Escape from oncogene-induced senescence is controlled by POU2F2 and memorized by chromatin scars
- PMID: 37082139
- PMCID: PMC10112333
- DOI: 10.1016/j.xgen.2023.100293
Escape from oncogene-induced senescence is controlled by POU2F2 and memorized by chromatin scars
Abstract
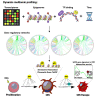
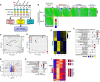
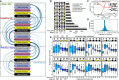
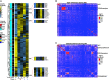
Although oncogene-induced senescence (OIS) is a potent tumor-suppressor mechanism, recent studies revealed that cells could escape from OIS with features of transformed cells. However, the mechanisms that promote OIS escape remain unclear, and evidence of post-senescent cells in human cancers is missing. Here, we unravel the regulatory mechanisms underlying OIS escape using dynamic multidimensional profiling. We demonstrate a critical role for AP1 and POU2F2 transcription factors in escape from OIS and identify senescence-associated chromatin scars (SACSs) as an epigenetic memory of OIS detectable during colorectal cancer progression. POU2F2 levels are already elevated in precancerous lesions and as cells escape from OIS, and its expression and binding activity to cis-regulatory elements are associated with decreased patient survival. Our results support a model in which POU2F2 exploits a precoded enhancer landscape necessary for senescence escape and reveal POU2F2 and SACS gene signatures as valuable biomarkers with diagnostic and prognostic potential.
Keywords: AP-1; OIS; OIS escape; Oct-2; POU2F2; SACS; cellular senescence; colorectal cancer; oncogene-induced senescence; senescence-associated chromatin scars.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Derepression of hTERT gene expression promotes escape from oncogene-induced cellular senescence.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016 Aug 23;113(34):E5024-33. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1602379113. Epub 2016 Aug 8. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2016. PMID: 27503890 Free PMC article.
-
Escape from p21-mediated oncogene-induced senescence leads to cell dedifferentiation and dependence on anti-apoptotic Bcl-xL and MCL1 proteins.J Biol Chem. 2011 Apr 15;286(15):12825-38. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M110.186437. Epub 2011 Feb 3. J Biol Chem. 2011. PMID: 21292770 Free PMC article.
-
Potential Use of Senolytics for Pharmacological Targeting of Precancerous Lesions.Mol Pharmacol. 2021 Dec;100(6):580-587. doi: 10.1124/molpharm.121.000361. Epub 2021 Sep 20. Mol Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34544896 Review.
-
Transcriptional landscape of oncogene-induced senescence: a machine learning-based meta-analytic approach.Ageing Res Rev. 2023 Mar;85:101849. doi: 10.1016/j.arr.2023.101849. Epub 2023 Jan 5. Ageing Res Rev. 2023. PMID: 36621646 Review.
-
The Immortal Senescence.Methods Mol Biol. 2017;1534:1-15. doi: 10.1007/978-1-4939-6670-7_1. Methods Mol Biol. 2017. PMID: 27812863 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Oncogene-Induced Senescence Is a Crucial Antitumor Defense Mechanism of Human Endometrial Stromal Cells.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 14;24(18):14089. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814089. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762392 Free PMC article.
-
The senescence journey in cancer immunoediting.Mol Cancer. 2024 Apr 1;23(1):68. doi: 10.1186/s12943-024-01973-5. Mol Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38561826 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Cellular senescence: Neither irreversible nor reversible.J Exp Med. 2024 Apr 1;221(4):e20232136. doi: 10.1084/jem.20232136. Epub 2024 Feb 22. J Exp Med. 2024. PMID: 38385946 Free PMC article.
-
Therapy-induced senescence through the redox lens.Redox Biol. 2024 Aug;74:103228. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2024.103228. Epub 2024 Jun 6. Redox Biol. 2024. PMID: 38865902 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Communication of the SASP: Dynamic, Interactive, and Adaptive Effects on the Microenvironment.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 28;24(13):10788. doi: 10.3390/ijms241310788. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37445973 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Fujita K., Mondal A.M., Horikawa I., Nguyen G.H., Kumamoto K., Sohn J.J., Bowman E.D., Mathe E.A., Schetter A.J., Pine S.R., et al. p53 isoforms Delta133p53 and p53beta are endogenous regulators of replicative cellular senescence. Nat. Cell Biol. 2009;11:1135–1142. doi: 10.1038/ncb1928. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

