Jul 9. Pest Manag Sci. 2015. PMID: 24863675
-
Current Strategies and Future Outlook for Managing the Neotropical Tomato Pest Tuta absoluta (Meyrick) in the Mediterranean Basin.Neotrop Entomol. 2019 Feb;48(1):1-17. doi: 10.1007/s13744-018-0636-1. Epub 2018 Oct 3. Neotrop Entomol. 2019. PMID: 30284151 Review.
Cited by
-
Identification of testis development-related genes by combining Iso-Seq and RNA-Seq in Zeugodacus tau.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024 Mar 11;12:1356151. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2024.1356151. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2024. PMID: 38529408 Free PMC article.
-
Transcriptome and Expression Analysis of Glycerol Biosynthesis-Related Genes in Glenea cantor Fabricius (Cerambycidae: Lamiinae).Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Nov 4;25(21):11834. doi: 10.3390/ijms252111834. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39519387 Free PMC article.
-
Differences in alternative splicing events in the adaptive strategies of two Daphnia galeata genotypes induced by fish kairomones.BMC Genomics. 2024 Jul 26;25(1):725. doi: 10.1186/s12864-024-10643-1. BMC Genomics. 2024. PMID: 39060996 Free PMC article.
-
Toxic Effect of Methyl-Thiophanate on Bombyx mori Based on Physiological and Transcriptomic Analysis.Genes (Basel). 2024 Sep 29;15(10):1279. doi: 10.3390/genes15101279. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39457404 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Desneux N., Wajnberg E., Wyckhuys K., Burgio G., Arpaia S., Narváez-Vasquez C., González-Cabrera J., Ruescas D.C., Tabone E., Frandon J. Biological invasion of European tomato crops by Tuta absoluta: Ecology, geographic expansion and prospects for biological control. J. Pest Sci. 2010;83:197–215. doi: 10.1007/s10340-010-0321-6. - DOI
-
- Guimapi R.A., Srinivasan R., Tonnang H.E., Sotelo-Cardona P., Mohamed S.A. Exploring the Mechanisms of the Spatiotemporal Invasion of Tuta absoluta in Asia. Agriculture. 2020;10:124. doi: 10.3390/agriculture10040124. - DOI
-
- Zhang G.-F., Wang Y.-S., Gao Y.-H., Liu W.-X., Zhang R., Fu W.-J., Xian X.-Q., Jun W., Kuang M., Wan F.-H. First report of the South American tomato leafminer, Tuta absoluta (Meyrick), in China. J. Integr. Agric. 2020;19:1912–1917. doi: 10.1016/S2095-3119(20)63165-3. - DOI
-
- Xian X., Han P., Wang S., Zhang G., Liu W., Desneux N., Wan F. The potential invasion risk and preventive measures against the tomato leafminer Tuta absoluta in China. Entomol. Gen. 2017;36:319–333. doi: 10.1127/entomologia/2017/0504. - DOI
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

