Controlling viral inflammatory lesions by inhibiting fatty acid metabolism
- PMID: 37085045
- PMCID: PMC10524470
- DOI: 10.1016/j.micinf.2023.105141
Controlling viral inflammatory lesions by inhibiting fatty acid metabolism
Abstract
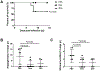
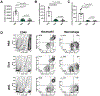
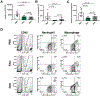
Herpes simplex virus infection is a major cause of vision loss in humans. Eye damaging consequences are often driven by inflammatory cells as a result of an immune response to the virus. In the present report, we have compared the effect of inhibiting energy metabolism with etomoxir (Etox), which acts on the fatty acid oxidation pathway and 2-Deoxy-d-glucose (2DG), which acts on glycolysis for their inhibitory effects on herpetic ocular lesions. Both drugs showed similar protective effects when therapy was started on the day of infection, but some 2DG recipients succumbed to encephalitis. In contrast, all Etox recipients remained healthy. Both drugs were compared for effects on inflammatory reactions in the trigeminal ganglion (TG), where virus replicates and then establishes latency. Results indicate that 2DG significantly reduced CD8 and CD4 Th1 T cells in the TG, whereas Etox had minimal or no effect on such cells, perhaps explaining why encephalitis occurred only in 2DG recipients. Unlike treatment with 2DG, Etox therapy was largely ineffective when started at the time of lesion expression. Reasons for the differential effects were discussed as was the relevance of combining metabolic reprogramming approaches to combat viral inflammatory lesions.
Keywords: 2DG; Etomoxir; FAO; HSV; Immunometabolism; Immunopathogenesis.
Published by Elsevier Masson SAS.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of competing interest There is no competing interest exist.
Figures
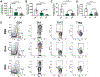

Similar articles
-
Controlling Herpes Simplex Virus-Induced Immunoinflammatory Lesions Using Metabolic Therapy: a Comparison of 2-Deoxy-d-Glucose with Metformin.J Virol. 2022 Jul 27;96(14):e0068822. doi: 10.1128/jvi.00688-22. Epub 2022 Jul 11. J Virol. 2022. PMID: 35862706 Free PMC article.
-
Inhibiting Glucose Metabolism Results in Herpes Simplex Encephalitis.J Immunol. 2021 Oct 1;207(7):1824-1835. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2100453. Epub 2021 Sep 1. J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34470854 Free PMC article.
-
Manipulating Glucose Metabolism during Different Stages of Viral Pathogenesis Can Have either Detrimental or Beneficial Effects.J Immunol. 2017 Sep 1;199(5):1748-1761. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.1700472. Epub 2017 Aug 2. J Immunol. 2017. PMID: 28768727 Free PMC article.
-
[Battle with herpes for 37 years].Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015 Mar;119(3):145-66; discussion 167. Nippon Ganka Gakkai Zasshi. 2015. PMID: 25854108 Review. Japanese.
-
Pathogenesis and virulence of herpes simplex virus.Virulence. 2021 Dec;12(1):2670-2702. doi: 10.1080/21505594.2021.1982373. Virulence. 2021. PMID: 34676800 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Meeting the Challenge of Controlling Viral Immunopathology.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr 1;25(7):3935. doi: 10.3390/ijms25073935. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38612744 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Zhang D, Li J, Wang F, Hu J, Wang S, Sun Y. 2-Deoxy-D-glucose targeting of glucose metabolism in cancer cells as a potential therapy. Cancer Lett 2014;355:176–83. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

