Chemical Space Virtual Screening against Hard-to-Drug RNA Methyltransferases DNMT2 and NSUN6
- PMID: 37047081
- PMCID: PMC10094593
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24076109
Chemical Space Virtual Screening against Hard-to-Drug RNA Methyltransferases DNMT2 and NSUN6
Abstract
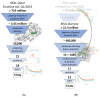
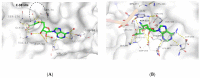
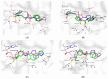
Targeting RNA methyltransferases with small molecules as inhibitors or tool compounds is an emerging field of interest in epitranscriptomics and medicinal chemistry. For two challenging RNA methyltransferases that introduce the 5-methylcytosine (m5C) modification in different tRNAs, namely DNMT2 and NSUN6, an ultra-large commercially available chemical space was virtually screened by physicochemical property filtering, molecular docking, and clustering to identify new ligands for those enzymes. Novel chemotypes binding to DNMT2 and NSUN6 with affinities down to KD,app = 37 µM and KD,app = 12 µM, respectively, were identified using a microscale thermophoresis (MST) binding assay. These compounds represent the first molecules with a distinct structure from the cofactor SAM and have the potential to be developed into activity-based probes for these enzymes. Additionally, the challenges and strategies of chemical space docking screens with special emphasis on library focusing and diversification are discussed.
Keywords: DNMT2; NSUN6; RNA methyltransferases; chemical spaces; molecular docking; ultra-large molecular libraries; virtual screening.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
NSUN6 is a human RNA methyltransferase that catalyzes formation of m5C72 in specific tRNAs.RNA. 2015 Sep;21(9):1532-43. doi: 10.1261/rna.051524.115. Epub 2015 Jul 9. RNA. 2015. PMID: 26160102 Free PMC article.
-
Cross-Talk between Dnmt2-Dependent tRNA Methylation and Queuosine Modification.Biomolecules. 2017 Feb 10;7(1):14. doi: 10.3390/biom7010014. Biomolecules. 2017. PMID: 28208632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sequence-specific and Shape-selective RNA Recognition by the Human RNA 5-Methylcytosine Methyltransferase NSun6.J Biol Chem. 2016 Nov 11;291(46):24293-24303. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M116.742569. Epub 2016 Oct 4. J Biol Chem. 2016. PMID: 27703015 Free PMC article.
-
RNA cytosine methylation by Dnmt2 and NSun2 promotes tRNA stability and protein synthesis.Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012 Sep;19(9):900-5. doi: 10.1038/nsmb.2357. Epub 2012 Aug 12. Nat Struct Mol Biol. 2012. PMID: 22885326
-
The Roles of Host 5-Methylcytosine RNA Methyltransferases during Viral Infections.Int J Mol Sci. 2020 Oct 31;21(21):8176. doi: 10.3390/ijms21218176. Int J Mol Sci. 2020. PMID: 33142933 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Dysregulation of tRNA methylation in cancer: Mechanisms and targeting therapeutic strategies.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Jul 17;10(1):327. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02097-x. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39019857 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The impact of tRNA modifications on translation in cancer: identifying novel therapeutic avenues.NAR Cancer. 2024 Mar 12;6(1):zcae012. doi: 10.1093/narcan/zcae012. eCollection 2024 Mar. NAR Cancer. 2024. PMID: 38476632 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure-based virtual screening of unbiased and RNA-focused libraries to identify new ligands for the HCV IRES model system.RSC Med Chem. 2024 Mar 18;15(5):1527-1538. doi: 10.1039/d3md00696d. eCollection 2024 May 22. RSC Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38784459 Free PMC article.
-
tRNA modifications and tRNA-derived small RNAs: new insights of tRNA in human disease.Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024 Sep 14;40(1):76. doi: 10.1007/s10565-024-09919-9. Cell Biol Toxicol. 2024. PMID: 39276283 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

