The Regulatory Roles of Ezh2 in Response to Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in Macrophages and Mice with Conditional Ezh2 Deletion with LysM-Cre System
- PMID: 36982437
- PMCID: PMC10049283
- DOI: 10.3390/ijms24065363
The Regulatory Roles of Ezh2 in Response to Lipopolysaccharide (LPS) in Macrophages and Mice with Conditional Ezh2 Deletion with LysM-Cre System
Abstract
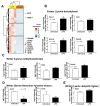
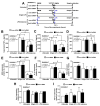
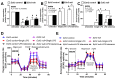
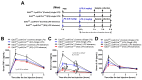
The responses of macrophages to lipopolysaccharide (LPS) might determine the direction of clinical manifestations of sepsis, which is the immune response against severe infection. Meanwhile, the enhancer of zeste homologue 2 (Ezh2), a histone lysine methyltransferase of epigenetic regulation, might interfere with LPS response. Transcriptomic analysis on LPS-activated wild-type macrophages demonstrated an alteration of several epigenetic enzymes. Although the Ezh2-silencing macrophages (RAW264.7), using small interfering RNA (siRNA), indicated a non-different response to the control cells after a single LPS stimulation, the Ezh2-reducing cells demonstrated a less severe LPS tolerance, after two LPS stimulations, as determined by the higher supernatant TNF-α. With a single LPS stimulation, Ezh2 null (Ezh2flox/flox; LysM-Crecre/-) macrophages demonstrated lower supernatant TNF-α than Ezh2 control (Ezh2fl/fl; LysM-Cre-/-), perhaps due to an upregulation of Socs3, which is a suppressor of cytokine signaling 3, due to the loss of the Ezh2 gene. In LPS tolerance, Ezh2 null macrophages indicated higher supernatant TNF-α and IL-6 than the control, supporting an impact of the loss of the Ezh2 inhibitory gene. In parallel, Ezh2 null mice demonstrated lower serum TNF-α and IL-6 than the control mice after an LPS injection, indicating a less severe LPS-induced hyper-inflammation in Ezh2 null mice. On the other hand, there were similar serum cytokines after LPS tolerance and the non-reduction of serum cytokines after the second dose of LPS, indicating less severe LPS tolerance in Ezh2 null mice compared with control mice. In conclusion, an absence of Ezh2 in macrophages resulted in less severe LPS-induced inflammation, as indicated by low serum cytokines, with less severe LPS tolerance, as demonstrated by higher cytokine production, partly through the upregulated Socs3.
Keywords: Ezh2; epigenetics; lipopolysaccharide; macrophages; sepsis.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Less Severe Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Conditional mgmt-Deleted Mice with LysM-Cre System: The Loss of DNA Repair in Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 14;24(12):10139. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210139. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373287 Free PMC article.
-
Less Severe Polymicrobial Sepsis in Conditional mgmt-Deleted Mice Using LysM-Cre System, Impacts of DNA Methylation and MGMT Inhibitor in Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10175. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210175. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373325 Free PMC article.
-
Less Severe Sepsis in Cecal Ligation and Puncture Models with and without Lipopolysaccharide in Mice with Conditional Ezh2-Deleted Macrophages (LysM-Cre System).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 10;24(10):8517. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108517. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239864 Free PMC article.
-
Pre-treatment of recombinant mouse MFG-E8 downregulates LPS-induced TNF-α production in macrophages via STAT3-mediated SOCS3 activation.PLoS One. 2011;6(11):e27685. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0027685. Epub 2011 Nov 15. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 22114683 Free PMC article.
-
Role of Myeloid Tet Methylcytosine Dioxygenase 2 in Pulmonary and Peritoneal Inflammation Induced by Lipopolysaccharide and Peritonitis Induced by Escherichia coli.Cells. 2021 Dec 28;11(1):82. doi: 10.3390/cells11010082. Cells. 2021. PMID: 35011643 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
What We Know About the Actual Role of Traditional Probiotics in Health and Disease.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024 Oct;16(5):1836-1856. doi: 10.1007/s12602-024-10275-7. Epub 2024 May 3. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2024. PMID: 38700762 Review.
-
Less Severe Lipopolysaccharide-Induced Inflammation in Conditional mgmt-Deleted Mice with LysM-Cre System: The Loss of DNA Repair in Macrophages.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 14;24(12):10139. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210139. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373287 Free PMC article.
-
Less Severe Polymicrobial Sepsis in Conditional mgmt-Deleted Mice Using LysM-Cre System, Impacts of DNA Methylation and MGMT Inhibitor in Sepsis.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 15;24(12):10175. doi: 10.3390/ijms241210175. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373325 Free PMC article.
-
Less Severe Sepsis in Cecal Ligation and Puncture Models with and without Lipopolysaccharide in Mice with Conditional Ezh2-Deleted Macrophages (LysM-Cre System).Int J Mol Sci. 2023 May 10;24(10):8517. doi: 10.3390/ijms24108517. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37239864 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

