The role of noncoding RNAs in pancreatic birth defects
- PMID: 37066622
- PMCID: PMC10579456
- DOI: 10.1002/bdr2.2178
The role of noncoding RNAs in pancreatic birth defects
Abstract
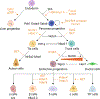
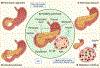
Congenital defects in the pancreas can cause severe health issues such as pancreatic cancer and diabetes which require lifelong treatment. Regenerating healthy pancreatic cells to replace malfunctioning cells has been considered a promising cure for pancreatic diseases including birth defects. However, such therapies are currently unavailable in the clinic. The developmental gene regulatory network underlying pancreatic development must be reactivated for in vivo regeneration and recapitulated in vitro for cell replacement therapy. Thus, understanding the mechanisms driving pancreatic development will pave the way for regenerative therapies. Pancreatic progenitor cells are the precursors of all pancreatic cells which use epigenetic changes to control gene expression during differentiation to generate all of the distinct pancreatic cell types. Epigenetic changes involving DNA methylation and histone modifications can be controlled by noncoding RNAs (ncRNAs). Indeed, increasing evidence suggests that ncRNAs are indispensable for proper organogenesis. Here, we summarize recent insight into the role of ncRNAs in the epigenetic regulation of pancreatic development. We further discuss how disruptions in ncRNA biogenesis and expression lead to developmental defects and diseases. This review summarizes in vivo data from animal models and in vitro studies using stem cell differentiation as a model for pancreatic development.
Keywords: epigenetic regulation; lncRNA; miRNA; ncRNA; pancreatic birth defects; pancreatic development.
© 2023 The Authors. Birth Defects Research published by Wiley Periodicals LLC.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Implication of epigenetics in pancreas development and disease.Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015 Dec;29(6):883-98. doi: 10.1016/j.beem.2015.10.010. Epub 2015 Oct 23. Best Pract Res Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2015. PMID: 26696517 Review.
-
Noncoding RNAs and pancreatic cancer.World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Jan 14;22(2):801-14. doi: 10.3748/wjg.v22.i2.801. World J Gastroenterol. 2016. PMID: 26811626 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Noncoding Rnas Emerging as Novel Biomarkers in Pancreatic Cancer.Curr Pharm Des. 2018;24(39):4601-4604. doi: 10.2174/1381612825666190119125804. Curr Pharm Des. 2018. PMID: 30659532 Review.
-
Noncoding RNA as an influential epigenetic modulator with promising roles in cancer therapeutics.Drug Discov Today. 2023 Sep;28(9):103690. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2023.103690. Epub 2023 Jun 26. Drug Discov Today. 2023. PMID: 37379906 Review.
-
Involvement of noncoding RNAs in epigenetic modifications of esophageal cancer.Biomed Pharmacother. 2019 Sep;117:109192. doi: 10.1016/j.biopha.2019.109192. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Biomed Pharmacother. 2019. PMID: 31387188 Review.
References
-
- Abernathy DG, Kim WK, McCoy MJ, Lake AM, Ouwenga R, Lee SW, Xing X, Li D, Lee HJ, Heuckeroth RO, Dougherty JD, Wang T, & Yoo AS (2017). MicroRNAs Induce a Permissive Chromatin Environment that Enables Neuronal Subtype-Specific Reprogramming of Adult Human Fibroblasts. Cell Stem Cell, 21(3), 332–348.e9. 10.1016/j.stem.2017.08.002 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akerman I, Tu Z, Beucher A, Rolando DMY, Sauty-Colace C, Benazra M, Nakic N, Yang J, Wang H, Pasquali L, Moran I, Garcia-Hurtado J, Castro N, Gonzalez-Franco R, Stewart AF, Bonner C, Piemonti L, Berney T, Groop L, … Ferrer J. (2017). Human Pancreatic β Cell lncRNAs Control Cell-Specific Regulatory Networks. Cell Metabolism, 25(2), 400–411. 10.1016/j.cmet.2016.11.016 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

