Cell biology of protein-lipid conjugation
- PMID: 37019684
- PMCID: PMC10721952
- DOI: 10.1247/csf.23016
Cell biology of protein-lipid conjugation
Abstract
Protein-lipid conjugation is a widespread modification involved in many biological processes. Various lipids, including fatty acids, isoprenoids, sterols, glycosylphosphatidylinositol, sphingolipids, and phospholipids, are covalently linked with proteins. These modifications direct proteins to intracellular membranes through the hydrophobic nature of lipids. Some of these membrane-binding processes are reversible through delipidation or by reducing the affinity to membranes. Many signaling molecules undergo lipid modification, and their membrane binding is important for proper signal transduction. The conjugation of proteins to lipids also influences the dynamics and function of organellar membranes. Dysregulation of lipidation has been associated with diseases such as neurodegenerative diseases. In this review, we first provide an overview of diverse forms of protein-lipid conjugation and then summarize the catalytic mechanisms, regulation, and roles of these modifications.Key words: lipid, lipidation, membrane, organelle, protein modification.
Keywords: lipid; lipidation; membrane; organelle; protein modification.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
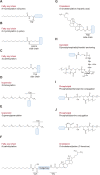
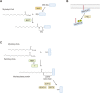
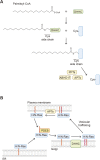

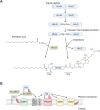
Similar articles
-
Protein Lipidation Types: Current Strategies for Enrichment and Characterization.Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Feb 21;23(4):2365. doi: 10.3390/ijms23042365. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35216483 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Sterol carrier protein-2 expression alters plasma membrane lipid distribution and cholesterol dynamics.Biochemistry. 2001 May 29;40(21):6493-506. doi: 10.1021/bi010217l. Biochemistry. 2001. PMID: 11371213
-
Genetic modification of membrane lipid.Annu Rev Biochem. 1975;44:315-39. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.44.070175.001531. Annu Rev Biochem. 1975. PMID: 1094912 Review. No abstract available.
-
Sterol carrier protein-2: new roles in regulating lipid rafts and signaling.Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007 Jun;1771(6):700-18. doi: 10.1016/j.bbalip.2007.04.005. Epub 2007 Apr 12. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2007. PMID: 17543577 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploiting bioorthogonal chemistry to elucidate protein-lipid binding interactions and other biological roles of phospholipids.Acc Chem Res. 2011 Sep 20;44(9):686-98. doi: 10.1021/ar200060y. Epub 2011 May 6. Acc Chem Res. 2011. PMID: 21548554
Cited by
-
Exploring protein lipidation by mass spectrometry-based proteomics.J Biochem. 2024 Mar 4;175(3):225-233. doi: 10.1093/jb/mvad109. J Biochem. 2024. PMID: 38102731 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Abrami, L., Audagnotto, M., Ho, S., Marcaida, M.J., Mesquita, F.S., Anwar, M.U., Sandoz, P.A., Fonti, G., Pojer, F., Dal Peraro, M., and van der Goot, F.G.. 2021. Palmitoylated acyl protein thioesterase APT2 deforms membranes to extract substrate acyl chains. Nat. Chem. Biol., 17: 438–447. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Antonny, B., Beraud-Dufour, S., Chardin, P., and Chabre, M.. 1997. N-terminal hydrophobic residues of the G-protein ADP-ribosylation factor-1 insert into membrane phospholipids upon GDP to GTP exchange. Biochemistry, 36: 4675–4684. - PubMed
-
- Bagchi, R.A., Robinson, E.L., Hu, T., Cao, J., Hong, J.Y., Tharp, C.A., Qasim, H., Gavin, K.M., Pires da Silva, J., Major, J.L., McConnell, B.K., Seto, E., Lin, H., and McKinsey, T.A.. 2022. Reversible lysine fatty acylation of an anchoring protein mediates adipocyte adrenergic signaling. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A., 119: e2119678119. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Briscoe, J. and Therond, P.P.. 2013. The mechanisms of Hedgehog signalling and its roles in development and disease. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol., 14: 416–429. - PubMed

