γ-tocotrienol regulates gastric cancer by targeting notch signaling pathway
- PMID: 37055846
- PMCID: PMC10100483
- DOI: 10.1186/s41065-023-00277-w
γ-tocotrienol regulates gastric cancer by targeting notch signaling pathway
Abstract
Background: Gastric cancer is a common cause of death from cancer and an important global health care issue. Consequently, there is an urgent need to find new drugs and therapeutic targets for the treatment of gastric cancer. Recent studies have shown that tocotrienols (T3) have significant anticancer ability in cancer cell lines. Our previous study found that γ-tocotrienol (γ-T3) induced apoptosis in gastric cancer cells. We further explored the possible mechanisms of γ-T3 therapy for gastric cancer.
Methods: In this study, we treated gastric cancer cells with γ-T3, collect and deposit the cells. γ-T3-treated gastric cancer cells group and untreated group were subjected to RNA-seq assay, and analysis of sequencing results.
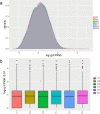
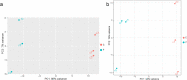
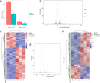
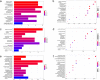
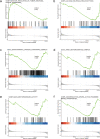
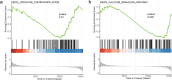
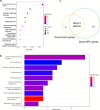
Results: Consistent with our previous findings, the results suggest that γ-T3 can inhibit mitochondrial complexes and oxidative phosphorylation. Analysis reveals that γ-T3 has altered mRNA and ncRNA in gastric cancer cells. Significantly altered signaling pathways after γ-T3 treatment were enriched for human papillomavirus infection (HPV) pathway and notch signaling pathway. The same significantly down-regulated genes notch1 and notch2 were present in both pathways in γ-T3-treated gastric cancer cells compared to controls.
Conclusions: It is indicated that γ-T3 may cure gastric cancer by inhibiting the notch signaling pathway. To provide a new and powerful basis for the clinical treatment of gastric cancer.
Keywords: Gastric cancer; Mitochondria; Notch signaling pathway; Oxidative phosphorylation; γ-tocotrienol.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Tocotrienols target PI3K/Akt signaling in anti-breast cancer therapy.Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013 Sep;13(7):1039-47. doi: 10.2174/18715206113139990116. Anticancer Agents Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 23272909 Review.
-
Transcriptomic Analysis of the Anticancer Effects of Annatto Tocotrienol, Delta-Tocotrienol and Gamma-Tocotrienol on Chondrosarcoma Cells.Nutrients. 2022 Oct 13;14(20):4277. doi: 10.3390/nu14204277. Nutrients. 2022. PMID: 36296960 Free PMC article.
-
Tocotrienols induce apoptosis in breast cancer cell lines via an endoplasmic reticulum stress-dependent increase in extrinsic death receptor signaling.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010 Nov;124(2):361-75. doi: 10.1007/s10549-010-0786-2. Epub 2010 Feb 16. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2010. PMID: 20157774
-
Gamma-tocotrienol induced apoptosis is associated with unfolded protein response in human breast cancer cells.J Nutr Biochem. 2012 Jan;23(1):93-100. doi: 10.1016/j.jnutbio.2010.11.012. Epub 2011 Mar 22. J Nutr Biochem. 2012. PMID: 21429729 Free PMC article.
-
Tocotrienol and cancer metastasis.Biofactors. 2016 Mar-Apr;42(2):149-62. doi: 10.1002/biof.1259. Epub 2016 Mar 7. Biofactors. 2016. PMID: 26948691 Review.
Cited by
-
Global transcriptomic network analysis of the crosstalk between microbiota and cancer-related cells in the oral-gut-lung axis.Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024 Aug 20;14:1425388. doi: 10.3389/fcimb.2024.1425388. eCollection 2024. Front Cell Infect Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39228892 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the Network regulatory mechanism of ncRNAs on the Ferroptosis Pathway: Implications for Preeclampsia.Int J Womens Health. 2024 Sep 30;16:1633-1651. doi: 10.2147/IJWH.S485653. eCollection 2024. Int J Womens Health. 2024. PMID: 39372667 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Agarwal MK, Agarwal ML, Athar M, Gupta S. Tocotrienol-rich fraction of palm oil activates p53, modulates Bax/Bcl2 ratio and induces apoptosis independent of cell cycle association. Cell Cycle (Georgetown, Tex.) . 2004;3:205–211. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

