Carcinogenic Effects of Areca Nut and Its Metabolites: A Review of the Experimental Evidence
- PMID: 36961055
- PMCID: PMC10037666
- DOI: 10.3390/clinpract13020030
Carcinogenic Effects of Areca Nut and Its Metabolites: A Review of the Experimental Evidence
Abstract
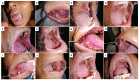
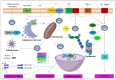
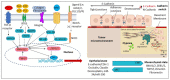
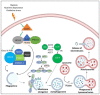
Oral cancers (OC) are among the most frequent malignancies encountered in Southeast Asia, primarily due to the prevalent habit of betel quid (BQ) and smokeless tobacco use in this region. Areca nut (AN), the primary ingredient in BQ, contains several alkaloids, including arecoline, arecaidine, guvacoline, and guvacine. These have been associated with both the AN abuse liability and carcinogenicity. Additionally, variations in AN alkaloid levels could lead to differences in the addictiveness and carcinogenic potential across various AN-containing products. Recent studies based on animal models and in vitro experiments show cellular and molecular effects induced by AN. These comprise promoting epithelial-mesenchymal transition, autophagy initiation, tissue hypoxia, genotoxicity, cytotoxicity, and cell death. Further, clinical research endorses these undesired harmful effects in humans. Oral submucosal fibrosis, a potentially malignant disease of the oral cavity, is predominantly reported from the geographical areas of the globe where AN is habitually chewed. OC in chronic AN users presents a more aggressive phenotype, such as resistance to anti-cancer drugs. The available evidence on the carcinogenicity of AN based on the findings reported in the recently published experimental studies is discussed in the present review.
Keywords: areca nut; carcinogenicity; cytotoxicity; genotoxicity; in vivo and in vitro studies; oral cancer.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Analysis of Alkaloids in Areca Nut-Containing Products by Liquid Chromatography-Tandem Mass Spectrometry.J Agric Food Chem. 2017 Mar 8;65(9):1977-1983. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.6b05140. Epub 2017 Feb 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2017. PMID: 28190359 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Mechanisms of Malignant Transformation of Oral Submucous Fibrosis by Different Betel Quid Constituents-Does Fibroblast Senescence Play a Role?Int J Mol Sci. 2022 Jan 31;23(3):1637. doi: 10.3390/ijms23031637. Int J Mol Sci. 2022. PMID: 35163557 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Role of areca nut in betel quid-associated chemical carcinogenesis: current awareness and future perspectives.Oral Oncol. 2001 Sep;37(6):477-92. doi: 10.1016/s1368-8375(01)00003-3. Oral Oncol. 2001. PMID: 11435174 Review.
-
Metabolism of the areca alkaloids - toxic and psychoactive constituents of the areca (betel) nut.Drug Metab Rev. 2022 Nov;54(4):343-360. doi: 10.1080/03602532.2022.2075010. Epub 2022 May 29. Drug Metab Rev. 2022. PMID: 35543097 Review.
-
Rapid green analytical methodology for simultaneous biomonitoring of five toxic areca nut alkaloids using UHPLC-MS/MS for predicting health hazardous risks.J Hazard Mater. 2022 Jan 15;422:126923. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126923. Epub 2021 Aug 17. J Hazard Mater. 2022. PMID: 34449334
Cited by
-
Proliferative verrucous leukoplakia/multifocal leukoplakia in patients with and without oral submucous fibrosis.Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2024 Jan 1;29(1):e119-e127. doi: 10.4317/medoral.26106. Med Oral Patol Oral Cir Bucal. 2024. PMID: 37992140 Free PMC article.
-
Bioactive Components of Areca Nut: An Overview of Their Positive Impacts Targeting Different Organs.Nutrients. 2024 Feb 29;16(5):695. doi: 10.3390/nu16050695. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 38474823 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Molecular Targets of Plant-Derived Bioactive Compounds in Oral Squamous Cell Carcinoma.Cancers (Basel). 2024 Oct 26;16(21):3612. doi: 10.3390/cancers16213612. Cancers (Basel). 2024. PMID: 39518052 Free PMC article. Review.
-
TUSC3, p53 and p21 genetic association with development of oral submucous fibrosis and oral squamous cell carcinoma among addictive tobacco chewers of Pakistan.BMC Oral Health. 2024 Jul 11;24(1):780. doi: 10.1186/s12903-024-04501-5. BMC Oral Health. 2024. PMID: 38992585 Free PMC article.
-
Biological Effects and Biomedical Applications of Areca Nut and Its Extract.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Feb 8;17(2):228. doi: 10.3390/ph17020228. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38399443 Free PMC article. Review.
References
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

