New Type of Tannins Identified from the Seeds of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS
- PMID: 36903273
- PMCID: PMC10004147
- DOI: 10.3390/molecules28052027
New Type of Tannins Identified from the Seeds of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. by HPLC-ESI-MS/MS
Abstract
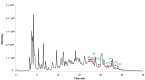
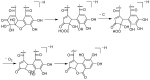
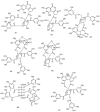
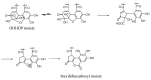
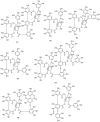
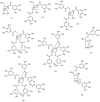
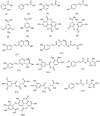
There is a lack of information on the compound profile of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. seeds. This greatly affects their optimal utilization. In our preliminary study, we found that the extract of the seeds displayed a strong positive reaction to the FeCl3 solution, indicating the presence of polyphenols. However, to date, only nine polyphenols have been isolated. In this study, HPLC-ESI-MS/MS was employed to fully reveal the polyphenol profile of the seed extracts. A total of 90 polyphenols were identified. They were classified into nine brevifolincarboxyl tannins and their derivatives, 34 ellagitannins, 21 gallotannins, and 26 phenolic acids and their derivatives. Most of these were first identified from the seeds of C. officinalis. More importantly, five new types of tannins were reported for the first time: brevifolincarboxyl-trigalloyl-hexoside, digalloyl-dehydrohexahydroxydiphenoyl (DHHDP)-hexdside, galloyl-DHHDP-hexoside, DHHDP-hexahydroxydiphenoyl(HHDP)-galloyl-gluconic acid, and peroxide product of DHHDP-trigalloylhexoside. Moreover, the total phenolic content was as high as 79,157 ± 563 mg gallic acid equivalent per 100 g in the seeds extract. The results of this study not only enrich the structure database of tannins, but also provide invaluable aid to its further utilization in industries.
Keywords: Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc.; mass spectrometry; polyphenol; seed extract; tannin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures

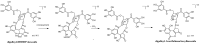

Similar articles
-
[Function of getting rid of cores of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc. and studies on method of processing in producing area].Zhong Yao Cai. 2006 Jan;29(1):60-3. Zhong Yao Cai. 2006. PMID: 16722322 Chinese.
-
Acid hydrolysis of crude tannins from infructescence of Platycarya strobilacea Sieb. et Zucc to produce ellagic acid.Nat Prod Res. 2014;28(19):1637-40. doi: 10.1080/14786419.2014.923998. Epub 2014 Jun 9. Nat Prod Res. 2014. PMID: 24911045
-
[Constituents of the leaves of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc.].Ceska Slov Farm. 2016 Fall;65(4):128-131. Ceska Slov Farm. 2016. PMID: 27860471 Czech.
-
Two-Dimensional Tannin Fingerprints by Liquid Chromatography Tandem Mass Spectrometry Offer a New Dimension to Plant Tannin Analyses and Help To Visualize the Tannin Diversity in Plants.J Agric Food Chem. 2018 Sep 5;66(35):9162-9171. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.8b02115. Epub 2018 Aug 23. J Agric Food Chem. 2018. PMID: 30136834 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology of Cornus officinalis Sieb. et Zucc.J Ethnopharmacol. 2018 Mar 1;213:280-301. doi: 10.1016/j.jep.2017.11.010. Epub 2017 Nov 17. J Ethnopharmacol. 2018. PMID: 29155174 Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

