Effects of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blockade and Statins on Kidney Injury Marker 1 (KIM-1) in Female Rats Receiving L-NAME and Angiotensin II
- PMID: 37047470
- PMCID: PMC10095483
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076500
Effects of Mineralocorticoid Receptor Blockade and Statins on Kidney Injury Marker 1 (KIM-1) in Female Rats Receiving L-NAME and Angiotensin II
Abstract
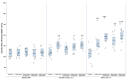
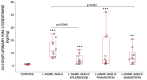
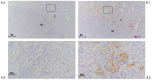
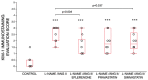
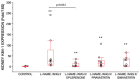
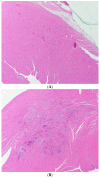
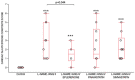
Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1) is a biomarker of renal injury and a predictor of cardiovascular disease. Aldosterone, via activation of the mineralocorticoid receptor, is linked to cardiac and renal injury. However, the impact of mineralocorticoid receptor activation and blockade on KIM-1 is uncertain. We investigated whether renal KIM-1 is increased in a cardiorenal injury model induced by L-NAME/ANG II, and whether mineralocorticoid receptor blockade prevents the increase in KIM-1. Since statin use is associated with lower aldosterone, we also investigated whether administering eiSther a lipophilic statin (simvastatin) or a hydrophilic statin (pravastatin) prevents the increase in renal KIM-1. Female Wistar rats (8-10 week old), consuming a high salt diet (1.6% Na+), were randomized to the following conditions for 14 days: control; L-NAME (0.2 mg/mL in drinking water)/ANG II (225 ug/kg/day on days 12-14); L-NAME/ANG II + eplerenone (100 mg/kg/day p.o.); L-NAME/ANG II + pravastatin (20 mg/kg/day p.o.); L-NAME/ANG II + simvastatin (20 mg/kg/day p.o.). Groups treated with L-NAME/ANG II had significantly higher blood pressure, plasma and urine aldosterone, cardiac injury/stroke composite score, and renal KIM-1 than the control group. Both eplerenone and simvastatin reduced 24-h urinary KIM-1 (p = 0.0046, p = 0.031, respectively) and renal KIM-1 immunostaining (p = 0.004, p = 0.037, respectively). Eplerenone also reduced renal KIM-1 mRNA expression (p = 0.012) and cardiac injury/stroke composite score (p = 0.04). Pravastatin did not affect these damage markers. The 24-h urinary KIM-1, renal KIM-1 immunostaining, and renal KIM-1 mRNA expression correlated with cardiac injury/stroke composite score (p < 0.0001, Spearman ranked correlation = 0.69, 0.66, 0.59, respectively). In conclusion, L-NAME/ANG II increases renal KIM-1 and both eplerenone and simvastatin blunt this increase in renal KIM-1.
Keywords: CVD (cardiovascular disease); N-omega-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester (L-NAME); angiotensin II (ANG II); kidney injury molecule (KIM-1); mineralocorticoid receptor (MR); pravastatin; simvastatin; statin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Cardiac damage prevention by eplerenone: comparison with low sodium diet or potassium loading.Hypertension. 2002 Feb;39(2 Pt 2):614-8. Hypertension. 2002. PMID: 11882618
-
Cooperative Role of Mineralocorticoid Receptor and Caveolin-1 in Regulating the Vascular Response to Low Nitric Oxide-High Angiotensin II-Induced Cardiovascular Injury.J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015 Oct;355(1):32-47. doi: 10.1124/jpet.115.226043. Epub 2015 Jul 16. J Pharmacol Exp Ther. 2015. PMID: 26183312 Free PMC article.
-
Systemic Aldosterone, But Not Angiotensin II, Plays a Pivotal Role in the Pathogenesis of Renal Injury in Chronic Nitric Oxide-Deficient Male Rats.Endocrinology. 2015 Jul;156(7):2657-66. doi: 10.1210/en.2014-1369. Epub 2015 Apr 14. Endocrinology. 2015. PMID: 25872005
-
Aldosterone and not plasminogen activator inhibitor-1 is a critical mediator of early angiotensin II/NG-nitro-L-arginine methyl ester-induced myocardial injury.Circulation. 2003 Nov 18;108(20):2517-23. doi: 10.1161/01.CIR.0000097000.51723.6F. Epub 2003 Oct 27. Circulation. 2003. PMID: 14581407
-
The antagonism of aldosterone receptor prevents the development of hypertensive heart failure induced by chronic inhibition of nitric oxide synthesis in rats.Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006 Apr;20(2):93-102. doi: 10.1007/s10557-006-8130-0. Cardiovasc Drugs Ther. 2006. PMID: 16761190
References
-
- Ichimura T., Bonventre J.V., Bailly V., Wei H., Hession C.A., Cate R.L., Sanicola M. Kidney injury molecule-1 (KIM-1), a putative epithelial cell adhesion molecule containing a novel immunoglobulin domain, is up-regulated in renal cells after injury. J. Biol. Chem. 1998;273:4135–4142. doi: 10.1074/jbc.273.7.4135. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Van Timmeren M.M., Vaidya V.S., van Ree R.M., Oterdoom L.H., de Vries A.P., Gans R.O., van Goor H., Stegeman C.A., Bonventre J.V., Bakker S.J. High urinary excretion of kidney injury molecule-1 is an independent predictor of graft loss in renal transplant recipients. Transplantation. 2007;84:1625–1630. doi: 10.1097/01.tp.0000295982.78039.ef. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Sabbisetti V.S., Waikar S.S., Antoine D.J., Smiles A., Wang C., Ravisankar A., Ito K., Sharma S., Ramadesikan S., Lee M., et al. Blood kidney injury molecule-1 is a biomarker of acute and chronic kidney injury and predicts progression to ESRD in type I diabetes. J. Am. Soc. Nephrol. 2014;25:2177–2186. doi: 10.1681/ASN.2013070758. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
- R01HL11476/National Institute of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood Institute
- R01HL136567/National Institute of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood
- K24HL103845/National Institute of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood
- T32HL007609/National Institute of Health National Heart, Lung, and Blood
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

