Change Profiles and Functional Targets of MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Obesity
- PMID: 37096418
- PMCID: PMC10404519
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0226
Change Profiles and Functional Targets of MicroRNAs in Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients with Obesity
Abstract
Backgruound: MicroRNAs (miRNAs) exert an essential contribution to obesity and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). This study aimed to investigate the differences of miRNAs in the presence and absence of T2DM in patients with obesity, as well as before and after bariatric surgery in T2DM patients with obesity. Characterization of the common changes in both was further analyzed.
Methods: We enrolled 15 patients with obesity but without T2DM and 15 patients with both obesity and T2DM. Their preoperative clinical data and serum samples were collected, as well as 1 month after bariatric surgery. The serum samples were analyzed by miRNA sequencing, and the miRNAs profiles and target genes characteristics were compared.
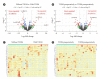
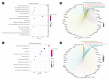
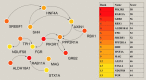
Results: Patients with T2DM had 16 up-regulated and 32 down-regulated miRNAs compared to patients without T2DM. Improvement in metabolic metrics after bariatric surgery of T2DM patients with obesity was correlated with changes in miRNAs, as evidenced by the upregulation of 20 miRNAs and the downregulation of 30 miRNAs. Analysis of the two miRNAs profiles identified seven intersecting miRNAs that showed opposite changes. The target genes of these seven miRNAs were substantially enriched in terms or pathways associated with T2DM.
Conclusion: We determined the expression profiles of miRNAs in the obese population, with and without diabetes, before and after bariatric surgery. The miRNAs that intersected in the two comparisons were discovered. Both the miRNAs discovered and their target genes were closely associated with T2DM, demonstrating that they might be potential targets for the regulation of T2DM.
Keywords: Bariatric surgery; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Metabolism; MicroRNAs; Obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
No potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Serum microRNA profiling and bioinformatics analysis of patients with type 2 diabetes mellitus in a Chinese population.Mol Med Rep. 2017 Apr;15(4):2143-2153. doi: 10.3892/mmr.2017.6239. Epub 2017 Feb 22. Mol Med Rep. 2017. PMID: 28260062 Free PMC article.
-
Circulating Soluble ACE2 and Upstream microRNA Expressions in Serum of Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus Patients.Int J Mol Sci. 2021 May 17;22(10):5263. doi: 10.3390/ijms22105263. Int J Mol Sci. 2021. PMID: 34067683 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of bariatric surgery on circulating and urinary mitochondrial DNA copy numbers in obesity with or without diabetes.BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020 Oct;8(1):e001372. doi: 10.1136/bmjdrc-2020-001372. BMJ Open Diabetes Res Care. 2020. PMID: 33020132 Free PMC article.
-
Physiologic Mechanisms of Type II Diabetes Mellitus Remission Following Bariatric Surgery: a Meta-analysis and Clinical Implications.J Gastrointest Surg. 2020 Mar;24(3):728-741. doi: 10.1007/s11605-019-04508-2. Epub 2020 Jan 2. J Gastrointest Surg. 2020. PMID: 31898109 Review.
-
The role of bariatric surgery to treat diabetes: current challenges and perspectives.BMC Endocr Disord. 2017 Aug 10;17(1):50. doi: 10.1186/s12902-017-0202-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2017. PMID: 28797248 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Early changes of microRNAs in blood one month after bariatric surgery.Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024 Jul 15;16(1):163. doi: 10.1186/s13098-024-01364-2. Diabetol Metab Syndr. 2024. PMID: 39010180 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Swinburn BA, Sacks G, Hall KD, McPherson K, Finegood DT, Moodie ML, et al. The global obesity pandemic: shaped by global drivers and local environments. Lancet. 2011;378:804–14. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

