Role of stem cell derivatives in inflammatory diseases
- PMID: 37006266
- PMCID: PMC10062329
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1153901
Role of stem cell derivatives in inflammatory diseases
Abstract
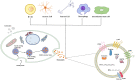
Mesenchymal stem cells (MSCs) are pluripotent stem cells of mesodermal origin with the ability of self-renewal and multidirectional differentiation, which have all the common characteristics of stem cells and the ability to differentiate into adipocytes, osteoblasts, neuron-like cells and other cells. Stem cell derivatives are extracellular vesicles(EVs) released from mesenchymal stem cells that are involved in the process of body's immune response, antigen presentation, cell differentiation, and anti-inflammatory. EVs are further divided into ectosomes and exosomes are widely used in degenerative diseases, cancer, and inflammatory diseases due to their parental cell characteristics. However, most diseases are closely related to inflammation, and exosomes can mitigate the damage caused by inflammation in terms of suppressing the inflammatory response, anti-apoptosis and promoting tissue repair. Stem cell-derived exosomes have become an emerging modality for cell-free therapy because of their high safety and ease of preservation and transportation through intercellular communication. In this review, we highlight the characteristics and functions of MSCs-derived exosomes and discuss the regulatory mechanisms of MSCs-derived exosomes in inflammatory diseases and their potential applications in clinical diagnosis and therapy.
Keywords: diagnose; exosome; inflammatory diseases; stem cells; treatment.
Copyright © 2023 Yang, Peng, Li, Shi, Luan and Yin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived secretome and extracellular vesicles: perspective and challenges in cancer therapy and clinical applications.Clin Transl Oncol. 2023 Jul;25(7):2056-2068. doi: 10.1007/s12094-023-03115-7. Epub 2023 Feb 17. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023. PMID: 36808392 Review.
-
Mesenchymal stem cells-derived exosomes are more immunosuppressive than microparticles in inflammatory arthritis.Theranostics. 2018 Feb 3;8(5):1399-1410. doi: 10.7150/thno.21072. eCollection 2018. Theranostics. 2018. PMID: 29507629 Free PMC article.
-
Research progress of engineered mesenchymal stem cells and their derived exosomes and their application in autoimmune/inflammatory diseases.Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023 Apr 11;14(1):71. doi: 10.1186/s13287-023-03295-7. Stem Cell Res Ther. 2023. PMID: 37038221 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Progress of Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Tissue Repair.Curr Pharm Des. 2020;26(17):2022-2037. doi: 10.2174/1381612826666200420144805. Curr Pharm Des. 2020. PMID: 32310043 Review.
-
Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Extracellular Vesicles: A Novel Cell-Free Therapy.Immunol Invest. 2020 Oct;49(7):758-780. doi: 10.1080/08820139.2020.1712416. Epub 2020 Feb 2. Immunol Invest. 2020. PMID: 32009478 Review.
Cited by
-
Role of Exosomes in the Pathogenesis and Theranostic of Alzheimer's Disease and Parkinson's Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jul 4;24(13):11054. doi: 10.3390/ijms241311054. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37446231 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Applications of Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Mar 21;25(6):3562. doi: 10.3390/ijms25063562. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38542535 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Roles of Microenvironment on Mesenchymal Stem Cells Therapy for Osteoarthritis.J Inflamm Res. 2024 Oct 3;17:7069-7079. doi: 10.2147/JIR.S475617. eCollection 2024. J Inflamm Res. 2024. PMID: 39377043 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

