Ebselen oxide and derivatives are new allosteric HER2 inhibitors for HER2-positive cancers
- PMID: 36912768
- PMCID: PMC10552892
- DOI: 10.1002/1878-0261.13419
Ebselen oxide and derivatives are new allosteric HER2 inhibitors for HER2-positive cancers
Abstract
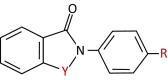
Human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (ErbB2/HER2) is a tyrosine kinase receptor that is overexpressed in 25% of primary human breast cancers, as well as in multiple other cancers. HER2-targeted therapies improved progression-free and overall survival in patients with HER2+ breast cancers. However, associated resistance mechanisms and toxicity highlight the need for new therapeutic approaches for these cancers. We recently established that, in normal cells, HER2 is stabilized in a catalytically repressed state by direct interaction with members of the ezrin/radixin/moesin (ERM) family. In HER2-overexpressing tumors, the low expression of moesin contributes to the aberrant activation of HER2. Through a screen designed to find moesin-mimicking compounds, we identified ebselen oxide. We show that ebselen oxide, and some derivatives, conferred an efficient allosteric inhibition of overexpressed HER2, as well as mutated and truncated oncogenic forms of HER2, which are resistant to current therapies. Ebselen oxide selectively inhibited anchorage-dependent and -independent proliferation of HER2+ cancer cells and showed a significant benefit in combination with current anti-HER2 therapeutic agents. Finally, ebselen oxide significantly blocked HER2+ breast tumor progression in vivo. Collectively, these data provide evidence that ebselen oxide is a newly identified allosteric inhibitor of HER2 to be considered for therapeutic intervention on HER2+ cancers.
Keywords: HER2 tyrosine kinase receptor; additive effects; breast cancer; resistance; small molecule inhibitor; targeted therapy.
© 2023 The Authors. Molecular Oncology published by John Wiley & Sons Ltd on behalf of Federation of European Biochemical Societies.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Allosteric Inhibition of HER2 by Moesin-Mimicking Compounds Targets HER2-Positive Cancers and Brain Metastases.Cancer Res. 2021 Nov 1;81(21):5464-5476. doi: 10.1158/0008-5472.CAN-21-0162. Epub 2021 Sep 7. Cancer Res. 2021. PMID: 34493594
-
A class I histone deacetylase inhibitor, entinostat, enhances lapatinib efficacy in HER2-overexpressing breast cancer cells through FOXO3-mediated Bim1 expression.Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014 Jul;146(2):259-72. doi: 10.1007/s10549-014-3014-7. Epub 2014 Jun 12. Breast Cancer Res Treat. 2014. PMID: 24916181 Free PMC article.
-
PTK6 inhibition promotes apoptosis of Lapatinib-resistant Her2(+) breast cancer cells by inducing Bim.Breast Cancer Res. 2015 Jun 19;17(1):86. doi: 10.1186/s13058-015-0594-z. Breast Cancer Res. 2015. PMID: 26084280 Free PMC article.
-
Lapatinib.Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018;211:19-44. doi: 10.1007/978-3-319-91442-8_2. Recent Results Cancer Res. 2018. PMID: 30069757 Review.
-
Acquired resistance to small molecule ErbB2 tyrosine kinase inhibitors.Clin Cancer Res. 2008 Nov 1;14(21):6730-4. doi: 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-08-0581. Clin Cancer Res. 2008. PMID: 18980964 Review.
Cited by
-
Therapeutic Opportunities in Breast Cancer by Targeting Macrophage Migration Inhibitory Factor as a Pleiotropic Cytokine.Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2024 Sep 6;18:11782234241276310. doi: 10.1177/11782234241276310. eCollection 2024. Breast Cancer (Auckl). 2024. PMID: 39246383 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Chumsri S, Sperinde J, Liu H, Gligorov J, Spano JP, Antoine M, et al. High p95HER2/HER2 ratio associated with poor outcome in trastuzumab‐treated HER2‐positive metastatic breast cancer NCCTG N0337 and NCCTG 98–32‐52 (alliance). Clin Cancer Res. 2018;24:3053–8. 10.1158/1078-0432.CCR-17-1864 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Saez R, Molina MA, Ramsey EE, Rojo F, Keenan EJ, Albanell J, et al. p95HER‐2 predicts worse outcome in patients with HER‐2‐positive breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12:424–31. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

