5-methyladenosine regulators play a crucial role in development of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
- PMID: 37045913
- PMCID: PMC10097674
- DOI: 10.1038/s41598-023-32452-4
5-methyladenosine regulators play a crucial role in development of chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis
Abstract
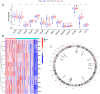
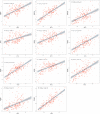
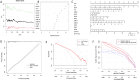
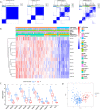
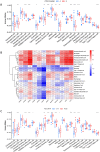
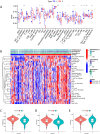
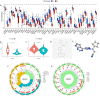
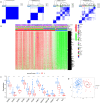
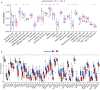
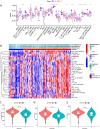
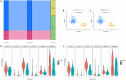
5-methyladenosine (m5C) modification regulates gene expression and biological functions in oncologic areas. However, the effect of m5C modification in chronic hypersensitivity pneumonitis (CHP) and idiopathic pulmonary fibrosis (IPF) remains unknown. Expression data for 12 significant m5C regulators were obtained from the interstitial lung disease dataset. Five candidate m5C regulators, namely tet methylcytosine dioxygenase 2, NOP2/Sun RNA methyltransferase 5, Y-box binding protein 1, tRNA aspartic acid methyltransferase 1, and NOP2/Sun RNA methyltransferase 3 were screened using random forest and nomogram models to predict risks of pulmonary fibrosis. Next, we applied the consensus clustering method to stratify the samples with different m5C patterns into two groups (cluster A and B). Finally, we calculated immune cell infiltration scores via single-sample gene set enrichment analysis, then compared immune cell infiltration, related functions as well as the expression of programmed cell death 1 (PD-1, PDCD1) and programmed death protein ligand-1 (PD-L1, CD274) between the two clusters. Principal component analysis of m5C-related scores across the 288 samples revealed that cluster A had higher immune-related expression than B. Notably, T helper cell (Th) 2 type cytokines and Th1 signatures were more abundant in clusters A and B, respectively. Our results suggest that m5C is associated with and plays a crucial role in development of pulmonary fibrosis. These m5C patterns could be potential biomarkers for identification of CHP and IPF, and guide future development of immunotherapy or other new drugs strategies for pulmonary fibrosis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Relevance of RNA N6-Methyladenosine Regulators for Pulmonary Fibrosis: Implications for Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis and Idiopathic Pulmonary Fibrosis.Front Genet. 2022 Jul 14;13:939175. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2022.939175. eCollection 2022. Front Genet. 2022. PMID: 35910226 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, an Interstitial Lung Disease with Distinct Molecular Signatures.Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020 Nov 15;202(10):1430-1444. doi: 10.1164/rccm.202001-0134OC. Am J Respir Crit Care Med. 2020. PMID: 32602730 Free PMC article.
-
Exploring the importance of m5c in the diagnosis and subtype classification of COPD using the GEO database.Gene. 2024 Feb 15;895:147987. doi: 10.1016/j.gene.2023.147987. Epub 2023 Nov 14. Gene. 2024. PMID: 37972696
-
Pathology of Chronic Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis What Is It? What Are the Diagnostic Criteria? Why Do We Care?Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018 Jan;142(1):109-119. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2017-0173-RA. Epub 2017 May 24. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2018. PMID: 28537805 Review.
-
Centrilobular Fibrosis in Fibrotic (Chronic) Hypersensitivity Pneumonitis, Usual Interstitial Pneumonia, and Connective Tissue Disease-Associated Interstitial Lung Disease.Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020 Dec 1;144(12):1509-1516. doi: 10.5858/arpa.2019-0628-RA. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2020. PMID: 32233994 Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials

