A Lipidated Single-B-Chain Derivative of Relaxin Exhibits Improved In Vitro Serum Stability without Altering Activity
- PMID: 37047588
- PMCID: PMC10094921
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076616
A Lipidated Single-B-Chain Derivative of Relaxin Exhibits Improved In Vitro Serum Stability without Altering Activity
Abstract
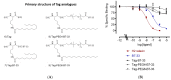
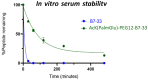
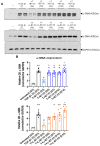
Human relaxin-2 (H2 relaxin) is therapeutically very important due to its strong anti-fibrotic, vasodilatory, and cardioprotective effects. Therefore, relaxin's receptor, relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1), is a potential target for the treatment of fibrosis and related disorders, including heart failure. H2 relaxin has a complex two-chain structure (A and B) and three disulfide bridges. Our laboratory has recently developed B7-33 peptide, a single-chain agonist based on the B-chain of H2 relaxin. However, the peptide B7-33 has a short circulation time in vitro in serum (t1/2 = ~6 min). In this study, we report structure-activity relationship studies on B7-33 utilizing different fatty-acid conjugations at different positions. We have shown that by fatty-acid conjugation with an appropriate spacer length, the in vitro half-life of B7-33 can be increased from 6 min to 60 min. In the future, the lead lipidated molecule will be studied in animal models to measure its PK/PD properties, which will lead to their pre-clinical applications.
Keywords: B7-33; H2 relaxin; RXFP1; structure-activity relationship (SAR).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 11;24(16):12670. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612670. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628851 Free PMC article.
-
A single-chain derivative of the relaxin hormone is a functionally selective agonist of the G protein-coupled receptor, RXFP1.Chem Sci. 2016 Jun 1;7(6):3805-3819. doi: 10.1039/c5sc04754d. Epub 2016 Feb 26. Chem Sci. 2016. PMID: 30155023 Free PMC article.
-
Single chain peptide agonists of relaxin receptors.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019 May 1;487:34-39. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2019.01.008. Epub 2019 Jan 11. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2019. PMID: 30641102 Review.
-
Development of Novel High-Affinity Antagonists for the Relaxin Family Peptide Receptor 1.ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023 May 3;6(5):842-853. doi: 10.1021/acsptsci.3c00053. eCollection 2023 May 12. ACS Pharmacol Transl Sci. 2023. PMID: 37200817 Free PMC article.
-
The relaxin family peptide receptor 1 (RXFP1): An emerging player in human health and disease.Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020 Apr;8(4):e1194. doi: 10.1002/mgg3.1194. Epub 2020 Feb 26. Mol Genet Genomic Med. 2020. PMID: 32100955 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Further Developments towards a Minimal Potent Derivative of Human Relaxin-2.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Aug 11;24(16):12670. doi: 10.3390/ijms241612670. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37628851 Free PMC article.
-
Engineering and Characterization of a Long-Half-Life Relaxin Receptor RXFP1 Agonist.Mol Pharm. 2024 Sep 2;21(9):4441-4449. doi: 10.1021/acs.molpharmaceut.4c00368. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Mol Pharm. 2024. PMID: 39134056 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Hisaw F.L. Experimental relaxation of the pubic ligament of the guinea pig. Proc. Soc. Exp. Biol. Med. 1926;23:661–663. doi: 10.3181/00379727-23-3107. - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

