A novel fluorogenic reporter substrate for 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma-2 (PLCγ2): Application to high-throughput screening for activators to treat Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36933698
- PMCID: PMC10251139
- DOI: 10.1016/j.slasd.2023.03.003
A novel fluorogenic reporter substrate for 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma-2 (PLCγ2): Application to high-throughput screening for activators to treat Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
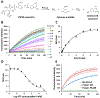
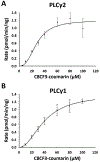
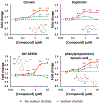
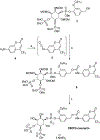
A rare coding variant in PLCγ2 (P522R) expressed in microglia induces a mild activation of enzymatic activity when compared to wild-type. This mutation is reported to be protective against the cognitive decline associated with late-onset Alzheimer's disease (LOAD) and therefore, activation of wild-type PLCγ2 has been suggested as a potential therapeutic target for the prevention and treatment of LOAD. Additionally, PLCγ2 has been associated with other diseases such as cancer and some autoimmune disorders where mutations with much greater increases in PLCγ2 activity have been identified. Here, pharmacological inhibition may provide a therapeutic effect. In order to facilitate our investigation of the activity of PLCγ2, we developed an optimized fluorogenic substrate to monitor enzymatic activity in aqueous solution. This was accomplished by first exploring the spectral properties of various "turn-on" fluorophores. The most promising turn-on fluorophore was incorporated into a water-soluble PLCγ2 reporter substrate, which we named C8CF3-coumarin. The ability of PLCγ2 to enzymatically process C8CF3-coumarin was confirmed, and the kinetics of the reaction were determined. Reaction conditions were optimized to identify small molecule activators, and a pilot screen of the Library of Pharmacologically Active Compounds 1280 (LOPAC1280) was performed with the goal of identifying small molecule activators of PLCγ2. The optimized screening conditions allowed identification of potential PLCγ2 activators and inhibitors, thus demonstrating the feasibility of this approach for high-throughput screening.
Keywords: Alzheimer's disease; C8CF3-coumarin; High throughput screening; PLCG2; Phospholipase C; Turn-on fluorophore.
Copyright © 2023 The Author(s). Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interest The authors declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures
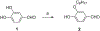
Similar articles
-
A novel micellular fluorogenic substrate for quantitating the activity of 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma (PLCγ) enzymes.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 29;19(3):e0299541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299541. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38551930 Free PMC article.
-
The Alzheimer's disease-associated protective Plcγ2-P522R variant promotes immune functions.Mol Neurodegener. 2020 Sep 11;15(1):52. doi: 10.1186/s13024-020-00402-7. Mol Neurodegener. 2020. PMID: 32917267 Free PMC article.
-
Alzheimer's disease phospholipase C-gamma-2 (PLCG2) protective variant is a functional hypermorph.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019 Feb 2;11(1):16. doi: 10.1186/s13195-019-0469-0. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2019. PMID: 30711010 Free PMC article.
-
Characterisation of molecular mechanisms for PLCγ2 disease-linked variants.Adv Biol Regul. 2024 Sep 19;94:101053. doi: 10.1016/j.jbior.2024.101053. Online ahead of print. Adv Biol Regul. 2024. PMID: 39313402 Review.
-
PLCγ2 impacts microglia-related effectors revealing variants and pathways important in Alzheimer's disease.Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022 Sep 6;10:999061. doi: 10.3389/fcell.2022.999061. eCollection 2022. Front Cell Dev Biol. 2022. PMID: 36147734 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
A novel micellular fluorogenic substrate for quantitating the activity of 1-phosphatidylinositol 4,5-bisphosphate phosphodiesterase gamma (PLCγ) enzymes.PLoS One. 2024 Mar 29;19(3):e0299541. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0299541. eCollection 2024. PLoS One. 2024. PMID: 38551930 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

