VISTA expression and patient selection for immune-based anticancer therapy
- PMID: 36891296
- PMCID: PMC9986543
- DOI: 10.3389/fimmu.2023.1086102
VISTA expression and patient selection for immune-based anticancer therapy
Abstract
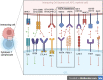
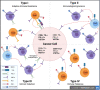
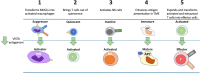
V-domain Ig suppressor of T-cell activation (VISTA) is a B7 family member that plays key roles in maintaining T cell quiescence and regulation of myeloid cell populations, which together establish it as a novel immunotherapy target for solid tumors. Here we review the growing literature on VISTA expression in relation to various malignancies to better understand the role of VISTA and its interactions with both tumor cells and immune cells expressing other checkpoint molecules within the tumor microenvironment (TME). The biology of VISTA creates several mechanisms to maintain the TME, including supporting the function of myeloid-derived suppressor cells, regulating natural killer cell activation, supporting the survival of regulatory T cells, limiting antigen presentation on antigen-presenting cells and maintaining T cells in a quiescent state. Understanding these mechanisms is an important foundation of rational patient selection for anti-VISTA therapy. We provide a general framework to describe distinct patterns of VISTA expression in correlation with other known predictive immunotherapy biomarkers (programmed cell death ligand 1 and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes) across solid tumors to facilitate investigation of the most efficacious TMEs for VISTA-targeted treatment as a single agent and/or in combination with anti-programmed death 1/anti-cytotoxic T lymphocyte antigen-4 therapies.
Keywords: VISTA; biomarkers; cancer; cancer immunotherapy; immune checkpoint; tumor immunity; tumor microenvironment.
Copyright © 2023 Martin, Molloy, Ugolkov, von Roemeling, Noelle, Lewis, Johnson, Radvanyi and Martell.
Conflict of interest statement
AM reports research support from the NIH. MM has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Curis, Inc. and for ImmuNext, and has intellectual property for VISTA antibodies. AU was employed by Curis, Inc. RR is employed by Curis, Inc. RN employed by ImmuNext, and has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Curis, Inc, and reports research support from the NIH. LL has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Curis, Inc. and has received research support from Curis, Inc; and reports additional research support from AbbVie, AstraZeneca, and Bristol Meyers Squibb, has served on a data safety monitoring board for G1 Therapeutics, and is the vice chair of the pharmacogenomics and population pharmacology committee of the Alliance for Clinical Trials in Oncology. MJ has received research support from Curis, Inc.; and reports additional research support to institution from AbbVie, Acerta, Adaptimmune, Amgen, Apexigen, Arcus Biosciences, Array BioPharma, Artios Pharma, AstraZeneca, Atreca, BeiGene, BerGenBio, BioAtla, Boehringer Ingeheim, Calithera Biosciences, Checkpoint Therapeutics, Corvus Pharmaceuticals, Cytomx, Daiichi Sankyo, Dracen Pharmaceuticals, Dynavax, Lilly, EMD Serono, Erasca, Exelixis, Fate Therapeutics, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Genocea Biosciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Gritstone Oncology, Guardant Health, Harpoon, Helsinn Healthcare, Hengrui Therapeutics, Hutchison MediPharma, IDEAYA Biosciences, IGM Biosciences, Immunocore, Incyte, Janssen, Jounce Therapeutics, Kadmon Pharmaceuticals, Loxo Oncology, Lycera, Memorial Sloan-Kettering, Merck, Merus, NeoImmune Tech, Neovia Oncology, Novartis, Numab Therapeutics, Nuvalent, OncoMed Pharmaceuticals, Pfizer, PMV Pharmaceuticals, RasCal Therapeutics, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Relay Therapeutics, Revolution Medicine, Ribon Therapeutics, Rubius Therapeutics, Sanofi, Seven and Eight Biopharmaceuticals / Birdie Biopharmaceuticals, Shattuck Labs, Silicon Therapeutics, Stem CentRx, Syndax Pharmaceuticals, Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Tarveda, TCR2 Therapeutics, Tempest Therapeutics, Tizona Therapeutics, TMUNITY