suPAR links a dysregulated immune response to tissue inflammation and sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
- PMID: 37036003
- PMCID: PMC10132159
- DOI: 10.1172/jci.insight.165740
suPAR links a dysregulated immune response to tissue inflammation and sepsis-induced acute kidney injury
Abstract
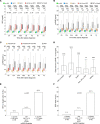
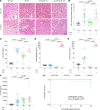
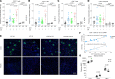
Acute kidney injury (AKI) secondary to sepsis results in poor outcomes and conventional kidney function indicators lack diagnostic value. Soluble urokinase plasminogen activator receptor (suPAR) is an innate immune-derived molecule implicated in inflammatory organ damage. We characterized the diagnostic ability of longitudinal serum suPAR levels to discriminate severity and course of sepsis-induced AKI (SI-AKI) in 200 critically ill patients meeting Sepsis-3 criteria. The pathophysiologic relevance of varying suPAR levels in SI-AKI was explored in a polymicrobial sepsis model in WT, (s)uPAR-knockout, and transgenic suPAR-overexpressing mice. At all time points studied, suPAR provided a robust classification of SI-AKI disease severity, with improved prediction of renal replacement therapy (RRT) and mortality compared with established kidney biomarkers. Patients with suPAR levels of greater than 12.7 ng/mL were at highest risk for RRT or death, with an adjusted odds ratio of 7.48 (95% CI, 3.00-18.63). suPAR deficiency protected mice against SI-AKI. suPAR-overexpressing mice exhibited greater kidney damage and poorer survival through inflamed kidneys, accompanied by local upregulation of potent chemoattractants and pronounced kidney T cell infiltration. Hence, suPAR allows for an innate immune-derived and kidney function-independent staging of SI-AKI and offers improved longitudinal risk stratification. suPAR promotes T cell-based kidney inflammation, while suPAR deficiency improves SI-AKI.
Keywords: Clinical practice; Diagnostics; Inflammation; Nephrology; T cells.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
Similar articles
-
Clinical value of soluble urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor in predicting sepsis-associated acute kidney injury.Ren Fail. 2024 Dec;46(1):2307959. doi: 10.1080/0886022X.2024.2307959. Epub 2024 Jan 30. Ren Fail. 2024. PMID: 38289005 Free PMC article.
-
suPAR as a marker of infection in acute kidney injury - a prospective observational study.BMC Nephrol. 2018 Aug 2;19(1):191. doi: 10.1186/s12882-018-0990-6. BMC Nephrol. 2018. PMID: 30071826 Free PMC article. Clinical Trial.
-
Soluble Urokinase Receptor and Acute Kidney Injury.N Engl J Med. 2020 Jan 30;382(5):416-426. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911481. N Engl J Med. 2020. PMID: 31995687 Free PMC article.
-
The Perspective of Vitamin D on suPAR-Related AKI in COVID-19.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Sep 14;23(18):10725. doi: 10.3390/ijms231810725. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 36142634 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Predictive value of suPAR in AKI: a systematic review and meta-analysis.Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023 Jan;27(1):1-11. doi: 10.1007/s10157-022-02300-2. Epub 2022 Dec 5. Clin Exp Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36469196 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor (uPAR) in Inflammation and Disease: A Unique Inflammatory Pathway Activator.Biomedicines. 2024 May 24;12(6):1167. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12061167. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38927374 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of Formyl Peptide Receptors and β-Arrestin-1 in suPAR Signal Transduction in Mouse Podocytes: Interactions with αVβ3-Integrin.Cells. 2024 Jan 17;13(2):172. doi: 10.3390/cells13020172. Cells. 2024. PMID: 38247863 Free PMC article.
-
Soluble Urokinase-Type Plasminogen Activator Receptor and Inflammatory Biomarker Response with Prognostic Significance after Acute Neuronal Injury - a Prospective Cohort Study.Inflammation. 2024 Nov 14. doi: 10.1007/s10753-024-02185-1. Online ahead of print. Inflammation. 2024. PMID: 39540961
-
Elevated Activated Partial Thromboplastin Time as a Predictor of 28-Day Mortality in Sepsis-Associated Acute Kidney Injury: A Retrospective Cohort Analysis.Int J Gen Med. 2024 Apr 30;17:1739-1753. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S459583. eCollection 2024. Int J Gen Med. 2024. PMID: 38706747 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy of immediate versus delayed renal replacement therapy in septic patients undergoing continuous renal replacement therapy.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Aug 15;16(8):3646-3653. doi: 10.62347/XSTK3213. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 39262694 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kellum JA, Prowle JR. Paradigms of acute kidney injury in the intensive care setting. Nat Rev Nephrol. 2018;307(4):2265–2230. - PubMed
-
- Kellum JA, et al. Kidney disease: improving global outcomes (KDIGO) acute kidney injury work group. KDIGO clinical practice guideline for acute kidney injury. Kidney Int. 2012;138:1–138.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

