Understanding the roles and regulation patterns of circRNA on its host gene in tumorigenesis and tumor progression
- PMID: 37060016
- PMCID: PMC10105446
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02657-6
Understanding the roles and regulation patterns of circRNA on its host gene in tumorigenesis and tumor progression
Abstract
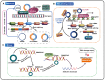
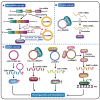
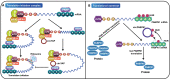
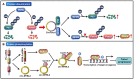
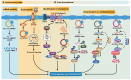
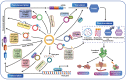
Circular RNAs (circRNAs) are a novel type of endogenous non-coding RNAs, which are covalently closed loop structures formed by precursor mRNAs (pre-mRNAs) through back-splicing. CircRNAs are abnormally expressed in many tumors, and play critical roles in a variety of tumors as oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes by sponging miRNAs, regulating alternative splicing and transcription, cis-regulating host genes, interacting with RNA binding proteins (RBPs) or encoding polypeptides. Among them, the regulation of circRNAs on their corresponding host genes is a critical way for circRNAs to exit their functions. Accumulating evidence suggests that circRNAs are able to regulate the expression of host genes at the transcriptional level, post-transcriptional level, translational level, post-translational level, or by encoding polypeptides. Therefore, this paper mainly summarized the roles and association of circRNAs and their corresponding host genes in tumorigenesis and tumor progression, generalized the circRNAs that function synergistically or antagonistically with their host genes, and elaborated the mechanisms of mutual regulation between circRNAs and their host genes. More importantly, this review provides specific references for revealing the potential application of circRNAs combined with their host genes in tumor diagnosis, treatment and prognosis.
Keywords: CircRNA; Host gene; Regulation; Tumor progression; Tumorigenesis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Emerging Roles and Clinical Potential of circSMARCA5 in Cancer.Cells. 2022 Sep 30;11(19):3074. doi: 10.3390/cells11193074. Cells. 2022. PMID: 36231036 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs are a novel type of non-coding RNAs in ROS regulation, cardiovascular metabolic inflammations and cancers.Pharmacol Ther. 2021 Apr;220:107715. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2020.107715. Epub 2020 Oct 24. Pharmacol Ther. 2021. PMID: 33141028 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in hematological malignancies.J Hematol Oncol. 2020 Oct 17;13(1):138. doi: 10.1186/s13045-020-00976-1. J Hematol Oncol. 2020. PMID: 33069241 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs with protein-coding ability in oncogenesis.Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023 Jul;1878(4):188909. doi: 10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188909. Epub 2023 May 10. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023. PMID: 37172651 Review.
-
Biological role and regulation of circular RNA as an emerging biomarker and potential therapeutic target for cancer.Mol Biol Rep. 2024 Feb 10;51(1):296. doi: 10.1007/s11033-024-09211-3. Mol Biol Rep. 2024. PMID: 38340202 Review.
Cited by
-
A Circular RNA Derived from the Pumilio 1 Gene Could Regulate PTEN in Human Cumulus Cells.Genes (Basel). 2024 Jan 19;15(1):124. doi: 10.3390/genes15010124. Genes (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38275605 Free PMC article.
-
The multifaceted roles of circular RNAs in cancer hallmarks: From mechanisms to clinical implications.Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024 Jul 20;35(3):102286. doi: 10.1016/j.omtn.2024.102286. eCollection 2024 Sep 10. Mol Ther Nucleic Acids. 2024. PMID: 39188305 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Circular RNAs: Novel Players in Cancer Mechanisms and Therapeutic Strategies.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Sep 20;25(18):10121. doi: 10.3390/ijms251810121. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39337606 Free PMC article. Review.
-
circGRHPR inhibits aberrant epithelial-mesenchymal transformation progression of lung epithelial cells associated with idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Jan 25;40(1):7. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09839-8. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 38267743 Free PMC article.
-
CircBRD7 attenuates tumor growth and metastasis in nasopharyngeal carcinoma via epigenetic activation of its host gene.Cancer Sci. 2024 Jan;115(1):139-154. doi: 10.1111/cas.15998. Epub 2023 Nov 8. Cancer Sci. 2024. PMID: 37940358 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

