ClpC2 protects mycobacteria against a natural antibiotic targeting ClpC1-dependent protein degradation
- PMID: 36944713
- PMCID: PMC10030653
- DOI: 10.1038/s42003-023-04658-9
ClpC2 protects mycobacteria against a natural antibiotic targeting ClpC1-dependent protein degradation
Abstract
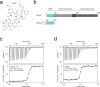
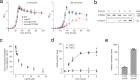
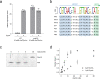
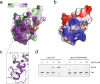
Mycobacterium tuberculosis Clp proteases are targeted by several antitubercular compounds, including cyclomarin A (CymA). CymA exerts its toxicity by binding to AAA + chaperone ClpC1. Here, we show that CymA can also bind a partial homologue of ClpC1, known as ClpC2, and we reveal the molecular basis of these interactions by determining the structure of the M. tuberculosis ClpC2:CymA complex. Furthermore, we show deletion of clpC2 in Mycobacterium smegmatis increases sensitivity to CymA. We find CymA exposure leads to a considerable upregulation of ClpC2 via a mechanism in which binding of CymA to ClpC2 prevents binding of ClpC2 to its own promoter, resulting in upregulation of its own transcription in response to CymA. Our study reveals that ClpC2 not only senses CymA, but that through this interaction it can act as a molecular sponge to counteract the toxic effects of CymA and possibly other toxins targeting essential protease component ClpC1 in mycobacteria.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Structural basis of mycobacterial inhibition by cyclomarin A.J Biol Chem. 2013 Oct 25;288(43):30883-91. doi: 10.1074/jbc.M113.493767. Epub 2013 Sep 10. J Biol Chem. 2013. PMID: 24022489 Free PMC article.
-
Clp-targeting BacPROTACs impair mycobacterial proteostasis and survival.Cell. 2023 May 11;186(10):2176-2192.e22. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2023.04.009. Epub 2023 May 2. Cell. 2023. PMID: 37137307
-
Mutant noxy8 exposes functional specificities between the chloroplast chaperones CLPC1 and CLPC2 in the response to organelle stress and plant defence.Plant Cell Environ. 2024 Jul;47(7):2336-2350. doi: 10.1111/pce.14882. Epub 2024 Mar 18. Plant Cell Environ. 2024. PMID: 38500380
-
Anti-tuberculosis lead molecules from natural products targeting Mycobacterium tuberculosis ClpC1.J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016 Mar;43(2-3):205-12. doi: 10.1007/s10295-015-1709-3. Epub 2015 Nov 19. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol. 2016. PMID: 26586403 Review.
-
Chaperone-protease systems in regulation and protein quality control in Bacillus subtilis.Res Microbiol. 2009 Nov;160(9):637-44. doi: 10.1016/j.resmic.2009.08.020. Epub 2009 Sep 23. Res Microbiol. 2009. PMID: 19781636 Review.
Cited by
-
Protein quality control: from molecular mechanisms to therapeutic intervention-EMBO workshop, May 21-26 2023, Srebreno, Croatia.Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023 Nov;28(6):631-640. doi: 10.1007/s12192-023-01383-4. Epub 2023 Sep 20. Cell Stress Chaperones. 2023. PMID: 37731161 Free PMC article. Review.
-
BacPROTACs targeting Clp protease: a promising strategy for anti-mycobacterial drug discovery.Front Chem. 2024 Jan 31;12:1358539. doi: 10.3389/fchem.2024.1358539. eCollection 2024. Front Chem. 2024. PMID: 38357296 Free PMC article.
-
ApoE Mimetic Peptide COG1410 Kills Mycobacterium smegmatis via Directly Interfering ClpC's ATPase Activity.Antibiotics (Basel). 2024 Mar 19;13(3):278. doi: 10.3390/antibiotics13030278. Antibiotics (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38534713 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

