Design Considerations, Formulation Approaches, and Strategic Advances of Hydrogel Dressings for Chronic Wound Management
- PMID: 36910992
- PMCID: PMC9996804
- DOI: 10.1021/acsomega.2c06806
Design Considerations, Formulation Approaches, and Strategic Advances of Hydrogel Dressings for Chronic Wound Management
Abstract
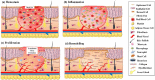
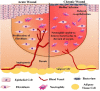
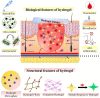
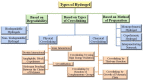
Wound healing is a complex and dynamic physiological process consisting of a series of cellular and molecular events that initiate immediately after a tissue lesion, to reconstruct the skin layer. It is indubitable that patients with chronic wounds, severely infected wounds, or any metabolic disorder of the wound microenvironment always endure severe pain and discomfort that affect their quality of life. It is essential to treat chronic wounds for conserving the physical as well as mental well-being of affected patients and for convalescing to improve their quality of life. For supporting and augmenting the healing process, the selection of pertinent wound dressing is essential. A substantial reduction in healing duration, disability, associated cost, and risk of recurrent infections can be achieved via engineering wound dressings. Hydrogels play a leading role in the path of engineering ideal wound dressings. Hydrogels, comprising water to a large extent, providing a moist environment, being comfortable to patients, and having biocompatible and biodegradable properties, have found their success as suitable wound dressings in the market. The exploitation of hydrogels is increasing perpetually after substantiation of their broader therapeutic actions owing to their resemblance to dermal tissues, their capability to stimulate partial skin regeneration, and their ability to incorporate therapeutic moieties promoting wound healing. This review entails properties of hydrogel supporting wound healing, types of hydrogels, cross-linking mechanisms, design considerations, and formulation strategies of hydrogel engineering. Various categories of hydrogel wound dressing fabricated recently are discussed based on their gel network composition, degradability, and physical and chemical cross-linking mechanisms, which provide an outlook regarding the importance of tailoring the physicochemical properties of hydrogels. The examples of marketed hydrogel wound dressings are also incorporated along with the future perspectives and challenges associated with them.
© 2023 The Authors. Published by American Chemical Society.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Design Considerations for Hydrogel Wound Dressings: Strategic and Molecular Advances.Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020 Jun;26(3):230-248. doi: 10.1089/ten.TEB.2019.0281. Epub 2020 Feb 28. Tissue Eng Part B Rev. 2020. PMID: 31928151 Review.
-
Polysaccharide-Based Hydrogels for Wound Dressing: Design Considerations and Clinical Applications.Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022 Mar 7;10:845735. doi: 10.3389/fbioe.2022.845735. eCollection 2022. Front Bioeng Biotechnol. 2022. PMID: 35321022 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hydrogel Dressings for Advanced Wound Management.Curr Med Chem. 2018;25(41):5782-5797. doi: 10.2174/0929867324666170920161246. Curr Med Chem. 2018. PMID: 28933299 Review.
-
Research progress related to thermosensitive hydrogel dressings in wound healing: a review.Nanoscale Adv. 2023 Oct 26;5(22):6017-6037. doi: 10.1039/d3na00407d. eCollection 2023 Nov 7. Nanoscale Adv. 2023. PMID: 37941954 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Pullulan-Based Hydrogels in Wound Healing and Skin Tissue Engineering Applications: A Review.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Mar 4;24(5):4962. doi: 10.3390/ijms24054962. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 36902394 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Composite Hydrogels of Ultrasound-Assisted-Digested Formic Acid-Decellularized Extracellular Matrix and Sacchachitin Nanofibers Incorporated with Platelet-Rich Plasma for Diabetic Wound Treatment.J Funct Biomater. 2023 Aug 11;14(8):423. doi: 10.3390/jfb14080423. J Funct Biomater. 2023. PMID: 37623667 Free PMC article.
-
In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of Chitosan/HPMC/Insulin Hydrogel for Wound Healing Applications.Bioengineering (Basel). 2024 Feb 9;11(2):168. doi: 10.3390/bioengineering11020168. Bioengineering (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38391653 Free PMC article.
-
Unveiling the antimicrobial, antivirulence, and wound-healing accelerating potentials of resveratrol against carbapenem-resistant Pseudomonas aeruginosa (CRPA)-septic wound in a murine model.Inflammopharmacology. 2024 Nov 7. doi: 10.1007/s10787-024-01591-z. Online ahead of print. Inflammopharmacology. 2024. PMID: 39508957
-
Insights into Translational and Biomedical Applications of Hydrogels as Versatile Drug Delivery Systems.AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024 Jan 22;25(1):17. doi: 10.1208/s12249-024-02731-y. AAPS PharmSciTech. 2024. PMID: 38253917 Review.
-
Characterization, Biocompatibility and Antioxidant Activity of Hydrogels Containing Propolis Extract as an Alternative Treatment in Wound Healing.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 30;17(5):575. doi: 10.3390/ph17050575. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38794145 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Zeng D.; Shen S.; Fan D. Molecular design, synthesis strategies and recent advances of hydrogels for wound dressing applications. Chinese J. Chem. Eng. 2021, 30, 308–20. 10.1016/j.cjche.2020.12.005. - DOI
-
- Kurakula M.; Rao G. K.; Kiran V.; Hasnain M. S.; Nayak A. K. Alginate-based hydrogel systems for drug releasing in wound healing. Alginates Drug Delivery 2020, 323–358. 10.1016/B978-0-12-817640-5.00013-3. - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

