The 20 years transition of clinical characteristics and metabolic risk factors in primary liver cancer patients from China
- PMID: 36998463
- PMCID: PMC10043326
- DOI: 10.3389/fonc.2023.1109980
The 20 years transition of clinical characteristics and metabolic risk factors in primary liver cancer patients from China
Abstract
Background: The clinical characteristics of primary liver cancer (PLC) patients are changing, maybe due to hepatitis viral vaccination and lifestyle changes, etc. The linkage between these changes and outcomes among these PLCs has not yet been fully elucidated.
Methods: It was identified total of 1691 PLC cases diagnosed between 2000 ~ 2020. Cox proportional hazards models were utilized to determine the connections between the clinical presentations and their close risk factor(s) from PLC patients.
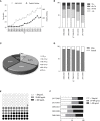
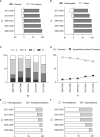
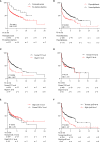
Results: The average age of PLC patients increased gradually from 52.74 ± 0.5 years in 2000 ~ 2004 to 58.63 ± 0.44 years in 2017 ~ 2020, accompanied by an increased proportion of females from 11.11% to 22.46%, and non-viral hepatitis-related PLC was raised from 1.5% to 22.35%. 840 (49.67%) PLC patients with alpha-fetoprotein (AFP) < 20ng/mL (AFP-negative). The mortality was 285 (16.85%) or 532 (31.46%) PLC patients with alanine transaminase (ALT) between 40 ~ 60 IU/L or ALT > 60 IU/L. The PLC patients with pre-diabetes/diabetes or dyslipidemia also increased from 4.29% or 11.1% in 2000 ~ 2004 to 22.34% or 46.83% in 2017 ~ 2020. The survival period of the PLC patients with normoglycemia or normolipidemic was 2.18 or 3.14 folds longer than those patients with pre-diabetes/diabetes or hyperlipidemia (P<0.05).
Conclusions: It was gradually increased that age, the proportion of females, non-viral hepatitis-related causes, AFP-negative, and abnormal glucose/lipids among PLC patients. Proper control of glucose/lipids or ALT may improve the prognosis of PLCs.
Keywords: alanine transaminase; clinical traits; fetoprotein; glycolipid; liver cancer.
Copyright © 2023 Ding, Feng, Ma, Zhao, Wang, An, Xu, Lou, Lin, Xie, Liu, Bao and Wang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Total cholesterol, alanine aminotransferase and the risk of primary liver cancer: A population-based prospective study.Medicine (Baltimore). 2021 May 7;100(18):e25746. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000025746. Medicine (Baltimore). 2021. PMID: 33950959 Free PMC article.
-
α-fetoprotein levels after interferon therapy and risk of hepatocarcinogenesis in chronic hepatitis C.Hepatology. 2013 Oct;58(4):1253-62. doi: 10.1002/hep.26442. Epub 2013 Aug 19. Hepatology. 2013. PMID: 23564522
-
Evaluation of high-risk factors and the diagnostic value of alpha-fetoprotein in the stratification of primary liver cancer.World J Clin Cases. 2022 Sep 16;10(26):9264-9275. doi: 10.12998/wjcc.v10.i26.9264. World J Clin Cases. 2022. PMID: 36159417 Free PMC article.
-
Systematic review with meta-analysis: the proportion of chronic hepatitis B patients with normal alanine transaminase ≤ 40 IU/L and significant hepatic fibrosis.Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014 Feb;39(4):349-58. doi: 10.1111/apt.12590. Epub 2014 Jan 6. Aliment Pharmacol Ther. 2014. PMID: 24387289 Review.
-
Hepatitis BS antigen, malaria titers, and primary liver cancer in South Vietnam.Gastroenterology. 1976 Mar;70(3):392-6. Gastroenterology. 1976. PMID: 55372 Review.
Cited by
-
The urgency to expand the antiviral indications of general chronic hepatitis B patients.Front Med (Lausanne). 2023 May 19;10:1165891. doi: 10.3389/fmed.2023.1165891. eCollection 2023. Front Med (Lausanne). 2023. PMID: 37275355 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Clinical efficacy of precision liver resection for primary liver cancer.Am J Transl Res. 2024 Mar 15;16(3):897-904. doi: 10.62347/QBBO2532. eCollection 2024. Am J Transl Res. 2024. PMID: 38586102 Free PMC article.
-
Involvement of S100A6/S100A11 in T-Cell Immune Regulatory in HCC Revealed by Single Cell RNA-seq.Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024 Jan-Dec;23:15330338241252610. doi: 10.1177/15330338241252610. Technol Cancer Res Treat. 2024. PMID: 38766816 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Global Burden of Disease Cancer C. Fitzmaurice C, Abate D, Abbasi N, Abbastabar H, Abd-Allah F, et al. . Global, regional, and national cancer incidence, mortality, years of life lost, years lived with disability, and disability-adjusted life-years for 29 cancer groups, 1990 to 2017: A systematic analysis for the global burden of disease study. JAMA Oncol (2019) 5(12):1749–68. doi: 10.1001/jamaoncol.2019.2996 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen VL, Yeh ML, Le AK, Jun M, Saeed WK, Yang JD, et al. . Anti-viral therapy is associated with improved survival but is underutilised in patients with hepatitis b virus-related hepatocellular carcinoma: Real-world East and West experience. Aliment Pharmacol Ther (2018) 48(1):44–54. doi: 10.1111/apt.14801 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

