Role and mechanism of fibroblast-activated protein-α expression on the surface of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
- PMID: 37006278
- PMCID: PMC10064071
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1135384
Role and mechanism of fibroblast-activated protein-α expression on the surface of fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis
Abstract
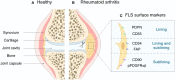
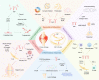
Fibroblast-activated protein-α (FAP) is a type II integrated serine protease expressed by activated fibroblasts during fibrosis or inflammation. Fibroblast-like synoviocytes (FLSs) in rheumatoid arthritis (RA) synovial sites abundantly and stably overexpress FAP and play important roles in regulating the cellular immune, inflammatory, invasion, migration, proliferation, and angiogenesis responses in the synovial region. Overexpression of FAP is regulated by the initial inflammatory microenvironment of the disease and epigenetic signaling, which promotes RA development by regulating FLSs or affecting the signaling cross-linking FLSs with other cells at the local synovium and inflammatory stimulation. At present, several treatment options targeting FAP are in the process of development. This review discusses the basic features of FAP expressed on the surface of FLSs and its role in RA pathophysiology and advances in targeted therapies.
Keywords: cell function; fibroblast-activated protein-α; fibroblast-like synoviocytes; rheumatoid arthritis; targeted therapy.
Copyright © 2023 Wang, Wang, Lan, Zhang, Yan, Zhang, Xu and Tao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Role of Fibroblast Activation Protein Alpha in Fibroblast-like Synoviocytes of Rheumatoid Arthritis.Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021 Jun 6;20(3):338-349. doi: 10.18502/ijaai.v20i3.6335. Iran J Allergy Asthma Immunol. 2021. PMID: 34134455
-
Fibroblast activation protein is expressed by rheumatoid myofibroblast-like synoviocytes.Arthritis Res Ther. 2006;8(6):R171. doi: 10.1186/ar2080. Arthritis Res Ther. 2006. PMID: 17105646 Free PMC article.
-
Transforming growth factor β1 promotes fibroblast-like synoviocytes migration and invasion via TGF-β1/Smad signaling in rheumatoid arthritis.Mol Cell Biochem. 2019 Sep;459(1-2):141-150. doi: 10.1007/s11010-019-03557-0. Epub 2019 Jul 11. Mol Cell Biochem. 2019. PMID: 31297660
-
The role of non-coding RNAs in fibroblast-like synoviocytes in rheumatoid arthritis.Int J Rheum Dis. 2024 Oct;27(10):e15376. doi: 10.1111/1756-185X.15376. Int J Rheum Dis. 2024. PMID: 39439368 Review.
-
Regulation of Immune Responses and Chronic Inflammation by Fibroblast-Like Synoviocytes.Front Immunol. 2019 Jun 19;10:1395. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2019.01395. eCollection 2019. Front Immunol. 2019. PMID: 31275325 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Targeting pathogenic fibroblast-like synoviocyte subsets in rheumatoid arthritis.Arthritis Res Ther. 2024 May 23;26(1):103. doi: 10.1186/s13075-024-03343-4. Arthritis Res Ther. 2024. PMID: 38783357 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A Review of Advances in Molecular Imaging of Rheumatoid Arthritis: From In Vitro to Clinic Applications Using Radiolabeled Targeting Vectors with Technetium-99m.Life (Basel). 2024 Jun 12;14(6):751. doi: 10.3390/life14060751. Life (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38929734 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Targeting FAP-positive chondrocytes in osteoarthritis: a novel lipid nanoparticle siRNA approach to mitigate cartilage degeneration.J Nanobiotechnology. 2024 Oct 26;22(1):659. doi: 10.1186/s12951-024-02946-y. J Nanobiotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39456041 Free PMC article.
-
Diagnostic and evaluative efficiency of 68Ga-FAPI-04 in skeletal muscle injury.EJNMMI Res. 2024 Oct 2;14(1):88. doi: 10.1186/s13550-024-01147-w. EJNMMI Res. 2024. PMID: 39356393 Free PMC article.
-
The Notch signaling-regulated angiogenesis in rheumatoid arthritis: pathogenic mechanisms and therapeutic potentials.Front Immunol. 2023 Oct 26;14:1272133. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1272133. eCollection 2023. Front Immunol. 2023. PMID: 38022508 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

