The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Liver Cirrhosis Patients with Refractory Ascites: A Literature Review
- PMID: 36983252
- PMCID: PMC10056954
- DOI: 10.3390/jcm12062253
The Effects of SGLT2 Inhibitors on Liver Cirrhosis Patients with Refractory Ascites: A Literature Review
Abstract
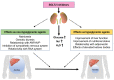
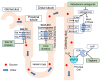
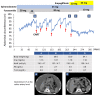
Decompensated liver cirrhosis is often complicated by refractory ascites, and intractable ascites are a predictor of poor prognosis in patients with liver cirrhosis. The treatment of ascites in patients with cirrhosis is based on the use of aldosterone blockers and loop diuretics, and occasionally vasopressin receptor antagonists are also used. Recent reports suggest that sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors may be a new treatment for refractory ascites with a different mechanism with respect to conventional agents. The main mechanisms of ascites reduction with SGLT2 inhibitors appear to be natriuresis and osmotic diuresis. However, other mechanisms, including improvements in glucose metabolism and nutritional status, hepatoprotection by ketone bodies and adiponectin, amelioration of the sympathetic nervous system, and inhibition of the renin-angiotensin-aldosterone system, may also contribute to the reduction of ascites. This literature review describes previously reported cases in which SGLT2 inhibitors were used to effectively treat ascites caused by liver cirrhosis. The discussion of the mechanisms involved is expected to contribute to establishing SGLT2 therapy for ascites in the future.
Keywords: ascites; decompensated liver cirrhosis; diuretics; sodium–glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitors.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Combined with Conventional Diuretics Ameliorate Body Fluid Retention without Excessive Plasma Volume Reduction.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;14(11):1194. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111194. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893720 Free PMC article.
-
Association of the G-protein and α2-adrenergic receptor gene and plasma norepinephrine level with clonidine improvement of the effects of diuretics in patients with cirrhosis with refractory ascites: a randomised clinical trial.Gut. 2010 Nov;59(11):1545-53. doi: 10.1136/gut.2010.210732. Epub 2010 Sep 9. Gut. 2010. PMID: 20833658 Clinical Trial.
-
Treatment for ascites in adults with decompensated liver cirrhosis: a network meta-analysis.Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020 Jan 16;1(1):CD013123. doi: 10.1002/14651858.CD013123.pub2. Cochrane Database Syst Rev. 2020. PMID: 31978257 Free PMC article.
-
Diuretic Action of Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitors and Its Importance in the Management of Heart Failure.Circ J. 2016 Oct 25;80(11):2277-2281. doi: 10.1253/circj.CJ-16-0780. Epub 2016 Sep 7. Circ J. 2016. PMID: 27599528 Review.
-
Management of refractory ascites.Am J Ther. 2012 Mar;19(2):121-32. doi: 10.1097/MJT.0b013e3181ff7a8b. Am J Ther. 2012. PMID: 21192246 Review.
Cited by
-
Empagliflozin in Diuretic-Refractory Ascites (DRAin-Em): Results of a Single-Center Feasibility Study.J Gen Intern Med. 2024 Nov 19. doi: 10.1007/s11606-024-09191-x. Online ahead of print. J Gen Intern Med. 2024. PMID: 39560900 No abstract available.
-
Ascites: Under- and Overfill: Is Amiloride the Answer?J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024 Nov 1;35(11):1453-1455. doi: 10.1681/ASN.0000000000000493. Epub 2024 Sep 11. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2024. PMID: 39259605 No abstract available.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Dapagliflozin in Recurrent Ascites: A Pilot Study.Dig Dis Sci. 2024 Oct 9. doi: 10.1007/s10620-024-08667-4. Online ahead of print. Dig Dis Sci. 2024. PMID: 39384712
-
Sodium-Glucose Cotransporter 2 Inhibitor Combined with Conventional Diuretics Ameliorate Body Fluid Retention without Excessive Plasma Volume Reduction.Diagnostics (Basel). 2024 Jun 5;14(11):1194. doi: 10.3390/diagnostics14111194. Diagnostics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38893720 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological Interventions for Cirrhotic Ascites: From Challenges to Emerging Therapeutic Horizons.Gut Liver. 2024 Nov 15;18(6):934-948. doi: 10.5009/gnl240038. Epub 2024 Aug 29. Gut Liver. 2024. PMID: 39205495 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- McMurray J.J.V., Solomon S.D., Inzucchi S.E., Køber L., Kosiborod M.N., Martinez F.A., Ponikowski P., Sabatine M.S., Anand I.S., Bělohlávek J., et al. Dapagliflozin in Patients with Heart Failure and Reduced Ejection Fraction. N. Engl. J. Med. 2019;381:1995–2008. doi: 10.1056/NEJMoa1911303. - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

