Cell cycle regulation for meiosis in mammalian germ cells
- PMID: 36927827
- PMCID: PMC10267585
- DOI: 10.1262/jrd.2023-010
Cell cycle regulation for meiosis in mammalian germ cells
Abstract
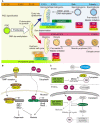
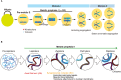
In mouse fetal gonads, germ cell development is accompanied by changes in cell cycle mode in response to external signals and intrinsic mechanisms of cells. During fetal development, male germ cells undergo G0/G1 arrest, while female germ cells exit the mitotic cell cycle and enter meiosis. In fetal testes, NANOS2 and CYP26B1 force germ cells to stay in G0/G1 arrest phase, preventing them from entering the meiotic cell cycle. In the fetal ovary, external signals, such as RA, BMP, and WNT, promote the competency of female germ cells to enter the meiotic cell cycle. MEIOSIN and STRA8 ensure the establishment of the meiotic cell cycle by activating meiotic genes, such that meiotic entry coincides with the S phase. This review discusses germ cell development from the viewpoint of cell cycle regulation and highlights the mechanism of the entry of germ cells into meiosis.
Keywords: Cell cycle; Germ cell; MEIOSIN; Meiosis; STRA8.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Retinoic Acid signalling and the control of meiotic entry in the human fetal gonad.PLoS One. 2011;6(6):e20249. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0020249. Epub 2011 Jun 3. PLoS One. 2011. PMID: 21674038 Free PMC article.
-
Cyp26b1 expression in murine Sertoli cells is required to maintain male germ cells in an undifferentiated state during embryogenesis.PLoS One. 2009 Oct 19;4(10):e7501. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0007501. PLoS One. 2009. PMID: 19838304 Free PMC article.
-
CYP26B1 promotes male germ cell differentiation by suppressing STRA8-dependent meiotic and STRA8-independent mitotic pathways.Dev Biol. 2014 May 15;389(2):173-81. doi: 10.1016/j.ydbio.2014.02.013. Epub 2014 Feb 24. Dev Biol. 2014. PMID: 24576537
-
Mechanism of initiation of meiosis in mouse germ cells.Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023;151:1-26. doi: 10.1016/bs.ctdb.2022.04.005. Epub 2022 Jun 3. Curr Top Dev Biol. 2023. PMID: 36681467 Review.
-
Control of mammalian germ cell entry into meiosis.Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014 Jan 25;382(1):488-497. doi: 10.1016/j.mce.2013.09.026. Epub 2013 Sep 27. Mol Cell Endocrinol. 2014. PMID: 24076097 Review.
Cited by
-
A novel tumor-derived exosomal gene signature predicts prognosis in patients with pancreatic cancer.Transl Cancer Res. 2024 Aug 31;13(8):4324-4340. doi: 10.21037/tcr-23-2354. Epub 2024 Aug 26. Transl Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39262474 Free PMC article.
-
Histone demethylase KDM2A recruits HCFC1 and E2F1 to orchestrate male germ cell meiotic entry and progression.EMBO J. 2024 Oct;43(19):4197-4227. doi: 10.1038/s44318-024-00203-4. Epub 2024 Aug 19. EMBO J. 2024. PMID: 39160277 Free PMC article.
-
DNA methylation in mammalian development and disease.Nat Rev Genet. 2025 Jan;26(1):7-30. doi: 10.1038/s41576-024-00760-8. Epub 2024 Aug 12. Nat Rev Genet. 2025. PMID: 39134824 Review.
-
MAX controls meiotic entry in sexually undifferentiated germ cells.Sci Rep. 2024 Mar 4;14(1):5236. doi: 10.1038/s41598-024-55506-7. Sci Rep. 2024. PMID: 38433229 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Ginsburg M, Snow MH, McLaren A. Primordial germ cells in the mouse embryo during gastrulation. Development 1990; 110: 521–528. - PubMed
-
- Tam PP, Snow MH. Proliferation and migration of primordial germ cells during compensatory growth in mouse embryos. J Embryol Exp Morphol 1981; 64: 133–147. - PubMed
-
- Bowles J, Knight D, Smith C, Wilhelm D, Richman J, Mamiya S, Yashiro K, Chawengsaksophak K, Wilson MJ, Rossant J, Hamada H, Koopman P. Retinoid signaling determines germ cell fate in mice. Science 2006; 312: 596–600. - PubMed

