Overexpression of soybean trypsin inhibitor genes decreases defoliation by corn earworm (Helicoverpa zea) in soybean (Glycine max) and Arabidopsis thaliana
- PMID: 36875574
- PMCID: PMC9982021
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1129454
Overexpression of soybean trypsin inhibitor genes decreases defoliation by corn earworm (Helicoverpa zea) in soybean (Glycine max) and Arabidopsis thaliana
Abstract
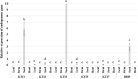
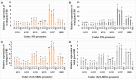
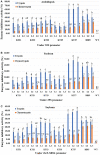
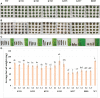
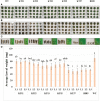
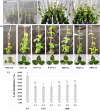
Trypsin inhibitors (TIs) are widely distributed in plants and are known to play a protective role against herbivores. TIs reduce the biological activity of trypsin, an enzyme involved in the breakdown of many different proteins, by inhibiting the activation and catalytic reactions of proteins. Soybean (Glycine max) contains two major TI classes: Kunitz trypsin inhibitor (KTI) and Bowman-Birk inhibitor (BBI). Both genes encoding TI inactivate trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes, which are the main digestive enzymes in the gut fluids of Lepidopteran larvae feeding on soybean. In this study, the possible role of soybean TIs in plant defense against insects and nematodes was investigated. A total of six TIs were tested, including three known soybean trypsin inhibitors (KTI1, KTI2 and KTI3) and three genes encoding novel inhibitors identified in soybean (KTI5, KTI7, and BBI5). Their functional role was further examined by overexpression of the individual TI genes in soybean and Arabidopsis. The endogenous expression patterns of these TI genes varied among soybean tissues, including leaf, stem, seed, and root. In vitro enzyme inhibitory assays showed significant increase in trypsin and chymotrypsin inhibitory activities in both transgenic soybean and Arabidopsis. Detached leaf-punch feeding bioassays detected significant reduction in corn earworm (Helicoverpa zea) larval weight when larvae fed on transgenic soybean and Arabidopsis lines, with the greatest reduction observed in KTI7 and BBI5 overexpressing lines. Whole soybean plant greenhouse feeding bioassays with H. zea on KTI7 and BBI5 overexpressing lines resulted in significantly reduced leaf defoliation compared to non-transgenic plants. However, bioassays of KTI7 and BBI5 overexpressing lines with soybean cyst nematode (SCN, Heterodera glycines) showed no differences in SCN female index between transgenic and non-transgenic control plants. There were no significant differences in growth and productivity between transgenic and non-transgenic plants grown in the absence of herbivores to full maturity under greenhouse conditions. The present study provides further insight into the potential applications of TI genes for insect resistance improvement in plants.
Keywords: corn earworm; overexpression; soybean cyst nematode; tissue-specific promoter; transgenic soybean and Arabidopsis; trypsin and chymotrypsin enzymes inhibition; trypsin inhibitors.
Copyright © 2023 Sultana, Mazarei, Jurat-Fuentes, Hewezi, Millwood and Stewart.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Development of new mutant alleles and markers for KTI1 and KTI3 via CRISPR/Cas9-mediated mutagenesis to reduce trypsin inhibitor content and activity in soybean seeds.Front Plant Sci. 2023 May 8;14:1111680. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1111680. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 37223818 Free PMC article.
-
Bowman-Birk Inhibitor Mutants of Soybean Generated by CRISPR-Cas9 Reveal Drastic Reductions in Trypsin and Chymotrypsin Inhibitor Activities.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 21;25(11):5578. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115578. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38891766 Free PMC article.
-
Identification of a new soybean kunitz trypsin inhibitor mutation and its effect on bowman-birk protease inhibitor content in soybean seed.J Agric Food Chem. 2015 Feb 11;63(5):1352-9. doi: 10.1021/jf505220p. Epub 2015 Jan 29. J Agric Food Chem. 2015. PMID: 25608918
-
Immunoassays of soy proteins.J Agric Food Chem. 2002 Oct 23;50(22):6635-42. doi: 10.1021/jf020186g. J Agric Food Chem. 2002. PMID: 12381163 Review.
-
The Bowman-Birk inhibitor. Trypsin- and chymotrypsin-inhibitor from soybeans.Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985 Feb;25(2):113-31. doi: 10.1111/j.1399-3011.1985.tb02155.x. Int J Pept Protein Res. 1985. PMID: 3886572 Review.
Cited by
-
Enzyme Inhibitors as Multifaceted Tools in Medicine and Agriculture.Molecules. 2024 Sep 11;29(18):4314. doi: 10.3390/molecules29184314. Molecules. 2024. PMID: 39339309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Arabidopsis Transcriptomics Reveals the Role of Lipoxygenase2 (AtLOX2) in Wound-Induced Responses.Int J Mol Sci. 2024 May 28;25(11):5898. doi: 10.3390/ijms25115898. Int J Mol Sci. 2024. PMID: 38892085 Free PMC article.
-
Overexpression of RpKTI2 from Robinia pseudoacacia Affects the Photosynthetic Physiology and Endogenous Hormones of Tobacco.Plants (Basel). 2024 Jul 6;13(13):1867. doi: 10.3390/plants13131867. Plants (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38999707 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Alba J. M., Glas J. J., Schimmel B. C., Kant M. R. (2011). Avoidance and suppression of plant defenses by herbivores and pathogens. J. Plant Interact. 6, 221–227. doi: 10.1080/17429145.2010.551670 - DOI
-
- Alvarez-Alfageme F., Martínez M., Pascual-Ruiz S., Castañera P., Diaz I., Ortego F. (2007). Effects of potato plants expressing a barley cystatin on the predatory bug Podisus maculiventris via herbivorous prey feeding on the plant. Transgenic Res. 16, 1–13. doi: 10.1007/s11248-006-9022-6 - DOI - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

