Breaking Barriers in Eye Treatment: Polymeric Nano-Based Drug-Delivery System for Anterior Segment Diseases and Glaucoma
- PMID: 36987154
- PMCID: PMC10054733
- DOI: 10.3390/polym15061373
Breaking Barriers in Eye Treatment: Polymeric Nano-Based Drug-Delivery System for Anterior Segment Diseases and Glaucoma
Abstract
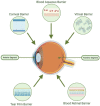
The eye has anatomical structures that function as robust static and dynamic barriers, limiting the penetration, residence time, and bioavailability of medications administered topically. The development of polymeric nano-based drug-delivery systems (DDS) could be the solution to these challenges: it can pass through ocular barriers, offering higher bioavailability of administered drugs to targeted tissues that are otherwise inaccessible; it can stay in ocular tissues for longer periods of time, requiring fewer drug administrations; and it can be made up of polymers that are biodegradable and nano-sized, minimizing the undesirable effects of the administered molecules. Therefore, therapeutic innovations in polymeric nano-based DDS have been widely explored for ophthalmic drug-delivery applications. In this review, we will give a comprehensive overview of polymeric nano-based drug-delivery systems (DDS) used in the treatment of ocular diseases. We will then examine the current therapeutic challenges of various ocular diseases and analyze how different types of biopolymers can potentially enhance our therapeutic options. A literature review of the preclinical and clinical studies published between 2017 and 2022 was conducted. Thanks to the advances in polymer science, the ocular DDS has rapidly evolved, showing great promise to help clinicians better manage patients.
Keywords: anterior segment diseases; biodegradable polymers; glaucoma; ocular diseases; ocular drug-delivery; polymeric biomaterials; polymeric nanocarriers.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Overcoming Treatment Challenges in Posterior Segment Diseases with Biodegradable Nano-Based Drug Delivery Systems.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Mar 29;15(4):1094. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15041094. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37111579 Free PMC article. Review.
-
A New Era in Ocular Therapeutics: Advanced Drug Delivery Systems for Uveitis and Neuro-Ophthalmologic Conditions.Pharmaceutics. 2023 Jul 14;15(7):1952. doi: 10.3390/pharmaceutics15071952. Pharmaceutics. 2023. PMID: 37514137 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Fundamentals, challenges, and nanomedicine-based solutions for ocular diseases.Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2019 Jul;11(4):e1548. doi: 10.1002/wnan.1548. Epub 2018 Dec 3. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Nanomed Nanobiotechnol. 2019. PMID: 30506871 Review.
-
An insight on ophthalmic drug delivery systems: Focus on polymeric biomaterials-based carriers.J Control Release. 2023 Oct;362:446-467. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2023.08.041. Epub 2023 Sep 8. J Control Release. 2023. PMID: 37640109 Review.
-
Advances in Biodegradable Nano-Sized Polymer-Based Ocular Drug Delivery.Polymers (Basel). 2019 Aug 20;11(8):1371. doi: 10.3390/polym11081371. Polymers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31434273 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Hydrogels in Ophthalmology: Novel Strategies for Overcoming Therapeutic Challenges.Materials (Basel). 2023 Dec 23;17(1):86. doi: 10.3390/ma17010086. Materials (Basel). 2023. PMID: 38203940 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Therapeutic Potential of Cannabinoids in Glaucoma.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023 Aug 14;16(8):1149. doi: 10.3390/ph16081149. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2023. PMID: 37631064 Free PMC article. Review.
-
miRNA Studies in Glaucoma: A Comprehensive Review of Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 28;24(19):14699. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914699. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834147 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Exploring the Potential of Nanoporous Materials for Advancing Ophthalmic Treatments.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Oct 26;24(21):15599. doi: 10.3390/ijms242115599. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37958583 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Novel Biomaterials in Glaucoma Treatment.Biomedicines. 2024 Apr 7;12(4):813. doi: 10.3390/biomedicines12040813. Biomedicines. 2024. PMID: 38672168 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Ridolfo R., Tavakoli S., Junnuthula V., Williams D.S., Urtti A., van Hest J.C.M. Exploring the Impact of Morphology on the Properties of Biodegradable Nanoparticles and Their Diffusion in Complex Biological Medium. Biomacromolecules. 2021;22:126–133. doi: 10.1021/acs.biomac.0c00726. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Orasugh J.T., Dutta S., Das D., Nath J., Pal C., Chattopadhyay D. Utilization of Cellulose Nanocrystals (CNC) Biopolymer Nanocomposites in Ophthalmic Drug Delivery System (ODDS) J. Nanotechnol. Res. 2019;1:75–87.
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources