Clinical and Pharmacological Implications of Time to Treatment with Interleukin-1 Blockade in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
- PMID: 37037651
- PMCID: PMC10353076
- DOI: 10.1124/jpet.123.001601
Clinical and Pharmacological Implications of Time to Treatment with Interleukin-1 Blockade in ST-Segment Elevation Myocardial Infarction
Abstract
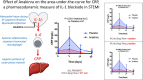
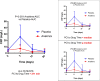
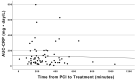
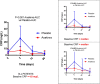
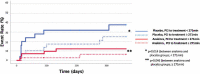
Interleukin-1 (IL-1) blockade with anakinra given within 12 hours from reperfusion has been shown to reduce the inflammatory response as well as prevent heart failure (HF) events in patients with STEMI. We sought to determine whether time-to-treatment influences the efficacy of anakinra on systemic inflammation and incidence of HF events in patients with STEMI. We divided the cohort in two groups base6d on the median time from percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI) to investigational drug, and analyzed the effects of anakinra on the area-under-the-curve for C reactive protein (AUC-CRP) and on incidence of the composite endpoint of death or new onset HF. We analyzed data from 139 patients: 84 (60%) treated with anakinra and 55 (40%) with placebo. The median time from PCI to investigational treatment was 271 (182-391) minutes. The AUC-CRP was significantly higher in patients receiving placebo versus anakinra both in those with time from PCI to treatment <271 minutes (222.6 [103.9-325.2] vs. 78.4 [44.3-131.2], P < 0.001) and those with time from PCI to treatment ≥271 minute (235.2 [131.4-603.4] vs. 75.5 [38.9-171.9], P < 0.001) (P > 0.05 for interaction). Anakinra significantly reduced the combined endpoint of death or new onset HF in patients with time from PCI to treatment <271 minutes (5 [11%] vs. 9n[36%], log-rank χ 2 5.985, P = 0.014) as well as in patients with time from PCI to drug ≥271 minutes (2n[5%] vs. 7 [23%], log-rank χ 2 3.995, P = 0.046) (P > 0.05 for interaction). IL-1 blockade with anakinra blunts the acute systemic inflammatory response and prevents HF events independent of time-to-treatment. SIGNIFICANCE STATEMENT: In patients with ST segment elevation presenting within 12 hours of pain onset and treated within 12 hours of reperfusion, interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra blunts the acute systemic inflammatory response, a surrogate of interleukin-1 activity, and prevents heart failure events independent of time-to-treatment.
Copyright © 2023 by The American Society for Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Interleukin-1 Blockade Inhibits the Acute Inflammatory Response in Patients With ST-Segment-Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Am Heart Assoc. 2020 Mar 3;9(5):e014941. doi: 10.1161/JAHA.119.014941. Epub 2020 Mar 3. J Am Heart Assoc. 2020. PMID: 32122219 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Response to interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra in women and men with ST-segment elevation myocardial infarction.Minerva Cardiol Angiol. 2024 Feb;72(1):67-75. doi: 10.23736/S2724-5683.23.06439-6. Epub 2023 Nov 21. Minerva Cardiol Angiol. 2024. PMID: 37987681
-
Impact of C-reactive protein levels and role of anakinra in patients with ST-elevation myocardial infarction.Int J Cardiol. 2024 Mar 1;398:131610. doi: 10.1016/j.ijcard.2023.131610. Epub 2023 Nov 26. Int J Cardiol. 2024. PMID: 38016623 Free PMC article.
-
Effect of IL-1 Blockade With Anakinra on Heart Failure Outcomes in Patients With Anterior Versus Nonanterior ST Elevation Myocardial Infarction.J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022 Jun 1;79(6):774-780. doi: 10.1097/FJC.0000000000001240. J Cardiovasc Pharmacol. 2022. PMID: 35170493 Free PMC article.
-
Anakinra in Heart Failure: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis of Randomized Controlled Trials.Med Sci (Basel). 2022 Dec 26;11(1):4. doi: 10.3390/medsci11010004. Med Sci (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36649041 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
IL-1 signaling pathway, an important target for inflammation surrounding in myocardial infarction.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Aug;32(4):2235-2252. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01481-4. Epub 2024 Apr 27. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 38676853 Review.
References
-
- Abbate A, Kontos MC, Grizzard JD, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Van Tassell BW, Robati R, Roach LM, Arena RA, Roberts CS, Varma A, et al. ; VCU-ART Investigators (2010) Interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra to prevent adverse cardiac remodeling after acute myocardial infarction (Virginia Commonwealth University Anakinra Remodeling Trial [VCU-ART] Pilot study). Am J Cardiol 105:1371–1377.e1. - PubMed
-
- Abbate A, Salloum FN, Vecile E, Das A, Hoke NN, Straino S, Biondi-Zoccai GG, Houser JE, Qureshi IZ, Ownby ED, et al. (2008) Anakinra, a recombinant human interleukin-1 receptor antagonist, inhibits apoptosis in experimental acute myocardial infarction. Circulation 117:2670–2683. - PubMed
-
- Abbate A, Van Tassell BW, Biondi-Zoccai G, Kontos MC, Grizzard JD, Spillman DW, Oddi C, Roberts CS, Melchior RD, Mueller GH, et al. (2013) Effects of interleukin-1 blockade with anakinra on adverse cardiac remodeling and heart failure after acute myocardial infarction [from the Virginia Commonwealth University-Anakinra Remodeling Trial (2) (VCU-ART2) pilot study]. Am J Cardiol 111:1394–1400. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
