Effects of PEG-Linker Chain Length of Folate-Linked Liposomal Formulations on Targeting Ability and Antitumor Activity of Encapsulated Drug
- PMID: 37020691
- PMCID: PMC10069508
- DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S402418
Effects of PEG-Linker Chain Length of Folate-Linked Liposomal Formulations on Targeting Ability and Antitumor Activity of Encapsulated Drug
Abstract
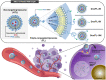
Introduction: Ligand-conjugated liposomes are promising for the treatment of specific receptor-overexpressing cancers. However, previous studies have shown inconsistent results because of the varying properties of the ligand, presence of a polyethylene glycol (PEG) coating on the liposome, length of the linker, and density of the ligand.
Methods: Here, we prepared PEGylated liposomes using PEG-linkers of various lengths conjugated with folate and evaluated the effect of the PEG-linker length on the nanoparticle distribution and pharmacological efficacy of the encapsulated drug both in vitro and in vivo.
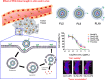
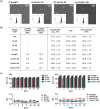
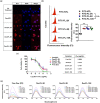
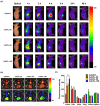
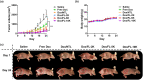
Results: When folate was conjugated to the liposome surface, the cellular uptake efficiency in folate receptor overexpressed KB cells dramatically increased compared to that of the normal liposome. However, when comparing the effect of the PEG-linker length in vitro, no significant difference between the formulations was observed. In contrast, the level of tumor accumulation of particles in vivo significantly increased when the length of the PEG-linker was increased. The tumor size was reduced by >40% in the Dox/FL-10K-treated group compared to that in the Dox/FL-2K- or 5K-treated groups.
Discussion: Our study suggests that as the length of PEG-linker increases, the tumor-targeting ability can be enhanced under in vivo conditions, which can lead to an increase in the antitumor activity of the encapsulated drug.
Keywords: PEG-linker length; PEGylated liposome; folate receptor; ligand-conjugated liposome.
© 2023 Lim et al.
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest to declare.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Design of folate-linked liposomal doxorubicin to its antitumor effect in mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Dec 15;14(24):8161-8. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0159. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 19088031
-
Delivery of antisense oligodeoxyribonucleotides against the human epidermal growth factor receptor into cultured KB cells with liposomes conjugated to folate via polyethylene glycol.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995 Apr 11;92(8):3318-22. doi: 10.1073/pnas.92.8.3318. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1995. PMID: 7724560 Free PMC article.
-
In vivo fate of folate-targeted polyethylene-glycol liposomes in tumor-bearing mice.Clin Cancer Res. 2003 Dec 15;9(17):6551-9. Clin Cancer Res. 2003. PMID: 14695160
-
Tumor cell targeting of liposome-entrapped drugs with phospholipid-anchored folic acid-PEG conjugates.Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004 Apr 29;56(8):1177-92. doi: 10.1016/j.addr.2004.01.011. Adv Drug Deliv Rev. 2004. PMID: 15094214 Review.
-
Pros and cons of the liposome platform in cancer drug targeting.J Liposome Res. 2006;16(3):175-83. doi: 10.1080/08982100600848769. J Liposome Res. 2006. PMID: 16952872 Review.
References
-
- Atlihan-Gundogdu E, Ilem-Ozdemir D, Ekinci M, et al. Recent developments in cancer therapy and diagnosis. J Pharm Investig. 2020;50:1–13.
-
- Tran P, Lee S-E, Kim D-H, Pyo Y-C, Park J-SJ. Recent advances of nanotechnology for the delivery of anticancer drugs for breast cancer treatment. J Pharm Investig. 2020;50(3):261–270.
-
- Gupta B, Kim JOJ. Recent progress in cancer immunotherapy approaches based on nanoparticle delivery devices. J Pharm Investig. 2021;51:1–14.
-
- Ha E-S, Kang H-T, Park H, Kim S, Kim M-S. Advanced technology using supercritical fluid for particle production in pharmaceutical continuous manufacturing. J Pharm Investig. 2022;2022. doi:10.1007/s40005-022-00601-y - DOI
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

