Long-read sequencing of diagnosis and post-therapy medulloblastoma reveals complex rearrangement patterns and epigenetic signatures
- PMID: 37082141
- PMCID: PMC10112291
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100281
Long-read sequencing of diagnosis and post-therapy medulloblastoma reveals complex rearrangement patterns and epigenetic signatures
Abstract
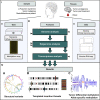
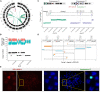
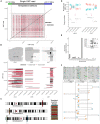
Cancer genomes harbor a broad spectrum of structural variants (SVs) driving tumorigenesis, a relevant subset of which escape discovery using short-read sequencing. We employed Oxford Nanopore Technologies (ONT) long-read sequencing in a paired diagnostic and post-therapy medulloblastoma to unravel the haplotype-resolved somatic genetic and epigenetic landscape. We assembled complex rearrangements, including a 1.55-Mbp chromothripsis event, and we uncover a complex SV pattern termed templated insertion (TI) thread, characterized by short (mostly <1 kb) insertions showing prevalent self-concatenation into highly amplified structures of up to 50 kbp in size. TI threads occur in 3% of cancers, with a prevalence up to 74% in liposarcoma, and frequent colocalization with chromothripsis. We also perform long-read-based methylome profiling and discover allele-specific methylation (ASM) effects, complex rearrangements exhibiting differential methylation, and differential promoter methylation in cancer-driver genes. Our study shows the advantage of long-read sequencing in the discovery and characterization of complex somatic rearrangements.
Keywords: Nanopore methylation calling; cancer genomics; chromothripsis; complex rearrangements; epigenetic signatures; long read sequencing; templated insertions.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
E.B. is a paid consultant and shareholder of ONT. A.L. has received financial support from ONT for consumables during the course of the project and is currently an employee of ONT. O.S. is a paid consultant of Insitro, Inc.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Combined use of Oxford Nanopore and Illumina sequencing yields insights into soybean structural variation biology.BMC Biol. 2022 Feb 23;20(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12915-022-01255-w. BMC Biol. 2022. PMID: 35197050 Free PMC article.
-
Application of long-read sequencing to the detection of structural variants in human cancer genomes.Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021 Jul 28;19:4207-4216. doi: 10.1016/j.csbj.2021.07.030. eCollection 2021. Comput Struct Biotechnol J. 2021. PMID: 34527193 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Comparison of Structural Variant Calling from Short-Read and Nanopore-Based Whole-Genome Sequencing Using Optical Genome Mapping as a Benchmark.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jul 16;15(7):925. doi: 10.3390/genes15070925. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39062704 Free PMC article.
-
Mapping and phasing of structural variation in patient genomes using nanopore sequencing.Nat Commun. 2017 Nov 6;8(1):1326. doi: 10.1038/s41467-017-01343-4. Nat Commun. 2017. PMID: 29109544 Free PMC article.
-
Resolving complex structural variants via nanopore sequencing.Front Genet. 2023 Aug 16;14:1213917. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1213917. eCollection 2023. Front Genet. 2023. PMID: 37674481 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Long-read sequencing for brain tumors.Front Oncol. 2024 Jun 10;14:1395985. doi: 10.3389/fonc.2024.1395985. eCollection 2024. Front Oncol. 2024. PMID: 38915364 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A multiomic characterization of the leukemia cell line REH using short- and long-read sequencing.Life Sci Alliance. 2024 May 22;7(8):e202302481. doi: 10.26508/lsa.202302481. Print 2024 Aug. Life Sci Alliance. 2024. PMID: 38777370 Free PMC article.
-
Small polymorphisms are a source of ancestral bias in structural variant breakpoint placement.Genome Res. 2024 Feb 7;34(1):7-19. doi: 10.1101/gr.278203.123. Genome Res. 2024. PMID: 38176712 Free PMC article.
-
Beijing Children's Hospital guidelines on the design and conduction of the first standardized database for medulloblastoma.Metab Brain Dis. 2023 Oct;38(7):2393-2400. doi: 10.1007/s11011-023-01233-3. Epub 2023 Jun 1. Metab Brain Dis. 2023. PMID: 37261631
-
Scrambling the genome in cancer: causes and consequences of complex chromosome rearrangements.Nat Rev Genet. 2024 Mar;25(3):196-210. doi: 10.1038/s41576-023-00663-0. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Nat Rev Genet. 2024. PMID: 37938738 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Gröbner S.N., Worst B.C., Weischenfeldt J., Buchhalter I., Kleinheinz K., Rudneva V.A., Johann P.D., Balasubramanian G.P., Segura-Wang M., Brabetz S., et al. The landscape of genomic alterations across childhood cancers. Nature. 2018;555:321–327. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

