Study of NAD-interacting proteins highlights the extent of NAD regulatory roles in the cell and its potential as a therapeutic target
- PMID: 36880517
- PMCID: PMC10389049
- DOI: 10.1515/jib-2022-0049
Study of NAD-interacting proteins highlights the extent of NAD regulatory roles in the cell and its potential as a therapeutic target
Abstract
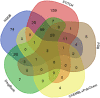
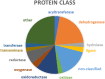
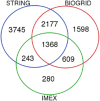
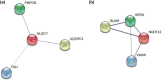
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) levels are essential for the normal physiology of the cell and are strictly regulated to prevent pathological conditions. NAD functions as a coenzyme in redox reactions, as a substrate of regulatory proteins, and as a mediator of protein-protein interactions. The main objectives of this study were to identify the NAD-binding and NAD-interacting proteins, and to uncover novel proteins and functions that could be regulated by this metabolite. It was considered if cancer-associated proteins were potential therapeutic targets. Using multiple experimental databases, we defined datasets of proteins that directly interact with NAD - the NAD-binding proteins (NADBPs) dataset - and of proteins that interact with NADBPs - the NAD-protein-protein interactions (NAD-PPIs) dataset. Pathway enrichment analysis revealed that NADBPs participate in several metabolic pathways, while NAD-PPIs are mostly involved in signalling pathways. These include disease-related pathways, namely, three major neurodegenerative disorders: Alzheimer's disease, Huntington's disease, and Parkinson's disease. Then, the complete human proteome was further analysed to select potential NADBPs. TRPC3 and isoforms of diacylglycerol (DAG) kinases, which are involved in calcium signalling, were identified as new NADBPs. Potential therapeutic targets that interact with NAD were identified, that have regulatory and signalling functions in cancer and neurodegenerative diseases.
Keywords: NAD metabolism; cancer; interactome; neurodegenerative disorders; signalling.
© 2023 the author(s), published by De Gruyter, Berlin/Boston.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Implications of NAD metabolism in pathophysiology and therapeutics for neurodegenerative diseases.Nutr Neurosci. 2021 May;24(5):371-383. doi: 10.1080/1028415X.2019.1637504. Epub 2019 Jul 7. Nutr Neurosci. 2021. PMID: 31280708 Review.
-
[Therapeutic potential of NADH: in neurodegenerative diseases characterizde by mitochondrial dysfunction].Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024 Jan;38(1):57-62. doi: 10.13201/j.issn.2096-7993.2024.01.009. Lin Chuang Er Bi Yan Hou Tou Jing Wai Ke Za Zhi. 2024. PMID: 38297850 Free PMC article. Review. Chinese.
-
NAD+ : A key metabolic regulator with great therapeutic potential.J Neuroendocrinol. 2017 Oct;29(10). doi: 10.1111/jne.12508. J Neuroendocrinol. 2017. PMID: 28718934 Review.
-
NAD metabolism and functions: a common therapeutic target for neoplastic, metabolic and neurodegenerative diseases.Curr Top Med Chem. 2013;13(23):2918-29. doi: 10.2174/15680266113136660207. Curr Top Med Chem. 2013. PMID: 24171774 Review.
-
Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide metabolism as an attractive target for drug discovery.Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007 May;11(5):695-705. doi: 10.1517/14728222.11.5.695. Expert Opin Ther Targets. 2007. PMID: 17465726 Review.
Cited by
-
Adenylyl cyclase 2 expression and function in neurological diseases.CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024 Jul;30(7):e14880. doi: 10.1111/cns.14880. CNS Neurosci Ther. 2024. PMID: 39073001 Free PMC article. Review.
-
HIV-1 Infection Reduces NAD Capping of Host Cell snRNA and snoRNA.ACS Chem Biol. 2024 Jun 21;19(6):1243-1249. doi: 10.1021/acschembio.4c00151. Epub 2024 May 15. ACS Chem Biol. 2024. PMID: 38747804 Free PMC article.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
