An All-in-One Tool for 2D Atherosclerotic Disease Assessment and 3D Coronary Artery Reconstruction
- PMID: 36975894
- PMCID: PMC10056488
- DOI: 10.3390/jcdd10030130
An All-in-One Tool for 2D Atherosclerotic Disease Assessment and 3D Coronary Artery Reconstruction
Abstract
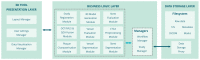
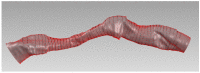
Diagnosis of coronary artery disease is mainly based on invasive imaging modalities such as X-ray angiography, intravascular ultrasound (IVUS) and optical coherence tomography (OCT). Computed tomography coronary angiography (CTCA) is also used as a non-invasive imaging alternative. In this work, we present a novel and unique tool for 3D coronary artery reconstruction and plaque characterization using the abovementioned imaging modalities or their combination. In particular, image processing and deep learning algorithms were employed and validated for the lumen and adventitia borders and plaque characterization at the IVUS and OCT frames. Strut detection is also achieved from the OCT images. Quantitative analysis of the X-ray angiography enables the 3D reconstruction of the lumen geometry and arterial centerline extraction. The fusion of the generated centerline with the results of the OCT or IVUS analysis enables hybrid coronary artery 3D reconstruction, including the plaques and the stent geometry. CTCA image processing using a 3D level set approach allows the reconstruction of the coronary arterial tree, the calcified and non-calcified plaques as well as the detection of the stent location. The modules of the tool were evaluated for efficiency with over 90% agreement of the 3D models with the manual annotations, while a usability assessment using external evaluators demonstrated high usability resulting in a mean System Usability Scale (SUS) score equal to 0.89, classifying the tool as "excellent".
Keywords: 3D reconstruction; CTCA; IVUS analysis; OCT analysis; coronary artery disease (CAD).
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

Similar articles
-
A three-dimensional quantification of calcified and non-calcified plaques in coronary arteries based on computed tomography coronary angiography images: Comparison with expert's annotations and virtual histology intravascular ultrasound.Comput Biol Med. 2019 Oct;113:103409. doi: 10.1016/j.compbiomed.2019.103409. Epub 2019 Aug 27. Comput Biol Med. 2019. PMID: 31480007
-
In vivo comparison of arterial lumen dimensions assessed by co-registered three-dimensional (3D) quantitative coronary angiography, intravascular ultrasound and optical coherence tomography.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012 Aug;28(6):1315-27. doi: 10.1007/s10554-012-0016-6. Epub 2012 Jan 20. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2012. PMID: 22261998 Free PMC article.
-
Automatic quantification and characterization of coronary atherosclerosis with computed tomography coronary angiography: cross-correlation with intravascular ultrasound virtual histology.Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013 Jun;29(5):1177-90. doi: 10.1007/s10554-013-0194-x. Epub 2013 Feb 16. Int J Cardiovasc Imaging. 2013. PMID: 23417447
-
[New methods of coronary imaging II. Intracoronary ultrasonography in clinical practice].Ital Heart J Suppl. 2001 Jun;2(6):579-92. Ital Heart J Suppl. 2001. PMID: 11460831 Review. Italian.
-
The diagnostic value of intracoronary optical coherence tomography.Herz. 2011 Aug;36(5):417-29. doi: 10.1007/s00059-011-3487-7. Herz. 2011. PMID: 21744151 Review.
References
-
- Sakellarios A.I., Rigas G., Kigka V., Siogkas P., Tsompou P., Karanasiou G., Exarchos T., Andrikos I., Tachos N., Pelosi G., et al. SMARTool: A Tool for Clinical Decision Support for the Management of Patients with Coronary Artery Disease Based on Modeling of Atherosclerotic Plaque Process; Proceedings of the 2017 39th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC); Jeju Island, South Korea. 11–15 July 2017; pp. 96–99. - PubMed
-
- Frangi A.F., Niessen W.J., Vincken K.L., Viergever M.A. Multiscale Vessel Enhancement Filtering. Volume 1496. Springer; Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany: 1998. pp. 130–137. - DOI
-
- Dicom.Offis.de-DICOM Software Made by OFFIS-DCMTK-DICOM Toolkit. OFFIS: Oldenburg, Germany. [(accessed on 18 May 2021)]. Available online: https://dicom.offis.de/dcmtk.php.en.
-
- Emgu CV: OpenCV in. NET (C#, VB, C++ and More) [(accessed on 18 May 2021)]. Available online: https://www.emgu.com/wiki/index.php/Main_Page.
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

