Chronic CD27-CD70 costimulation promotes type 1-specific polarization of effector Tregs
- PMID: 36993956
- PMCID: PMC10041113
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1023064
Chronic CD27-CD70 costimulation promotes type 1-specific polarization of effector Tregs
Abstract
Introduction: Most T lymphocytes, including regulatory T cells, express the CD27 costimulatory receptor in steady state conditions. There is evidence that CD27 engagement on conventional T lymphocytes favors the development of Th1 and cytotoxic responses in mice and humans, but the impact on the regulatory lineage is unknown.
Methods: In this report, we examined the effect of constitutive CD27 engagement on both regulatory and conventional CD4+ T cells in vivo, in the absence of intentional antigenic stimulation.
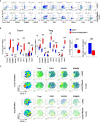
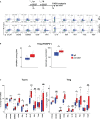
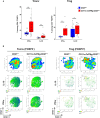
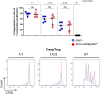
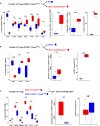
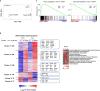
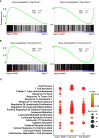
Results: Our data show that both T cell subsets polarize into type 1 Tconvs or Tregs, characterized by cell activation, cytokine production, response to IFN-γ and CXCR3-dependent migration to inflammatory sites. Transfer experiments suggest that CD27 engagement triggers Treg activation in a cell autonomous fashion.
Conclusion: We conclude that CD27 may regulate the development of Th1 immunity in peripheral tissues as well as the subsequent switch of the effector response into long-term memory.
Keywords: CD27 costimulation; CXCR3; dendritic cells; eomes; regulatory T cells.
Copyright © 2023 Bowakim-Anta, Acolty, Azouz, Yagita, Leo, Goriely, Oldenhove and Moser.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CD27-CD70 costimulation controls T cell immunity during acute and persistent cytomegalovirus infection.J Virol. 2013 Jun;87(12):6851-65. doi: 10.1128/JVI.03305-12. Epub 2013 Apr 10. J Virol. 2013. PMID: 23576505 Free PMC article.
-
Chronic CD70-driven costimulation impairs IgG responses by instructing T cells to inhibit germinal center B cell formation through FasL-Fas interactions.J Immunol. 2009 Nov 15;183(10):6442-51. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.0901565. Epub 2009 Oct 28. J Immunol. 2009. PMID: 19864607
-
CD70 Inversely Regulates Regulatory T Cells and Invariant NKT Cells and Modulates Type 1 Diabetes in NOD Mice.J Immunol. 2020 Oct 1;205(7):1763-1777. doi: 10.4049/jimmunol.2000148. Epub 2020 Aug 31. J Immunol. 2020. PMID: 32868408 Free PMC article.
-
CD27/CD70 interactions regulate T dependent B cell differentiation.Immunol Res. 2000;21(1):23-30. doi: 10.1385/IR:21:1:23. Immunol Res. 2000. PMID: 10803880 Review.
-
The role of CD27 in anti-viral T-cell immunity.Curr Opin Virol. 2017 Feb;22:77-88. doi: 10.1016/j.coviro.2016.12.001. Epub 2017 Jan 12. Curr Opin Virol. 2017. PMID: 28086150 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell sequencing analysis and multiple machine-learning models revealed the cellular crosstalk of dendritic cells and identified FABP5 and KLRB1 as novel biomarkers for psoriasis.Front Immunol. 2024 Mar 26;15:1374763. doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2024.1374763. eCollection 2024. Front Immunol. 2024. PMID: 38596682 Free PMC article.
-
Nasopharyngeal carcinoma cells promote regulatory T cell development and suppressive activity via CD70-CD27 interaction.Nat Commun. 2023 Apr 6;14(1):1912. doi: 10.1038/s41467-023-37614-6. Nat Commun. 2023. PMID: 37024479 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

