Unraveling the Complex Interplay between Alpha-Synuclein and Epigenetic Modification
- PMID: 37047616
- PMCID: PMC10094812
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076645
Unraveling the Complex Interplay between Alpha-Synuclein and Epigenetic Modification
Abstract
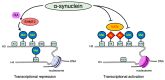
Alpha-synuclein (αS) is a small, presynaptic neuronal protein encoded by the SNCA gene. Point mutations and gene multiplication of SNCA cause rare familial forms of Parkinson's disease (PD). Misfolded αS is cytotoxic and is a component of Lewy bodies, which are a pathological hallmark of PD. Because SNCA multiplication is sufficient to cause full-blown PD, gene dosage likely has a strong impact on pathogenesis. In sporadic PD, increased SNCA expression resulting from a minor genetic background and various environmental factors may contribute to pathogenesis in a complementary manner. With respect to genetic background, several risk loci neighboring the SNCA gene have been identified, and epigenetic alterations, such as CpG methylation and regulatory histone marks, are considered important factors. These alterations synergistically upregulate αS expression and some post-translational modifications of αS facilitate its translocation to the nucleus. Nuclear αS interacts with DNA, histones, and their modifiers to alter epigenetic status; thereby, influencing the stability of neuronal function. Epigenetic changes do not affect the gene itself but can provide an appropriate transcriptional response for neuronal survival through DNA methylation or histone modifications. As a new approach, publicly available RNA sequencing datasets from human midbrain-like organoids may be used to compare transcriptional responses through epigenetic alterations. This informatic approach combined with the vast amount of transcriptomics data will lead to the discovery of novel pathways for the development of disease-modifying therapies for PD.
Keywords: alpha-synuclein; bioinformatics; epigenome; organoids.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Deregulation of α-synuclein in Parkinson's disease: Insight from epigenetic structure and transcriptional regulation of SNCA.Prog Neurobiol. 2017 Jul;154:21-36. doi: 10.1016/j.pneurobio.2017.04.004. Epub 2017 Apr 23. Prog Neurobiol. 2017. PMID: 28445713 Free PMC article. Review.
-
DNA methylation in Parkinson's disease.J Neurochem. 2016 Oct;139 Suppl 1:108-120. doi: 10.1111/jnc.13646. Epub 2016 Jun 10. J Neurochem. 2016. PMID: 27120258 Review.
-
CpG demethylation enhances alpha-synuclein expression and affects the pathogenesis of Parkinson's disease.PLoS One. 2010 Nov 24;5(11):e15522. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0015522. PLoS One. 2010. PMID: 21124796 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation regulates alpha-synuclein expression and is decreased in Parkinson's disease patients' brains.J Neurosci. 2010 May 5;30(18):6355-9. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.6119-09.2010. J Neurosci. 2010. PMID: 20445061 Free PMC article.
-
Methylation of α-synuclein and leucine-rich repeat kinase 2 in leukocyte DNA of Parkinson's disease patients.Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014 Mar;20(3):308-13. doi: 10.1016/j.parkreldis.2013.12.002. Epub 2013 Dec 16. Parkinsonism Relat Disord. 2014. PMID: 24398085
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