Therapeutics, Turning Point Therapeutics, University of Michigan, Vyriad, WindMIL, Y-mAbs Therapeutics, Black Diamond, Carisma Therapeutics, Elicio Therapeutics, EQRx, Impact, Kartos Therapeutics, Mirati Therapeutics, Palleon Pharmaceuticals, and Rain Therapeutics, and has served as a consultant for AbbVie, Amgen, Astellas, AstraZeneca, Axelia Oncology, Black Diamond, Calithera Biosciences, Checkpoint Therapeutics, CytomX Therapeutics, Daiichi Sankyo, EcoR1, Editas Medicine, Eisai, EMD Serono, G1 Therapeutics, Genentech/Roche, Genmab, Genocea Biosciences, GlaxoSmithKline, Gritstone Oncology, Ideaya Biosciences, iTeos, Janssen, Lilly, Merck, Mirati Therapeutics, Molecular Axiom, Novartis, Oncorus, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Ribon Therapeutics, Sanofi-Aventis, Turning Point Therapeutics, and VBL Therapeutics. LR has served on advisory boards and as a consultant for Curis, Inc. RM is employed by Curis, Inc. This manuscript received medical writing support funded by Curis, Inc. The funder was not involved in the study design, collection, analysis, interpretation of data, the writing of this article or the decision to submit it for publication. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
VISTA: A Novel Checkpoint for Cancer Immunotherapy.Drug Discov Today. 2024 Jul;29(7):104045. doi: 10.1016/j.drudis.2024.104045. Epub 2024 May 24. Drug Discov Today. 2024. PMID: 38797321 Review.
-
VISTA: A Mediator of Quiescence and a Promising Target in Cancer Immunotherapy.Trends Immunol. 2021 Mar;42(3):209-227. doi: 10.1016/j.it.2020.12.008. Epub 2021 Jan 23. Trends Immunol. 2021. PMID: 33495077 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Differential contribution of three immune checkpoint (VISTA, CTLA-4, PD-1) pathways to antitumor responses against squamous cell carcinoma.Oral Oncol. 2016 Jun;57:54-60. doi: 10.1016/j.oraloncology.2016.04.005. Epub 2016 May 3. Oral Oncol. 2016. PMID: 27208845
-
VISTA immune regulatory effects in bypassing cancer immunotherapy: Updated.Life Sci. 2022 Dec 1;310:121083. doi: 10.1016/j.lfs.2022.121083. Epub 2022 Oct 17. Life Sci. 2022. PMID: 36265568 Review.
-
Hypoxia-Induced VISTA Promotes the Suppressive Function of Myeloid-Derived Suppressor Cells in the Tumor Microenvironment.Cancer Immunol Res. 2019 Jul;7(7):1079-1090. doi: 10.1158/2326-6066.CIR-18-0507. Epub 2019 May 14. Cancer Immunol Res. 2019. PMID: 31088847 Free PMC article.
Cited by
-
Mechanisms of immune checkpoint inhibitors: insights into the regulation of circular RNAS involved in cancer hallmarks.Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jan 4;15(1):3. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-06389-5. Cell Death Dis. 2024. PMID: 38177102 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Vista of the Future: Novel Immunotherapy Based on the Human V-Set Immunoregulatory Receptor for Digestive System Tumors.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Jun 9;24(12):9945. doi: 10.3390/ijms24129945. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37373091 Free PMC article. Review.
-
VISTA-mediated immune evasion in cancer.Exp Mol Med. 2024 Nov;56(11):2348-2356. doi: 10.1038/s12276-024-01336-6. Epub 2024 Nov 1. Exp Mol Med. 2024. PMID: 39482534 Free PMC article. Review.
-
The miRNA and PD-1/PD-L1 signaling axis: an arsenal of immunotherapeutic targets against lung cancer.Cell Death Discov. 2024 Sep 29;10(1):414. doi: 10.1038/s41420-024-02182-1. Cell Death Discov. 2024. PMID: 39343796 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Structure based virtual screening and molecular simulation study of FDA-approved drugs to inhibit human HDAC6 and VISTA as dual cancer immunotherapy.Sci Rep. 2023 Sep 2;13(1):14466. doi: 10.1038/s41598-023-41325-9. Sci Rep. 2023. PMID: 37660065 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Balar AV, Castellano D, O’Donnell PH, Grivas P, Vuky J, Powles T, et al. . First-line pembrolizumab in cisplatin-ineligible patients with locally advanced and unresectable or metastatic urothelial cancer (KEYNOTE-052): A multicentre, single-arm, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol (2017) 18:1483–92. doi: 10.1016/S1470-2045(17)30616-2 - DOI - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

