Cross-sectional analysis of pharmaceutical payments to Japanese board-certified gastroenterologists between 2016 and 2019
- PMID: 37072354
- PMCID: PMC10124293
- DOI: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-068237
Cross-sectional analysis of pharmaceutical payments to Japanese board-certified gastroenterologists between 2016 and 2019
Abstract
Objectives: Limited evidence is available regarding the financial relationships between gastroenterologists and pharmaceutical companies in Japan. This study analysed the magnitude, prevalence and trends of personal payments made by major pharmaceutical companies to board-certified gastroenterologists in Japan in recent years.
Design: Cross-sectional analysis SETTING AND PARTICIPANTS: Using payment data publicly disclosed by 92 major pharmaceutical companies, this study examined the non-research payments made to all board-certified gastroenterologists by the Japanese Society of Gastroenterology.
Primary and secondary outcome measures: The primary outcomes were payment amounts, the prevalence of gastroenterologists receiving payments, yearly trends in per-gastroenterologist payment values and the number of gastroenterologists with payments. Additionally, we evaluated the differences in payments among influential gastroenterologists, including clinical practice guideline authors, society board member gastroenterologists and other general gastroenterologists.
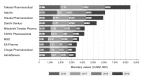
Results: Approximately 52.8% of all board-certified gastroenterologists received a total of US$89 151 253, entailing 134 249 payment contracts as the reimbursement for lecturing, consulting and writing, from 84 pharmaceutical companies between 2016 and 2019. The average and median payments per gastroenterologist were US$7670 (SD: US$26 842) and US$1533 (IQR: US$582-US$4781), respectively. The payment value per gastroenterologist did not significantly change during the study period, while the number of gastroenterologists with payments decreased by -1.01% (95% CI: -1.61% to -0.40%, p<0.001) annually. Board member gastroenterologists (median: US$132 777) and the guideline authoring gastroenterologists (median: US$106 069) received 29.9 times and 17.3 times higher payments, respectively, than general gastroenterologists (median: US$284).
Conclusion: Most gastroenterologists received personal payments from pharmaceutical companies, but only very few influential gastroenterologists with authority accepted substantial amounts in Japan. There should be transparent and rigorous management strategies for financial conflicts of interest among gastroenterologists working in influential positions.
Keywords: Clinical governance; Ethics (see Medical Ethics); Gastroenterology; Health policy; Health services administration & management.
© Author(s) (or their employer(s)) 2023. Re-use permitted under CC BY-NC. No commercial re-use. See rights and permissions. Published by BMJ.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests: HS received personal fees from Taiho Pharmaceutical Co outside the scope of the submitted work. AO and TT received personal fees from MNES, a company developing diagnostic AI tool, outside the scope of the submitted work. TT also received personal fees from Bionics Co, a medical device company, outside the scope of the submitted work. Regarding non-financial conflicts of interest among the study authors, all are engaged in ongoing research examining financial and non-financial conflicts of interest among healthcare professionals and pharmaceutical companies in Japan. HS is a board-certified gastroenterologist by the Japanese Society of Gastroenterology. The other authors have no example conflicts of interest to disclose.
Similar articles
-
Evaluation of non-research payments from pharmaceutical companies to urologists in Japan between 2016 and 2019.Int Urogynecol J. 2023 Jun;34(6):1285-1292. doi: 10.1007/s00192-023-05463-y. Epub 2023 Feb 1. Int Urogynecol J. 2023. PMID: 36723634
-
Financial Relationships Between Pharmaceutical Companies and Rheumatologists in Japan Between 2016 and 2019.J Clin Rheumatol. 2023 Apr 1;29(3):118-125. doi: 10.1097/RHU.0000000000001922. Epub 2022 Dec 7. J Clin Rheumatol. 2023. PMID: 36729793
-
Evaluation of Pharmaceutical Company Payments and Conflict of Interest Disclosures Among Oncology Clinical Practice Guideline Authors in Japan.JAMA Netw Open. 2019 Apr 5;2(4):e192834. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2019.2834. JAMA Netw Open. 2019. PMID: 31026027 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Pharmaceutical Company and Device Manufacturer Payments to Gastroenterologists and Their Participation in Clinical Practice Guideline Panels.JAMA Netw Open. 2018 Dec 7;1(8):e186343. doi: 10.1001/jamanetworkopen.2018.6343. JAMA Netw Open. 2018. PMID: 30646328 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Characteristics and Distribution of Scholarship Donations From Pharmaceutical Companies to Japanese Healthcare Institutions in 2017: A Cross-sectional Analysis.Int J Health Policy Manag. 2023;12:7621. doi: 10.34172/ijhpm.2023.7621. Epub 2023 Aug 21. Int J Health Policy Manag. 2023. PMID: 38618821 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Industry-Sponsored Research Payments to Gastroenterologists and Hepatologists in the United States Between 2014 and 2021.Cureus. 2023 Nov 7;15(11):e48449. doi: 10.7759/cureus.48449. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38073944 Free PMC article.
-
Assessment of Financial Relationships Between Otorhinolaryngologists and Pharmaceutical Companies in Japan Between 2016 and 2019.Cureus. 2023 Aug 17;15(8):e43633. doi: 10.7759/cureus.43633. eCollection 2023 Aug. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37719565 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-sectional analysis of pharmaceutical industry payments to authors of clinical practice guidelines for bipolar disorder and major depressive disorder in Japan.BMJ Open. 2024 Jun 21;14(6):e086396. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2024-086396. BMJ Open. 2024. PMID: 38908845 Free PMC article.
-
Financial Conflicts of Interest Among the Authors of the Clinical Practice Guidelines for Rheumatoid Arthritis in Japan.Cureus. 2023 Oct 7;15(10):e46650. doi: 10.7759/cureus.46650. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 37937008 Free PMC article.
-
Nature and Trend of Pharmaceutical Payments to Japanese Board-Certified Neurologists Between 2016 and 2019: A Pre-emergence Analysis Amidst the Development of Next-Generation Alzheimer's Disease Drugs.Cureus. 2024 Feb 8;16(2):e53848. doi: 10.7759/cureus.53848. eCollection 2024 Feb. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38465045 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources