Trans-species microRNA loci in the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris have a U6-like snRNA promoter
- PMID: 36896651
- PMCID: PMC10226579
- DOI: 10.1093/plcell/koad076
Trans-species microRNA loci in the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris have a U6-like snRNA promoter
Erratum in
-
Correction to: Trans-species microRNA loci in the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris have a U6-like snRNA promoter.Plant Cell. 2024 Feb 26;36(3):791. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad305. Plant Cell. 2024. PMID: 38108657 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
Small regulatory RNAs can move between organisms and regulate gene expression in the recipient. Whether the trans-species small RNAs being exported are distinguished from the normal endogenous small RNAs of the source organism is not known. The parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris (dodder) produces many microRNAs that specifically accumulate at the host-parasite interface, several of which have trans-species activity. We found that induction of C. campestris interface-induced microRNAs is similar regardless of host species and occurs in C. campestris haustoria produced in the absence of any host. The loci-encoding C. campestris interface-induced microRNAs are distinguished by a common cis-regulatory element. This element is identical to a conserved upstream sequence element (USE) used by plant small nuclear RNA loci. The properties of the interface-induced microRNA primary transcripts strongly suggest that they are produced via U6-like transcription by RNA polymerase III. The USE promotes accumulation of interface-induced miRNAs (IIMs) in a heterologous system. This promoter element distinguishes C. campestris IIM loci from other plant small RNAs. Our data suggest that C. campestris IIMs are produced in a manner distinct from canonical miRNAs. All confirmed C. campestris microRNAs with documented trans-species activity are interface-induced and possess these features. We speculate that RNA polymerase III transcription of IIMs may allow these miRNAs to be exported to hosts.
© American Society of Plant Biologists 2023. All rights reserved. For permissions, please e-mail: journals.permissions@oup.com.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement: S.M. and S.G. were employees of New England Biolabs, Inc. New England Biolabs is a manufacturer and vendor of molecular biology reagents, including several enzymes and buffers used in this study. This affiliation does not affect the authors’ impartiality, adherence to journal standards and policies, or availability of data. C.H., J.H., and M.J.A. declare no conflicts of interest.
Figures
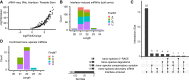
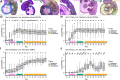
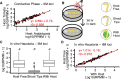
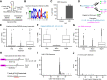
Comment in
-
A host of messages: trans-species micro-RNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris share a common promoter.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1619-1620. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad081. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36929910 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Similar articles
-
A host of messages: trans-species micro-RNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris share a common promoter.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1619-1620. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad081. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36929910 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
MicroRNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris target host messenger RNAs.Nature. 2018 Jan 3;553(7686):82-85. doi: 10.1038/nature25027. Nature. 2018. PMID: 29300014
-
Arabinogalactan Proteins Accumulate in the Cell Walls of Searching Hyphae of the Stem Parasitic Plants, Cuscuta campestris and Cuscuta japonica.Plant Cell Physiol. 2017 Nov 1;58(11):1868-1877. doi: 10.1093/pcp/pcx121. Plant Cell Physiol. 2017. PMID: 29016904
-
Small RNA warfare: exploring origins and function of trans-species microRNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta.Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019 Aug;50:76-81. doi: 10.1016/j.pbi.2019.03.014. Epub 2019 Apr 28. Curr Opin Plant Biol. 2019. PMID: 31029811 Review.
-
RNA mobility in parasitic plant - host interactions.RNA Biol. 2017 Apr 3;14(4):450-455. doi: 10.1080/15476286.2017.1291482. Epub 2017 Feb 14. RNA Biol. 2017. PMID: 28277936 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Focus on RNA biology.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1617-1618. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad082. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36943779 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
-
The role of small RNAs in resistant melon cultivar against Phelipanche aegyptiaca parasitization.Front Microbiol. 2024 May 7;15:1408926. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1408926. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38774502 Free PMC article.
-
Insights into Mobile Small-RNAs Mediated Signaling in Plants.Plants (Basel). 2022 Nov 18;11(22):3155. doi: 10.3390/plants11223155. Plants (Basel). 2022. PMID: 36432884 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The Non-Coding RNA Journal Club: Highlights on Recent Papers-13.Noncoding RNA. 2023 Dec 14;9(6):76. doi: 10.3390/ncrna9060076. Noncoding RNA. 2023. PMID: 38133210 Free PMC article.
-
A host of messages: trans-species micro-RNAs from the parasitic plant Cuscuta campestris share a common promoter.Plant Cell. 2023 May 29;35(6):1619-1620. doi: 10.1093/plcell/koad081. Plant Cell. 2023. PMID: 36929910 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

