Small-molecule BCL6 inhibitor protects chronic cardiac transplant rejection and inhibits T follicular helper cell expansion and humoral response
- PMID: 37007047
- PMCID: PMC10063191
- DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2023.1140703
Small-molecule BCL6 inhibitor protects chronic cardiac transplant rejection and inhibits T follicular helper cell expansion and humoral response
Abstract
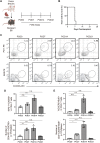
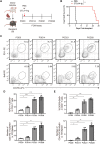
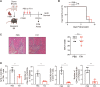
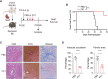
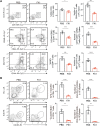
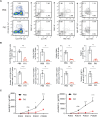
Background: B cell lymphoma 6 (BCL6) is an important transcription factor of T follicular helper (Tfh) cells, which regulate the humoral response by supporting the maturation of germinal center B cells and plasma cells. The aim of this study is to investigate the expansion of T follicular helper cells and the effect of the BCL6 inhibitor FX1 in acute and chronic cardiac transplant rejection models. Methods: A mouse model of acute and chronic cardiac transplant rejection was established. Splenocytes were collected at different time points after transplantation for CXCR5+PD-1+ and CXCR5+BCL6+ Tfh cells detection by flow cytometry (FCM). Next, we treated the cardiac transplant with BCL6 inhibitor FX1 and the survival of grafts was recorded. The hematoxylin and eosin, Elastica van Gieson, and Masson staining of cardiac grafts was performed for the pathological analysis. Furthermore, the proportion and number of CD4+ T cells, effector CD4+ T cells (CD44+CD62L-), proliferating CD4+ T cells (Ki67+), and Tfh cells in the spleen were detected by FCM. The cells related to humoral response (plasma cells, germinal center B cells, IgG1+ B cells) and donor-specific antibody were also detected. Results: We found that the Tfh cells were significantly increased in the recipient mice on day 14 post transplantation. During the acute cardiac transplant rejection, even the BCL6 inhibitor FX1 did not prolong the survival or attenuate the immune response of cardiac graft, the expansion of Tfh cell expansion inhibit. During the chronic cardiac transplant rejection, FX1 prolonged survival of cardiac graft, and prevented occlusion and fibrosis of vascular in cardiac grafts. FX1 also decreased the proportion and number of splenic CD4+ T cells, effector CD4+ T cells, proliferating CD4+ T cells, and Tfh cells in mice with chronic rejection. Moreover, FX1 also inhibited the proportion and number of splenic plasma cells, germinal center B cells, IgG1+ B cells, and the donor-specific antibody in recipient mice. Conclusion: We found BCL6 inhibitor FX1 protects chronic cardiac transplant rejection and inhibits the expansion of Tfh cells and the humoral response, which suggest that BCL6 is a potential therapeutic target of the treatment for chronic cardiac transplant rejection.
Keywords: BCL6; FX1; T follicular helper cells; cardiac transplant rejection; humoral response.
Copyright © 2023 Xia, Jin and Wu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
BCL6 Inhibitor-Mediated Downregulation of Phosphorylated SAMHD1 and T Cell Activation Are Associated with Decreased HIV Infection and Reactivation.J Virol. 2019 Jan 4;93(2):e01073-18. doi: 10.1128/JVI.01073-18. Print 2019 Jan 15. J Virol. 2019. PMID: 30355686 Free PMC article.
-
BCL6 BTB-specific inhibition via FX1 treatment reduces Tfh cells and reverses lymphoid follicle hyperplasia in Indian rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta).J Med Primatol. 2020 Feb;49(1):26-33. doi: 10.1111/jmp.12438. Epub 2019 Oct 1. J Med Primatol. 2020. PMID: 31571234 Free PMC article.
-
BCL6 BTB-specific inhibitor reversely represses T-cell activation, Tfh cells differentiation, and germinal center reaction in vivo.Eur J Immunol. 2021 Oct;51(10):2441-2451. doi: 10.1002/eji.202049150. Epub 2021 Sep 16. Eur J Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34287839 Free PMC article.
-
Memory T follicular helper CD4 T cells.Front Immunol. 2015 Feb 2;6:16. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2015.00016. eCollection 2015. Front Immunol. 2015. PMID: 25699040 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Bcl6-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation of Follicular Helper T cells (TFH).Trends Immunol. 2021 Apr;42(4):336-349. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2021.02.002. Epub 2021 Mar 1. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33663954 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
B Cell Lymphoma 6 (BCL6): A Conserved Regulator of Immunity and Beyond.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Oct 11;25(20):10968. doi: 10.3390/ijms252010968. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 39456751 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Cai Y., Watkins M. A., Xue F., Ai Y., Cheng H., Midkiff C. C., et al. (2020). BCL6 BTB-specific inhibition via FX1 treatment reduces Tfh cells and reverses lymphoid follicle hyperplasia in Indian rhesus macaque (Macaca mulatta). J. Med. Primatol. 49 (1), 26–33. 10.1111/jmp.12438 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

