Immunological Features of LRRK2 Function and Its Role in the Gut-Brain Axis Governing Parkinson's Disease
- PMID: 37066923
- PMCID: PMC10200211
- DOI: 10.3233/JPD-230021
Immunological Features of LRRK2 Function and Its Role in the Gut-Brain Axis Governing Parkinson's Disease
Abstract
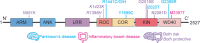
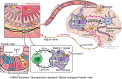
Emerging evidence implicates intestinal involvement in the onset and/or progression on the selective degeneration of dopaminergic neurons characterizing Parkinson's disease (PD). On the one hand, there are studies supporting the Braak hypothesis that holds that pathologic α-synuclein, a hallmark of PD, is secreted by enteric nerves into intestinal tissue and finds its way to the central nervous system (CNS) via retrograde movement in the vagus nerve. On the other hand, there is data showing that cells bearing leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 (LRRK2), a signaling molecule with genetic variants associated with both PD and with inflammatory bowel disease, can be activated in intestinal tissue and contribute locally to intestinal inflammation, or peripherally to PD pathogenesis via cell trafficking to the CNS. Importantly, these gut-centered factors affecting PD development are not necessarily independent of one another: they may interact and enhance their respective pathologic functions. In this review, we discuss this possibility by analysis of studies conducted in recent years focusing on the ability of LRRK2 to shape immunologic responses and the role of α-synuclein in influencing this ability.
Keywords: α-synuclein; Gut-brain axis; LRRK2; Parkinson’s disease; enteric nervous system; intestinal inflammation.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflict of interest to report.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interaction of LRRK2 and α-Synuclein in Parkinson's Disease.Adv Neurobiol. 2017;14:209-226. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-49969-7_11. Adv Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28353286 Review.
-
The role of LRRK2 in the periphery: link with Parkinson's disease and inflammatory diseases.Neurobiol Dis. 2022 Oct 1;172:105806. doi: 10.1016/j.nbd.2022.105806. Epub 2022 Jun 30. Neurobiol Dis. 2022. PMID: 35781002 Review.
-
The role of posttranslational modifications of α-synuclein and LRRK2 in Parkinson's disease: Potential contributions of environmental factors.Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019 Aug 1;1865(8):1992-2000. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2018.11.017. Epub 2018 Nov 24. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2019. PMID: 30481588 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Gut-Brain Axis: Two Ways Signaling in Parkinson's Disease.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022 Mar;42(2):315-332. doi: 10.1007/s10571-021-01066-7. Epub 2021 Mar 2. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2022. PMID: 33649989 Review.
-
Pathological Functions of LRRK2 in Parkinson's Disease.Cells. 2020 Nov 30;9(12):2565. doi: 10.3390/cells9122565. Cells. 2020. PMID: 33266247 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Multiple sclerosis in LRRK2 G2019S Parkinson's disease and isolated nigral degeneration in a homozygous variant carrier.Front Neurol. 2024 Aug 8;15:1450654. doi: 10.3389/fneur.2024.1450654. eCollection 2024. Front Neurol. 2024. PMID: 39175765 Free PMC article.
-
Role of leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 in severe acute pancreatitis.Front Immunol. 2024 Feb 19;15:1364839. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1364839. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38440723 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Parkinson's LRRK2-G2019S risk gene mutation drives sex-specific behavioral and cellular adaptations to chronic variable stress.Front Behav Neurosci. 2024 Sep 12;18:1445184. doi: 10.3389/fnbeh.2024.1445184. eCollection 2024. Front Behav Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 39328984 Free PMC article.
-
LRRK2 G2019S Promotes Colon Cancer Potentially via LRRK2-GSDMD Axis-Mediated Gut Inflammation.Cells. 2024 Mar 23;13(7):565. doi: 10.3390/cells13070565. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38607004 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Braak H, Del Tredici K, Rub U, de Vos RA, Jansen Steur EN, Braak E (2003) Staging of brain pathology related to sporadic Parkinson’s disease. Neurobiol Aging 24, 197–211. - PubMed
-
- Braak H, Rub U, Gai WP, Del Tredici K (2003) Idiopathic Parkinson’s disease: Possible routes by which vulnerable neuronal types may be subject to neuroinvasion by an unknown pathogen. J Neural Transm (Vienna) 110, 517–536. - PubMed
-
- de Guilhem de Lataillade A, Caillaud M, Oullier T, Naveilhan P, Pellegrini C, Tolosa E, Neunlist M, Rolli-Derkinderen M, Gelpi E, Derkinderen P (2023) LRRK2 expression in normal and pathologic human gut and in rodent enteric neural cell lines. J Neurochem 164, 193–209. - PubMed
-
- Xu E, Boddu R, Abdelmotilib HA, Sokratian A, Kelly K, Liu Z, Bryant N, Chandra S, Carlisle SM, Lefkowitz EJ, Harms AS, Benveniste EN, Yacoubian TA, Volpicelli-Daley LA, Standaert DG, West AB (2022) Pathological alpha-synuclein recruits LRRK2 expressing pro-inflammatory monocytes to the brain. Mol Neurodegener 17, 7. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

