The mitochondrial ribosomal protein mRpL4 regulates Notch signaling
- PMID: 37009823
- PMCID: PMC10240210
- DOI: 10.15252/embr.202255764
The mitochondrial ribosomal protein mRpL4 regulates Notch signaling
Abstract
Mitochondrial ribosomal proteins (MRPs) assemble as specialized ribosome to synthesize mtDNA-encoded proteins, which are essential for mitochondrial bioenergetic and metabolic processes. MRPs are required for fundamental cellular activities during animal development, but their roles beyond mitochondrial protein translation are poorly understood. Here, we report a conserved role of the mitochondrial ribosomal protein L4 (mRpL4) in Notch signaling. Genetic analyses demonstrate that mRpL4 is required in the Notch signal-receiving cells to permit target gene transcription during Drosophila wing development. We find that mRpL4 physically and genetically interacts with the WD40 repeat protein wap and activates the transcription of Notch signaling targets. We show that human mRpL4 is capable of replacing fly mRpL4 during wing development. Furthermore, knockout of mRpL4 in zebrafish leads to downregulated expression of Notch signaling components. Thus, we have discovered a previously unknown function of mRpL4 during animal development.
Keywords: Drosophila; Notch; mitochondrial ribosomal protein L4; wap; zebrafish.
© 2023 The Authors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
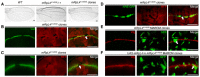
- A
Representative image of wings (n > 20 wings) from control adult flies, mRpL4 K14608 heterozygous flies and flies harboring mRpL4 K14608 homozygous mutant clones.
- B–D
Representative image of wing imaginal disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained for Cut and Wg, and wing disk expressing Notch signaling reporter NRE‐GFP, respectively.
- E, F
Representative images of wing disks (n > 10 wing disks) bearing MARCM clones stained for Wg. In (F), UAS‐mRpL4 are expressed under the control of tub‐Gal4 in the MARCM clones.
- A
Representative image of wings (n > 20 wings) from flies expressing mRpL4 RNAi, UAS‐mRpL4 and both under the control of nub‐Gal4.
- B
Representative image of wing imaginal disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained for Cut, from flies expressing mRpL4 RNAi, UAS‐mRpL4 and both under the control of nub‐Gal4.
- C
Representative images of wing disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained for Cut and Wg from flies expressing UAS‐mRpL4‐RNAi under the control of hh‐Gal4 (marked by GFP).
- D
The level of Su(H) occupancy at E(spl)mβ gene family regions as assessed by qPCR following ChIP, from wild‐type and UAS‐mRpL4‐RNAi‐expressing wing disks. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, two biological replicates for each genotype and three technical replicates for each sample. Statistical significance was tested using two‐tailed unpaired t‐test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01.
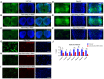
- A–C
Representative image showing the expression of NRE‐GFP in larval neuroblasts (n > 10 larvae) of control (A), mRpL24 RNAi (B) and mRpL4 RNAi (C) larvae.
- D–F
Representative image showing the expression of NRE‐GFP in salivary gland imaginal rings (n > 10 larvae) of control (D), mRpL24 RNAi (E) and mRpL4 RNAi (F) larvae.
- G–I
Representative image showing the expression of Su(H)‐LacZ in midgut cells (n > 10 flies) of control (G) and mRpL4 RNAi (H, I) adult flies.
- J
The level of Su(H) occupancy at Wg, Cut and Vg genomic regions as assessed by qPCR following ChIP, from wild‐type and UAS‐mRpL4‐RNAi‐expressing wing disks. Data are presented as mean ± SEM, two biological replicates for each genotype and three technical replicates for each sample. Statistical significance was tested using two‐tailed unpaired t‐test. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns means “not significant”.
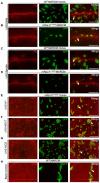
- A–D
Representative image of wing imaginal disks (n > 10 wing disks) containing MARCM clones stained for Wg. Notch signaling ligand Dl is overexpressed in wild‐type (A) or mRpL4 K14608 mutant (B) cells. Notch signaling ligand Ser is overexpressed in wild‐type (C) or mRpL4 K14608 mutant (D) cells.
- E–H
Representative image of wing imaginal disks (n > 10 wing disks) containing MARCM clones stained for NICD. Full‐length Notch protein (NFL) (E), NEXT (F) and NICD (G) are overexpressed in mRpL4 K14608 mutant cells. Blank MARCM clones are generated in the wild‐type wing disks (H).
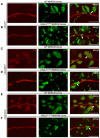
- A–F
Representative image of wing disks (n > 10 wing disks) bearing MARCM clones stained for Cut. NFL (A, B), NEXT (C, D) and NICD (E, F) are overexpressed in wild‐type (A, C, E) or mRpL4 K14608 mutant (B, D, F) cells. The MARCM clones are marked by GFP and representative clones are marked by white arrows. Scale bars = 100 μm.
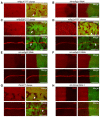
- A, B
Representative images of wing disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained with DHE. The mRpL4 K14608 mutant clones are marked by the absence of GFP (A), while UAS‐mRpL4‐RNAi are expressed in the posterior region (B).
- C, D
Representative images of wing disks (n > 10 wing disks) bearing mRpS28 k13104 (C) and mRpL24 f06692 (D) mutant clones stained with DHE and Cut.
- E, F
Representative images of wing disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained with DHE and Cut. The hh‐Gal4 (marked by GFP) is used to drive the expression of RNAi against mRpS2 (E) and mRpS12 (F).
- G
Representative images of wing disks (n > 10 wing disks) bearing CoVa tend mutant clones stained with DHE and Cut.
- H
Representative images of wing disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained with DHE and Cut. UAS‐CoVa‐RNAi are expressed in the posterior region under the control of hh‐Gal4 (marked by GFP).
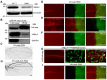
- A
Representative western blotting (n = 3 biological repeats) of lysates from wild‐type and UAS‐mRpL4‐RNAi‐expressing wing disks. The custom mRpL4 antibody was used and the β‐tubulin protein was included as loading control.
- B
Representative immunoprecipitation analysis (n = 3 biological repeats) using lysates from wing disks overexpressing HA‐tagged wap. Anti‐HA antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. Western blotting was performed using anti‐HA and anti‐mRpL4 antibodies to reveal wap and mRpL4, respectively. GAPDH was used as control.
- C
Representative image of wings (n > 15 wings) from flies expressing UAS‐wap‐RNAi under the control of hh‐Gal4.
- D–F
Representative images of wing disks (n > 15 wing disks) from flies expressing UAS‐wap‐RNAi under the control of hh‐Gal4 that have been stained for Cut (D), E(spl)mβ‐LacZ (E) and DHE (F).
- G
Representative image of wing disks (n > 10 wing disks) bearing MARCM clones (marked by GFP) stained for Wg. In the mRpL4 K14608 MARCM clones, UAS‐HA‐wap are expressed under the control of tub‐Gal4.
- H
Representative image of wings (n > 15 wings) from flies expressing UAS‐mnb‐RNAi under the control of hh‐Gal4.
- I
Representative image of wing disks (n > 15 wing disks) from flies expressing UAS‐mnb‐RNAi under the control of hh‐Gal4 that have been stained for Cut.
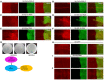
- A, B
Representative images of wing imaginal disks (n > 15 wing disks) expressing CoVa RNAi under the control of hh‐gal4 (marked by GFP) that are stained for DHE (A) and Cut (B).
- C–F
Representative images of wing imaginal disks (n > 20 wing disks) stained by DHE. The expression of ND‐42 (C), ND‐15.6 (D), Pdsw (E) and ND‐19 (F) RNAi are under the control of hh‐Gal4 (marked by GFP).
- G
Two proteins, mRpL50 and wap are isolated as mRpL4 interaction partners through yeast two‐hybridization. The GenBank accession numbers assigned to mRpL50 and wap are AfAF50594 and AAF50953.
- H
Representative image of wing imaginal disks (n > 15 wing disks) showing E(spl)mβ‐LacZ expression pattern, and cells in the posterior compartment are marked by GFP.
- I, J
Representative image of wing imaginal disks (n > 15 wing disks) stained for NICD (I) and Dl (J). In these wing disks, wap RNAi are expressed under the control of hh‐Gal4 (marked by GFP).
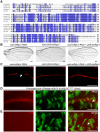
- A
Alignment of mRpL4 protein sequences from fly, human, mice, zebrafish and rat. The conserved residues are labeled with blue shadow.
- B
Representative images of wings (n > 15 wings) from flies expressing mRpL4 RNAi, UAS‐hmRpL4 and both under the control of nub‐Gal4.
- C
Representative images of wing imaginal disks (n > 10 wing disks) stained for Cut from flies expressing mRpL4 RNAi, UAS‐hmRpL4 and both under the control of nub‐Gal4. Representative regions showing Notch activity defects are marked by white arrow.
- D, E
Representative images of wing disks (n > 10 wing disks) bearing MARCM clones stained for Wg (D) and DHE (E). The MARCM clones are marked by GFP, and UAS‐hmRpL4 are expressed under the control of tub‐Gal4 in these clones.
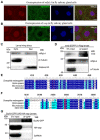
- A, B
Representative images of third instar larvae salivary glands (n > 10 larvae) from flies expressing FLAG‐tagged mRpL4 (A) and HA‐tagged wap (B). Immunostaining was performed using anti‐FLAG and anti‐HA antibodies to reveal mRpL4 and wap, respectively. Mitochondria are marked by GFP and cell nuclei are labeled by DAPI.
- C
Representative western blotting (n = 3 biological replicates) of mRpL4 protein distribution in cytoplasmic (Cyto) and nuclear (Nuc) fractions from wing disks lysates.
- D
Representative immunoprecipitation analysis (n = 3 biological replicates) using lysates from wing disks expressing GFP‐tagged mnb. Anti‐GFP antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. Western blotting was performed using anti‐GFP and anti‐mRpL4 antibodies to reveal mnb and mRpL4, respectively. α‐Tubulin was used as control.
- E
Alignment of Su(H) protein sequences from fly, human, mice and zebrafish. The region covering the mnb phosphorylation consensus sequence is shown, and the conserved Thr residue (T426) is labeled by red box.
- F
Alignment of Notch protein sequences from fly, human, mice and zebrafish. The region covering the mnb phosphorylation consensus sequence is shown, and the conserved Ser residue (S2659) is labeled by red box.
- G
Representative immunoprecipitation analysis (n = 2 biological replicates) using lysates from wing disks expressing GFP‐tagged Su(H) and HA‐tagged wap. Anti‐GFP antibodies were used for immunoprecipitation. Western blotting was performed using anti‐GFP and anti‐HA antibodies to reveal Su(H) and wap, respectively. GAPDH was used as control.
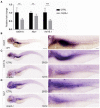
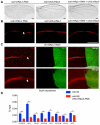
- A
Expression of notch1a, hey1, and her15.1 mRNA in mrpl4‐null larvae comparing to wild‐type control at 5 dpf as measured by quantitative PCR (three biological replicates for each genotype and three technical replicates for each sample). Statistical significance was tested using two‐tailed unpaired t‐test. Error bars represent ± SD; **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001.
- B
Representative bright field image of 5 dpf wild‐type larva (n > 30) illustrated by in situ hybridization with a mrpl4 riboprobe.
- C
Representative bright field image of 5 dpf CTRL (n = 26/29) and mrpl4 mutant (n = 12/15) illustrated by in situ hybridization with a notch1a riboprobe.
- D
Representative bright field images of 5 dpf CTRL (n = 28/30) and mrpl4 mutant (n = 10/12) illustrated by in situ hybridization with a hey1 riboprobe.
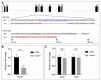
- A
Schematic diagrams of wild‐type (WT) and the zmRpL4 mutant allele (mu) generated by the CRISPR‐Cas9 genome editing system. The mutant allele contains a 24‐bp deletion (GTCCCAGCTCACTTGACACCAGCG, in blue) and a 2‐bp insertion (TA, in red) in the third exon. As a result, the mutant allele encodes a small polypeptide of 100 amino acid residues containing part of the wild‐type residues and a disordered Carbon‐terminal tail due to frame shifting (amino acid, in red).
- B
The mRNA levels of zmRpL4 in wild‐type control and mrpl4‐null larvae at 5 dpf as measured by quantitative PCR (three biological replicates for each genotype and three technical replicates for each sample). Statistical significance was tested using two‐tailed unpaired t‐test. Error bars represent ± SD, ****P < 0.00001.
- C
Bar graph showing relative levels of Notch signaling target genes her4.1 and her6 in mrpl4‐null larvae comparing to wild‐type control at 5 dpf as measured by quantitative PCR (n = 3 biological replicates per group). Statistical significance was tested using two‐tailed unpaired t‐test. Error bars represent ± SD; n.s., not significant.
Similar articles
-
A positive role of Sin3A in regulating Notch signaling during Drosophila wing development.Cell Signal. 2019 Jan;53:184-189. doi: 10.1016/j.cellsig.2018.10.008. Epub 2018 Oct 12. Cell Signal. 2019. PMID: 30316814
-
Use of FLP/FRT System to Screen for Notch Signaling Regulators in the Drosophila Wing.Methods Mol Biol. 2022;2472:39-48. doi: 10.1007/978-1-0716-2201-8_4. Methods Mol Biol. 2022. PMID: 35674890
-
Gliolectin positively regulates Notch signalling during wing-vein specification in Drosophila.Int J Dev Biol. 2015;59(4-6):187-94. doi: 10.1387/ijdb.140190LS. Int J Dev Biol. 2015. PMID: 26505251
-
Epigenetic Regulation of Notch Signaling During Drosophila Development.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020;1218:59-75. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-34436-8_4. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2020. PMID: 32060871 Review.
-
Integration of Drosophila and Human Genetics to Understand Notch Signaling Related Diseases.Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018;1066:141-185. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-89512-3_8. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2018. PMID: 30030826 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Amoebicidal Effect of COVID Box Molecules against Acanthamoeba: A Study of Cell Death.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Jun 20;17(6):808. doi: 10.3390/ph17060808. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38931475 Free PMC article.
-
Notch Signaling in Insect Development: A Simple Pathway with Diverse Functions.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 13;24(18):14028. doi: 10.3390/ijms241814028. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37762331 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Genome-wide analysis of WD40 protein family and functional characterization of BvWD40-82 in sugar beet.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Jun 2;14:1185440. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1185440. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37332716 Free PMC article.
-
The Identification of RPL4 as a Hub Gene Associated with Goat Litter Size via Weighted Gene Co-Expression Network Analysis.Animals (Basel). 2024 May 15;14(10):1470. doi: 10.3390/ani14101470. Animals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38791687 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Auer JS, Nagel AC, Schulz A, Wahl V, Preiss A (2015) MAPK‐dependent phosphorylation modulates the activity of suppressor of hairless in Drosophila . Cell Signal 27: 115–124 - PubMed
-
- Bailey AM, Posakony JW (1995) Suppressor of hairless directly activates transcription of Enhancer of split complex genes in response to Notch receptor activity. Genes Dev 9: 2609–2622 - PubMed
-
- Bray SJ (2006) Notch signalling: a simple pathway becomes complex. Nat Rev Mol Cell Bio 7: 678–689 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

