Differential microRNA expression for diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer
- PMID: 37089590
- PMCID: PMC10113479
- DOI: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1139362
Differential microRNA expression for diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer
Abstract
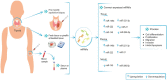
Papillary thyroid cancer accounts for 85% of thyroid cancer. The diagnosis is based on ultrasound methods and tumor biopsies (FNA). In recent years, research has revealed the importance of miRNAs, non-coding RNA molecules that regulate gene expression and are involved in many diseases. The present mini review describes upregulated and downregulated miRNAs expression in papillary thyroid cancer patient samples (tissue, serum, plasma) and the genes regulated by these non-coding molecules. In addition, a bibliographic search was performed to identify the expression of miRNAs that are common in tumor tissue and blood. The miRNAs miR-146b, miR-221-3p, miRNA 222, miR-21, miR-296-5p, and miR-145 are common in both tissue and bloodstream of PTC patient samples. Furthermore, these miRNAs regulate genes involved in biological processes such as cell differentiation, proliferation, migration, invasion, and apoptosis. In conclusion, miRNAs could potentially become valuable biomarkers, which could help in the early diagnosis and prognosis of papillary thyroid cancer.
Keywords: biomarkers; diagnosis; miRNAs; papillary thyroid cancer; tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2023 Ruiz-Pozo, Cadena-Ullauri, Guevara-Ramírez, Paz-Cruz, Tamayo-Trujillo and Zambrano.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
MicroRNA-146b-3p Promotes Cell Metastasis by Directly Targeting NF2 in Human Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Thyroid. 2018 Dec;28(12):1627-1641. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0626. Epub 2018 Oct 27. Thyroid. 2018. PMID: 30244634 Free PMC article.
-
Discriminatory miRNAs for the Management of Papillary Thyroid Carcinoma and Noninvasive Follicular Thyroid Neoplasms with Papillary-Like Nuclear Features.Thyroid. 2018 Mar;28(3):319-327. doi: 10.1089/thy.2017.0127. Epub 2018 Mar 2. Thyroid. 2018. PMID: 29378472
-
Comprehensive MicroRNA expression profiling identifies novel markers in follicular variant of papillary thyroid carcinoma.Thyroid. 2013 Nov;23(11):1383-9. doi: 10.1089/thy.2012.0632. Epub 2013 Sep 19. Thyroid. 2013. PMID: 23427895 Free PMC article.
-
MicroRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: What Is New in Diagnosis and Treatment.Front Oncol. 2022 Feb 3;11:755097. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2021.755097. eCollection 2021. Front Oncol. 2022. PMID: 35186709 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA-146b: A Novel Biomarker and Therapeutic Target for Human Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2017 Mar 15;18(3):636. doi: 10.3390/ijms18030636. Int J Mol Sci. 2017. PMID: 28294980 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Application of microRNAs in Papillary Thyroid Cancer: A Bibliometric and Visualized Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Oct 15;17:4681-4699. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S487239. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 39429957 Free PMC article.
-
Papillary Thyroid Cancer Remodels the Genetic Information Processing Pathways.Genes (Basel). 2024 May 14;15(5):621. doi: 10.3390/genes15050621. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38790250 Free PMC article.
-
Plasma miRNA-146b-3p, -222-3p, -221-5p, -21a-3p Expression Levels and TSHR Methylation: Diagnostic Potential and Association with Clinical and Pathological Features in Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 1;25(15):8412. doi: 10.3390/ijms25158412. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39125979 Free PMC article.
-
Gender Differences and miRNAs Expression in Cancer: Implications on Prognosis and Susceptibility.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 17;24(14):11544. doi: 10.3390/ijms241411544. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37511303 Free PMC article. Review.
-
MicroRNA Profiling in Papillary Thyroid Cancer.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Aug 29;25(17):9362. doi: 10.3390/ijms25179362. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39273308 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources