Novel Insights into RAD52's Structure, Function, and Druggability for Synthetic Lethality and Innovative Anticancer Therapies
- PMID: 36980703
- PMCID: PMC10046612
- DOI: 10.3390/cancers15061817
Novel Insights into RAD52's Structure, Function, and Druggability for Synthetic Lethality and Innovative Anticancer Therapies
Abstract
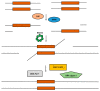
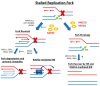
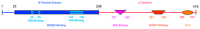
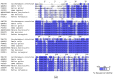
In recent years, the RAD52 protein has been highlighted as a mediator of many DNA repair mechanisms. While RAD52 was initially considered to be a non-essential auxiliary factor, its inhibition has more recently been demonstrated to be synthetically lethal in cancer cells bearing mutations and inactivation of specific intracellular pathways, such as homologous recombination. RAD52 is now recognized as a novel and critical pharmacological target. In this review, we comprehensively describe the available structural and functional information on RAD52. The review highlights the pathways in which RAD52 is involved and the approaches to RAD52 inhibition. We discuss the multifaceted role of this protein, which has a complex, dynamic, and functional 3D superstructural arrangement. This complexity reinforces the need to further investigate and characterize RAD52 to solve a challenging mechanistic puzzle and pave the way for a robust drug discovery campaign.
Keywords: RAD52; drug discovery; precision medicine; synthetic lethality.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
RAD52: Paradigm of Synthetic Lethality and New Developments.Front Genet. 2021 Nov 23;12:780293. doi: 10.3389/fgene.2021.780293. eCollection 2021. Front Genet. 2021. PMID: 34887904 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Replication Protein A Phosphorylation Facilitates RAD52-Dependent Homologous Recombination in BRCA-Deficient Cells.Mol Cell Biol. 2022 Feb 17;42(2):e0052421. doi: 10.1128/mcb.00524-21. Epub 2021 Dec 20. Mol Cell Biol. 2022. PMID: 34928169 Free PMC article.
-
RAD52 as a Potential Target for Synthetic Lethality-Based Anticancer Therapies.Cancers (Basel). 2019 Oct 14;11(10):1561. doi: 10.3390/cancers11101561. Cancers (Basel). 2019. PMID: 31615159 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Physiological and Pathological Roles of RAD52 at DNA Replication Forks.Cancers (Basel). 2020 Feb 10;12(2):402. doi: 10.3390/cancers12020402. Cancers (Basel). 2020. PMID: 32050645 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Reappearance from Obscurity: Mammalian Rad52 in Homologous Recombination.Genes (Basel). 2016 Sep 14;7(9):63. doi: 10.3390/genes7090063. Genes (Basel). 2016. PMID: 27649245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
An integrative structural study of the human full-length RAD52 at 2.2 Å resolution.Commun Biol. 2024 Aug 8;7(1):956. doi: 10.1038/s42003-024-06644-1. Commun Biol. 2024. PMID: 39112549 Free PMC article.
-
New Horizons of Synthetic Lethality in Cancer: Current Development and Future Perspectives.J Med Chem. 2024 Jul 25;67(14):11488-11521. doi: 10.1021/acs.jmedchem.4c00113. Epub 2024 Jul 2. J Med Chem. 2024. PMID: 38955347 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Rijkers T., Van Den Ouweland J., Morolli B., Rolink A.G., Baarends W.M., Van Sloun P.P., Lohman P.H., Pastink A. Targeted inactivation of mouse RAD52 reduces homologous recombination but not resistance to ionizing radiation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 1998;18:6423–6429. doi: 10.1128/MCB.18.11.6423. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

